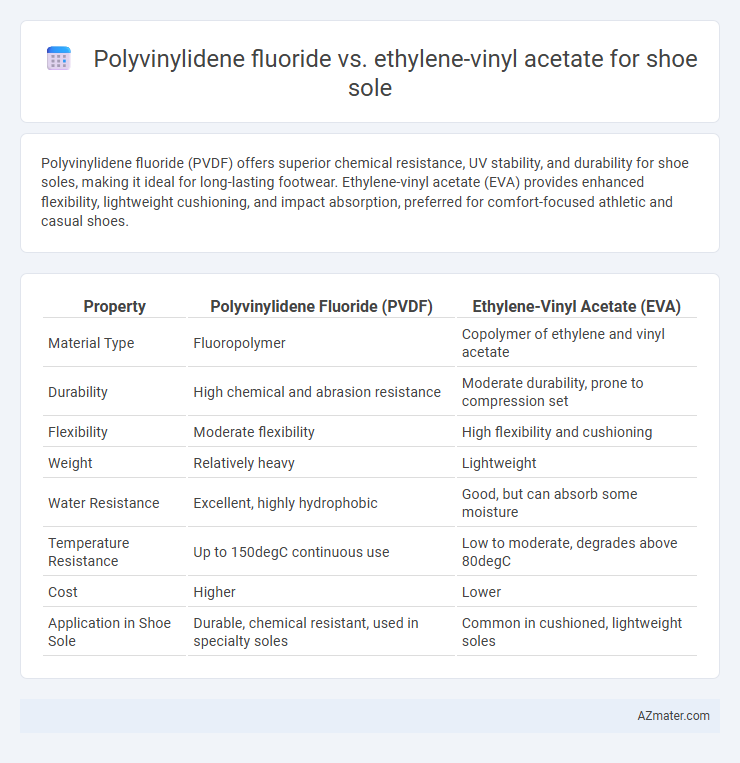
Polyvinylidene fluoride (PVDF) offers superior chemical resistance, UV stability, and durability for shoe soles, making it ideal for long-lasting footwear. Ethylene-vinyl acetate (EVA) provides enhanced flexibility, lightweight cushioning, and impact absorption, preferred for comfort-focused athletic and casual shoes.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Polyvinylidene Fluoride (PVDF) | Ethylene-Vinyl Acetate (EVA) |
|---|---|---|
| Material Type | Fluoropolymer | Copolymer of ethylene and vinyl acetate |
| Durability | High chemical and abrasion resistance | Moderate durability, prone to compression set |
| Flexibility | Moderate flexibility | High flexibility and cushioning |
| Weight | Relatively heavy | Lightweight |
| Water Resistance | Excellent, highly hydrophobic | Good, but can absorb some moisture |
| Temperature Resistance | Up to 150degC continuous use | Low to moderate, degrades above 80degC |
| Cost | Higher | Lower |
| Application in Shoe Sole | Durable, chemical resistant, used in specialty soles | Common in cushioned, lightweight soles |
Introduction to Polyvinylidene Fluoride and Ethylene-Vinyl Acetate
Polyvinylidene fluoride (PVDF) is a highly non-reactive and pure thermoplastic fluoropolymer renowned for its superior chemical resistance, durability, and weatherability, making it suitable for high-performance shoe soles requiring long-lasting protection. Ethylene-vinyl acetate (EVA) is a lightweight, flexible copolymer known for excellent cushioning, shock absorption, and comfort in footwear applications, enhancing flexibility and wearability. PVDF offers enhanced abrasion resistance and chemical inertness compared to EVA's primary advantage of softness and impact resilience in shoe sole materials.
Material Composition and Chemical Properties
Polyvinylidene fluoride (PVDF) is a highly non-reactive and pure thermoplastic fluoropolymer characterized by strong chemical resistance, high tensile strength, and excellent abrasion resistance, making it ideal for durable and long-lasting shoe soles. Ethylene-vinyl acetate (EVA) is a flexible copolymer composed mainly of ethylene and a varying percentage of vinyl acetate, known for its lightweight, cushioning properties, and superior shock absorption due to its soft and elastic chemical structure. PVDF offers superior chemical and thermal stability compared to EVA, while EVA excels in providing comfort and flexibility for footwear applications.
