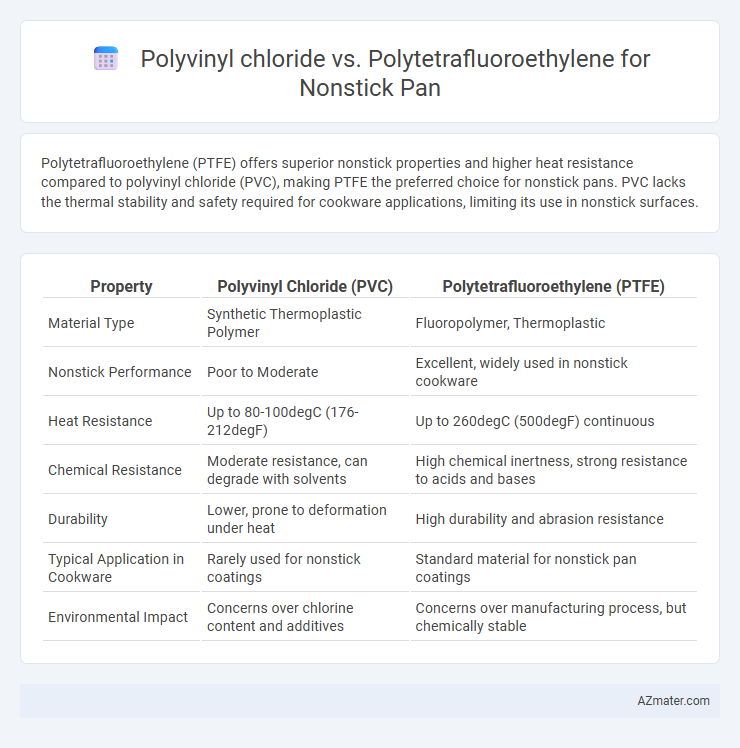
Polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE) offers superior nonstick properties and higher heat resistance compared to polyvinyl chloride (PVC), making PTFE the preferred choice for nonstick pans. PVC lacks the thermal stability and safety required for cookware applications, limiting its use in nonstick surfaces.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Polyvinyl Chloride (PVC) | Polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE) |
|---|---|---|
| Material Type | Synthetic Thermoplastic Polymer | Fluoropolymer, Thermoplastic |
| Nonstick Performance | Poor to Moderate | Excellent, widely used in nonstick cookware |
| Heat Resistance | Up to 80-100degC (176-212degF) | Up to 260degC (500degF) continuous |
| Chemical Resistance | Moderate resistance, can degrade with solvents | High chemical inertness, strong resistance to acids and bases |
| Durability | Lower, prone to deformation under heat | High durability and abrasion resistance |
| Typical Application in Cookware | Rarely used for nonstick coatings | Standard material for nonstick pan coatings |
| Environmental Impact | Concerns over chlorine content and additives | Concerns over manufacturing process, but chemically stable |
Introduction: Understanding Nonstick Pan Materials
Polyvinyl chloride (PVC) and polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE) are two distinct polymers used in nonstick pan coatings, with PTFE being the industry standard due to its superior heat resistance and nonstick properties. PVC, while common in various applications, lacks the thermal stability and safety profile required for cookware, making it an unsuitable choice for nonstick surfaces. Understanding the chemical composition and performance characteristics of PTFE ensures better durability and safer cooking experiences in nonstick pan materials.
Polyvinyl Chloride (PVC): Key Properties
Polyvinyl chloride (PVC) offers excellent chemical resistance and durability, making it a practical choice for nonstick pan coatings where heat resistance up to about 105degC is sufficient. PVC is inherently rigid but can be softened with plasticizers for flexibility, though it generally does not withstand the high temperatures required for cooking applications compared to polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE). Unlike PTFE, PVC has lower thermal stability and nonstick performance, which limits its widespread use in high-temperature cookware despite its affordability and versatility.
Polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE): Key Properties
Polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE) is a synthetic fluoropolymer known for its exceptional nonstick properties, chemical resistance, and high-temperature tolerance up to 260degC (500degF). Unlike polyvinyl chloride (PVC), PTFE exhibits excellent thermal stability and minimal friction, making it ideal for cookware coatings that prevent food from sticking and enable easy cleaning. PTFE's inertness and durability contribute to its widespread use in nonstick pans, enhancing cooking efficiency and safety.
Heat Resistance: PVC vs PTFE
Polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE) exhibits superior heat resistance compared to polyvinyl chloride (PVC), with PTFE tolerating temperatures up to 260degC (500degF) without degradation, making it ideal for nonstick pan coatings. PVC typically withstands temperatures only up to 80degC to 105degC before softening or releasing harmful fumes, rendering it unsuitable for direct cooking applications. The thermal stability of PTFE ensures nonstick performance and safety during high-heat cooking processes.
Chemical Resistance Comparison
Polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE) offers superior chemical resistance compared to polyvinyl chloride (PVC), making it highly effective for nonstick pans exposed to acidic and alkaline food substances. PTFE withstands most solvents, oils, and harsh cleaning agents without degradation, whereas PVC can degrade or release harmful compounds when exposed to strong chemicals or high temperatures. This enhanced chemical stability of PTFE ensures longer durability and safer cooking surfaces in nonstick cookware applications.
Nonstick Performance and Durability
Polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE) outperforms polyvinyl chloride (PVC) in nonstick pan applications due to its superior nonstick properties and high heat resistance, allowing it to maintain a smooth cooking surface even at elevated temperatures. PTFE coatings offer exceptional durability by resisting scratching, chemical degradation, and sticking of food, whereas PVC lacks the thermal stability and nonstick efficiency necessary for cookware. The inherent chemical inertness and robust molecular structure of PTFE ensure prolonged lifespan and consistent cooking performance compared to the limited and less resilient characteristics of PVC.
Safety and Food Contact Regulations
Polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE) is widely preferred for nonstick pans due to its superior chemical inertness and compliance with stringent food contact regulations such as those from the FDA and EFSA, ensuring safety at typical cooking temperatures. Polyvinyl chloride (PVC) is generally avoided for cookware applications because it can release harmful additives like phthalates and dioxins when heated, posing health risks and failing to meet food safety standards. Manufacturers favor PTFE coatings to deliver non-toxic, durable, and regulation-compliant surfaces suitable for high-temperature cooking without compromising consumer health.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
Polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE) is favored over Polyvinyl chloride (PVC) for nonstick pans due to its superior chemical stability and lower environmental toxicity during manufacturing and disposal. PVC production releases harmful dioxins and chlorine-based compounds, contributing to air and water pollution, while PTFE manufacturing emits fewer persistent organic pollutants. PTFE pans offer enhanced durability and longer use-life, reducing waste and supporting sustainability compared to PVC's potential leaching of toxic plasticizers and additives into the environment.
Cost and Market Availability
Polyvinyl chloride (PVC) offers a significantly lower production cost compared to polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE), making it more affordable for consumers in the nonstick pan market. PTFE, renowned for its superior nonstick properties and chemical resistance, is widely available but generally commands a higher price due to complex manufacturing processes. Market availability for PVC-coated pans is less common, as PTFE remains the industry standard in nonstick cookware applications.
Conclusion: Choosing Between PVC and PTFE for Nonstick Pans
Polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE) is generally preferred over polyvinyl chloride (PVC) for nonstick pans due to its superior heat resistance and non-reactive surface, ensuring safer and more durable cookware. PVC's lower thermal stability and potential release of harmful chemicals at high temperatures make it less suitable for cooking applications. Selecting PTFE-coated pans offers enhanced cooking performance and food safety compared to PVC alternatives.
Infographic: Polyvinyl chloride vs Polytetrafluoroethylene for Nonstick Pan
 azmater.com
azmater.com