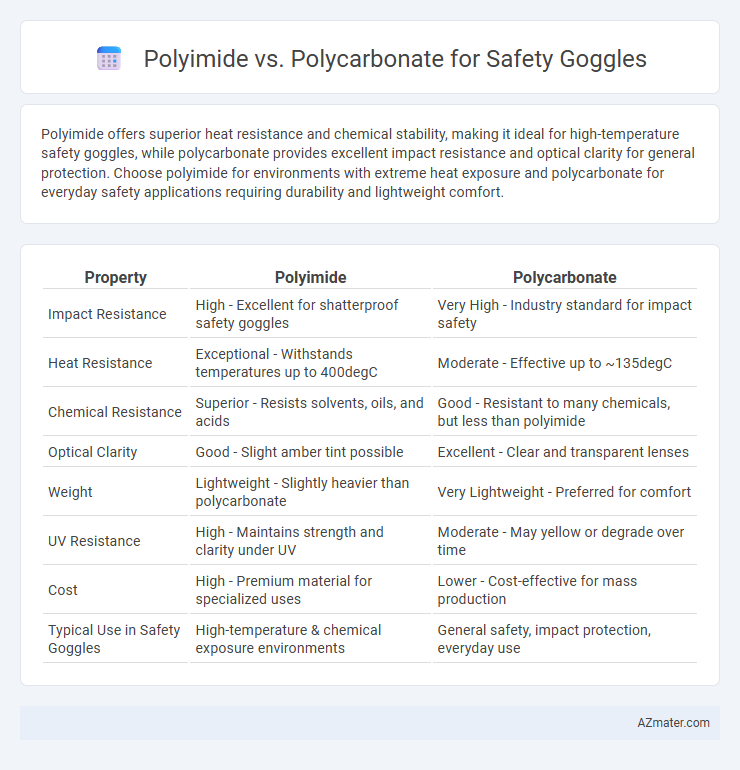
Polyimide offers superior heat resistance and chemical stability, making it ideal for high-temperature safety goggles, while polycarbonate provides excellent impact resistance and optical clarity for general protection. Choose polyimide for environments with extreme heat exposure and polycarbonate for everyday safety applications requiring durability and lightweight comfort.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Polyimide | Polycarbonate |
|---|---|---|
| Impact Resistance | High - Excellent for shatterproof safety goggles | Very High - Industry standard for impact safety |
| Heat Resistance | Exceptional - Withstands temperatures up to 400degC | Moderate - Effective up to ~135degC |
| Chemical Resistance | Superior - Resists solvents, oils, and acids | Good - Resistant to many chemicals, but less than polyimide |
| Optical Clarity | Good - Slight amber tint possible | Excellent - Clear and transparent lenses |
| Weight | Lightweight - Slightly heavier than polycarbonate | Very Lightweight - Preferred for comfort |
| UV Resistance | High - Maintains strength and clarity under UV | Moderate - May yellow or degrade over time |
| Cost | High - Premium material for specialized uses | Lower - Cost-effective for mass production |
| Typical Use in Safety Goggles | High-temperature & chemical exposure environments | General safety, impact protection, everyday use |
Introduction to Safety Goggles Materials
Safety goggles materials significantly impact durability, clarity, and chemical resistance, with polyimide and polycarbonate being two primary options. Polyimide offers exceptional thermal stability and resistance to harsh chemicals, making it ideal for high-temperature or chemically intensive environments. Polycarbonate provides superior impact resistance and optical clarity, commonly used in scenarios requiring robust protection against physical hazards.
Polyimide Overview: Properties and Applications
Polyimide is a high-performance polymer known for its exceptional thermal stability, chemical resistance, and mechanical strength, making it ideal for safety goggles used in extreme environments. Its ability to withstand temperatures exceeding 300degC and resist harsh chemicals ensures durable protection in industrial, aerospace, and laboratory settings. Polyimide lenses also offer excellent optical clarity and flexibility, enhancing comfort and safety during prolonged use.