Mechanical Strength and Durability Comparison
Polyvinylidene fluoride (PVDF) exhibits superior mechanical strength and chemical resistance compared to Ethylene-vinyl acetate (EVA), making it more durable for heavy-duty shoe soles. EVA offers excellent flexibility and shock absorption but tends to degrade faster under abrasion and prolonged UV exposure. The enhanced tensile strength and abrasion resistance of PVDF contribute to longer-lasting shoe soles in demanding environments.
Flexibility and Comfort in Footwear Applications
Polyvinylidene fluoride (PVDF) offers excellent chemical resistance and durability but tends to be less flexible than ethylene-vinyl acetate (EVA), which is renowned for its superior flexibility and cushioning properties in shoe sole applications. EVA's lightweight structure enhances comfort by providing better shock absorption and energy return, making it the preferred material for athletic and casual footwear focused on long-term wearability. PVDF soles are more suited for environments requiring toughness and resistance, while EVA excels in delivering softness and flexibility for everyday comfort.
Weight and Sole Thickness Considerations
Polyvinylidene fluoride (PVDF) offers a lightweight solution for shoe soles while maintaining high durability and chemical resistance, making it ideal for thin sole constructions requiring flexibility and strength. Ethylene-vinyl acetate (EVA) provides a thicker, cushioned sole with excellent shock absorption and lightweight properties but tends to be bulkier compared to PVDF. Weight optimization in shoe sole design must balance PVDF's structural thinness with EVA's enhanced comfort and thickness for impact protection.
Slip Resistance and Traction Performance
Polyvinylidene fluoride (PVDF) offers superior slip resistance due to its high chemical resistance and low surface energy, making it ideal for shoe soles in wet or oily conditions. Ethylene-vinyl acetate (EVA) provides excellent traction performance with its flexible, lightweight composition that enhances grip on various surfaces. While PVDF excels in durability and maintaining traction under harsh environments, EVA is preferred for comfort and shock absorption without compromising slip resistance.
Water and Chemical Resistance
Polyvinylidene fluoride (PVDF) offers superior water and chemical resistance compared to Ethylene-vinyl acetate (EVA), making it ideal for shoe soles exposed to harsh environments. PVDF exhibits excellent resistance to solvents, acids, and UV radiation, ensuring durability against chemical degradation. EVA provides good flexibility and cushioning but tends to absorb water and degrade faster when exposed to chemicals, limiting its use in demanding conditions.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
Polyvinylidene fluoride (PVDF) and Ethylene-vinyl acetate (EVA) differ significantly in environmental impact and sustainability for shoe soles. PVDF is a fluoropolymer known for chemical resistance and durability but has a high carbon footprint due to energy-intensive production and limited recyclability. EVA offers better sustainability with easier recyclability, lower greenhouse gas emissions during manufacturing, and biodegradability when formulated with bio-based additives.
Cost Analysis and Market Availability
Polyvinylidene fluoride (PVDF) offers superior chemical resistance and durability for shoe soles but comes with a higher cost compared to ethylene-vinyl acetate (EVA), which is more affordable and widely available in the market. EVA is favored in mass production due to its low price point and excellent cushioning properties, making it the dominant choice in athletic and casual footwear. Market availability of EVA is extensive globally, whereas PVDF is less common and typically reserved for specialty or high-performance shoe applications due to its premium pricing and limited suppliers.
Conclusion: Selecting the Ideal Material for Shoe Soles
Polyvinylidene fluoride (PVDF) offers superior chemical resistance, UV stability, and durability, making it ideal for long-lasting, high-performance shoe soles in demanding environments. Ethylene-vinyl acetate (EVA) provides excellent flexibility, lightweight cushioning, and shock absorption, enhancing comfort for everyday footwear. Choosing between PVDF and EVA depends on the specific balance of durability versus comfort requirements, with PVDF suited for robust, industrial applications and EVA preferred for casual or athletic shoes.
Infographic: Polyvinylidene fluoride vs Ethylene-vinyl acetate for Shoe sole
 azmater.com
azmater.com