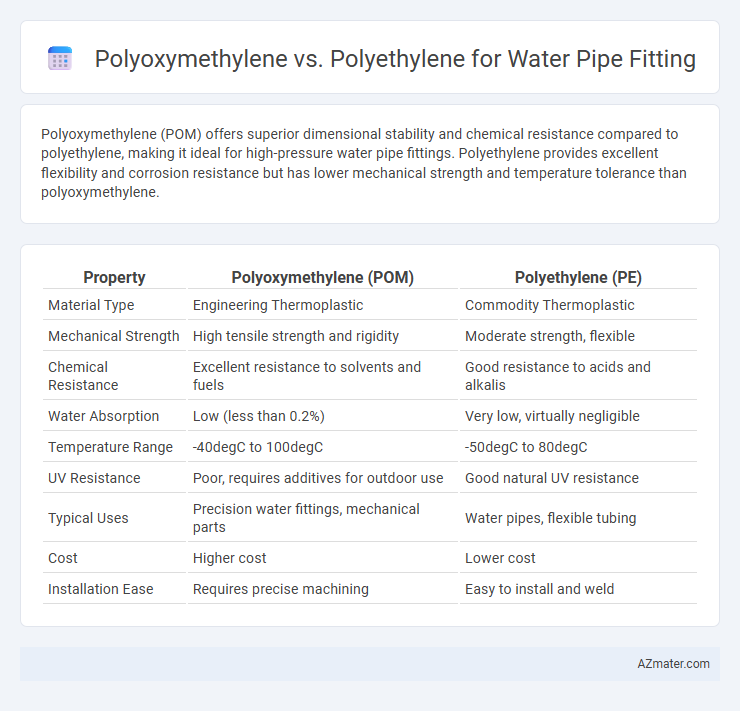
Polyoxymethylene (POM) offers superior dimensional stability and chemical resistance compared to polyethylene, making it ideal for high-pressure water pipe fittings. Polyethylene provides excellent flexibility and corrosion resistance but has lower mechanical strength and temperature tolerance than polyoxymethylene.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Polyoxymethylene (POM) | Polyethylene (PE) |
|---|---|---|
| Material Type | Engineering Thermoplastic | Commodity Thermoplastic |
| Mechanical Strength | High tensile strength and rigidity | Moderate strength, flexible |
| Chemical Resistance | Excellent resistance to solvents and fuels | Good resistance to acids and alkalis |
| Water Absorption | Low (less than 0.2%) | Very low, virtually negligible |
| Temperature Range | -40degC to 100degC | -50degC to 80degC |
| UV Resistance | Poor, requires additives for outdoor use | Good natural UV resistance |
| Typical Uses | Precision water fittings, mechanical parts | Water pipes, flexible tubing |
| Cost | Higher cost | Lower cost |
| Installation Ease | Requires precise machining | Easy to install and weld |
Overview: Polyoxymethylene and Polyethylene in Water Pipe Fittings
Polyoxymethylene (POM) offers high rigidity, excellent dimensional stability, and superior resistance to wear and chemicals, making it ideal for precision water pipe fittings requiring durability. Polyethylene (PE), known for its flexibility, impact resistance, and excellent corrosion resistance, is widely used in water pipe fittings where flexibility and resistance to environmental stress cracking are crucial. Both materials provide reliable performance in water applications, with POM preferred for mechanical strength and PE favored for adaptability and cost-effectiveness.
Material Composition and Structure Comparison
Polyoxymethylene (POM) features a highly crystalline structure composed of repeated formaldehyde units, offering superior rigidity, dimensional stability, and low moisture absorption compared to polyethylene (PE), which is a semi-crystalline polymer made from ethylene monomers with a more flexible, amorphous structure. POM's tightly packed molecular chains enhance resistance to chemicals, wear, and higher pressure, making it ideal for precise water pipe fittings where durability is critical. In contrast, polyethylene's less dense molecular arrangement provides excellent impact resistance and flexibility but lower mechanical strength and temperature tolerance, influencing its suitability for less demanding water pipe applications.