Polycarbonate Overview: Properties and Applications
Polycarbonate is a transparent thermoplastic known for its high impact resistance, lightweight nature, and excellent optical clarity, making it ideal for safety goggles. Its inherent UV protection and shatterproof qualities provide essential eye safety in industrial, medical, and sports environments. Polycarbonate goggles offer superior durability compared to polyimide, ensuring reliable performance in high-impact and harsh conditions.
Optical Clarity Comparison
Polyimide safety goggles exhibit superior optical clarity due to their inherent high transparency and minimal light distortion, making them ideal for precision tasks requiring clear vision. Polycarbonate lenses also offer good clarity but tend to have slightly lower light transmission and may introduce more optical aberrations under stress compared to polyimide. The choice between polyimide and polycarbonate for optical clarity depends on the application's demand for visual accuracy, with polyimide generally providing sharper and clearer viewing experiences.
Impact Resistance: Polyimide vs Polycarbonate
Polycarbonate offers superior impact resistance in safety goggles, with a high strength-to-weight ratio and the ability to absorb significant energy from sharp or high-velocity impacts without cracking. Polyimide, while known for excellent thermal stability and chemical resistance, generally has lower impact resistance compared to polycarbonate, making it less ideal for applications requiring maximum protection from sudden impacts. Safety goggles made from polycarbonate provide durable, clear visibility and compliance with industry impact safety standards like ANSI Z87.1, outperforming polyimide in impact-resistant environments.
Thermal and Chemical Resistance Differences
Polyimide offers superior thermal resistance withstanding continuous exposure up to 400degC, making it ideal for high-heat environments, whereas polycarbonate typically resists temperatures up to 115degC before deformation. In terms of chemical resistance, polyimide excels with strong resistance to solvents, acids, and bases, while polycarbonate is prone to degradation and stress cracking when exposed to many organic solvents and strong chemicals. These differences make polyimide safer for safety goggles used in extreme thermal and chemical conditions compared to polycarbonate.
Weight and Comfort Considerations
Polyimide safety goggles offer superior lightweight properties compared to polycarbonate, enhancing comfort during extended wear by reducing pressure and fatigue on the face. Polycarbonate lenses, while durable and impact-resistant, tend to be heavier, which can lead to discomfort over prolonged use. Prioritizing polyimide frames and lenses can significantly improve user comfort without compromising essential safety features in protective eyewear.
Cost-Effectiveness Analysis
Polycarbonate goggles typically offer greater cost-effectiveness due to their lower material and manufacturing expenses, making them more affordable for bulk safety equipment purchases. Polyimide goggles, while more expensive, provide superior chemical resistance and thermal stability, justifying their higher price in specialized industrial environments. Evaluating total cost of ownership, including durability and replacement frequency, is essential when choosing between polyimide and polycarbonate safety goggles.
Environmental and Durability Factors
Polyimide offers superior chemical resistance and thermal stability compared to polycarbonate, making it highly durable in harsh environmental conditions and ideal for long-term use in safety goggles. Polycarbonate provides excellent impact resistance and UV protection but is more susceptible to scratching and chemical degradation, reducing its lifespan in demanding environments. Considering environmental factors, polyimide's higher heat resistance and chemical inertness contribute to enhanced durability, while polycarbonate's recyclability offers some environmental benefits despite its lower endurance.
Which Material is Best for Safety Goggles?
Polycarbonate is the preferred material for safety goggles due to its superior impact resistance, lightweight nature, and excellent optical clarity, making it ideal for high-risk environments. Polyimide, while offering exceptional thermal stability and chemical resistance, lacks the impact resistance necessary for comprehensive eye protection. Therefore, polycarbonate provides the best balance of durability, safety, and comfort in safety goggles applications.
Infographic: Polyimide vs Polycarbonate for Safety Goggles
 azmater.com
azmater.com