Mechanical Strength and Durability Analysis
Polyoxymethylene (POM) exhibits superior mechanical strength and rigidity compared to polyethylene (PE), making it highly resistant to deformation under pressure in water pipe fittings. POM's enhanced durability is characterized by excellent fatigue resistance and long-term stability in harsh environments, whereas polyethylene offers greater flexibility but lower tensile strength. The choice between POM and PE depends on application requirements, with POM preferred for high-stress fittings demanding robust mechanical properties and PE favored for flexible, lightweight installations.
Chemical Resistance in Water Supply Environments
Polyoxymethylene (POM) exhibits superior chemical resistance in water supply environments compared to polyethylene (PE), effectively resisting degradation from chlorinated water and common disinfectants. Its low water absorption and high dimensional stability ensure prolonged pipe fitting durability under varying pH levels and temperatures found in potable water systems. Polyethylene's chemical resistance is adequate for basic water transport but may suffer from oxidation and stress cracking in aggressive water conditions, making POM a preferred choice for high-performance water pipe fittings.
Temperature Tolerance: Hot vs Cold Water Applications
Polyoxymethylene (POM) exhibits superior temperature tolerance for hot water applications, maintaining structural integrity up to approximately 120degC, whereas polyethylene (PE) generally performs better in cold water settings due to its higher flexibility but lower thermal resistance, typically up to 60degC. The higher melting point and thermal stability of POM make it suitable for hot water pipe fittings that require durability and resistance to deformation under heat stress. Conversely, polyethylene's excellent impact resistance and lower cost make it a preferred choice for cold water pipe fittings where high temperature resistance is less critical.
Installation and Processing Differences
Polyoxymethylene (POM) offers superior dimensional stability and rigidity compared to polyethylene (PE), making it ideal for precise water pipe fittings requiring tight tolerances during installation. PE pipe fittings are more flexible and easier to process through heat fusion methods, while POM components typically require machining or injection molding, leading to longer production times and higher costs. Installation of POM fittings demands specialized tools and adhesives for secure joints, whereas PE fittings often utilize fusion welding techniques allowing faster, leak-proof connections.
Cost Efficiency and Lifecycle Value
Polyoxymethylene (POM) exhibits higher initial costs compared to polyethylene (PE) but offers superior mechanical strength and chemical resistance, enhancing lifecycle value in water pipe fittings. Polyethylene's lower material and installation costs make it cost-efficient for large-scale, less demanding applications, while POM's durability reduces maintenance and replacement expenses over time. Evaluating total cost of ownership highlights POM's advantage in long-term performance despite polyethylene's upfront affordability.
Regulatory Approvals and Safety Standards
Polyoxymethylene (POM) water pipe fittings typically meet stringent regulatory approvals such as NSF/ANSI 61 for drinking water safety, ensuring compliance with U.S. and international standards. Polyethylene (PE) fittings also comply with rigorous standards including NSF/ANSI 14 for plastic piping components and ASTM F876 for potable water applications, emphasizing its widespread acceptance in water infrastructure. Both materials exhibit certifications for low toxicity and chemical resistance, but POM offers higher mechanical strength while PE provides superior flexibility and impact resistance in compliance with global safety regulations.
Common Applications: Choosing the Right Material
Polyoxymethylene (POM) is commonly used in water pipe fittings for applications requiring high stiffness, low friction, and excellent dimensional stability, such as precision components in plumbing systems. Polyethylene (PE), especially high-density polyethylene (HDPE), is preferred for flexible, corrosion-resistant water pipes and fittings in underground and municipal water supply due to its durability and chemical resistance. Selecting the right material depends on factors like pressure requirements, environmental exposure, and mechanical demands to ensure long-term performance in water distribution networks.
Environmental Impact: Recyclability and Sustainability
Polyoxymethylene (POM) offers high durability and chemical resistance, but its recyclability is limited compared to polyethylene (PE), which is widely accepted in recycling streams due to its simple polymer structure. PE's lower environmental footprint stems from its efficient recyclability and availability from bio-based sources, enhancing sustainability in water pipe fitting applications. Choosing PE can reduce plastic waste and promote circular economy practices, aligning with environmental goals.
Infographic: Polyoxymethylene vs Polyethylene for Water Pipe Fitting
 azmater.com
azmater.com