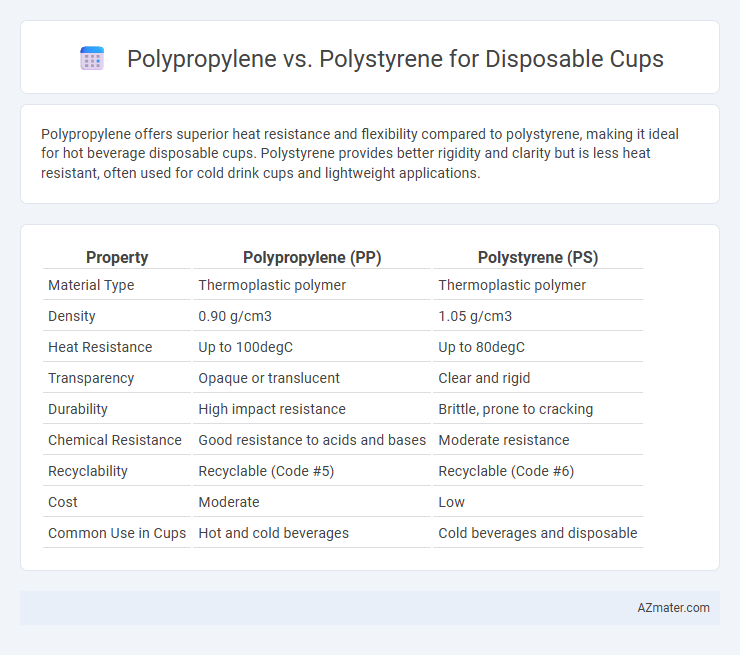
Polypropylene offers superior heat resistance and flexibility compared to polystyrene, making it ideal for hot beverage disposable cups. Polystyrene provides better rigidity and clarity but is less heat resistant, often used for cold drink cups and lightweight applications.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Polypropylene (PP) | Polystyrene (PS) |
|---|---|---|
| Material Type | Thermoplastic polymer | Thermoplastic polymer |
| Density | 0.90 g/cm3 | 1.05 g/cm3 |
| Heat Resistance | Up to 100degC | Up to 80degC |
| Transparency | Opaque or translucent | Clear and rigid |
| Durability | High impact resistance | Brittle, prone to cracking |
| Chemical Resistance | Good resistance to acids and bases | Moderate resistance |
| Recyclability | Recyclable (Code #5) | Recyclable (Code #6) |
| Cost | Moderate | Low |
| Common Use in Cups | Hot and cold beverages | Cold beverages and disposable |
Introduction to Polypropylene and Polystyrene
Polypropylene (PP) is a thermoplastic polymer known for its high chemical resistance, durability, and flexibility, making it suitable for disposable cups requiring heat resistance and strength. Polystyrene (PS) is a rigid, lightweight plastic valued for its clarity and insulating properties, commonly used in single-use beverage containers. Choosing between polypropylene and polystyrene depends on factors like thermal stability, environmental impact, and cost-effectiveness in disposable cup applications.
Chemical Composition and Structure
Polypropylene (PP) features a semi-crystalline polymer structure composed of repeating propylene monomers, resulting in high chemical resistance and a melting point around 160degC, making it suitable for hot beverage disposable cups. Polystyrene (PS), an amorphous polymer made from styrene monomers, offers rigidity and clarity but has lower heat resistance with a melting point near 240degC, often limiting its use to cold beverage cups. The differing chemical compositions--non-polar hydrocarbon chains in PP versus the aromatic rings in PS--directly influence their thermal properties, chemical inertness, and suitability in disposable cup applications.
Manufacturing Processes
Polypropylene (PP) cups are typically produced using injection molding and thermoplastic forming, which offer high efficiency and dimensional stability, while polystyrene (PS) cups are often manufactured through injection molding and extrusion foaming, creating lightweight and rigid structures. PP's lower melting point allows for faster cycle times and reduced energy consumption compared to PS production. The choice between these processes impacts the final cup's durability, clarity, and cost-effectiveness in disposable cup manufacturing.
Physical Properties Comparison
Polypropylene (PP) offers higher impact resistance and greater flexibility compared to polystyrene (PS), which is more rigid but brittle. PP exhibits a melting point around 160degC, allowing better heat tolerance for hot beverages, whereas PS melts at approximately 240degC but has lower thermal shock resistance. Polystyrene provides superior clarity and a smoother surface finish, making it more visually appealing, while polypropylene's lightweight and toughness enhance durability for disposable cup applications.
Heat Resistance and Performance
Polypropylene exhibits superior heat resistance compared to polystyrene, maintaining structural integrity at temperatures up to 160degC, making it ideal for hot beverage disposable cups. Polystyrene, with a lower heat tolerance of around 90degC, tends to warp or soften under high temperatures, limiting its use to cold or room temperature drinks. The performance of polypropylene in terms of thermal stability and durability under heat stress offers enhanced safety and user experience in disposable cup applications.
Environmental Impact and Recyclability
Polypropylene (PP) disposable cups offer a lower environmental impact due to their higher recyclability and lower energy requirements in production compared to polystyrene (PS) cups. Polystyrene cups, often made from expanded polystyrene (EPS), pose significant environmental challenges as they are less biodegradable and more difficult to recycle, frequently ending up in landfills or as litter. Choosing polypropylene cups reduces waste volume and supports circular economy initiatives with widely available recycling programs.
Cost and Market Availability
Polypropylene (PP) offers a lower production cost compared to polystyrene (PS), making it a more economical choice for disposable cups in high-volume markets. PP's widespread availability and recycling infrastructure enhance its market presence, whereas PS, although having a slightly higher price, provides superior clarity and rigidity. The cost-effectiveness and easy sourcing of polypropylene contribute to its dominance in the disposable cup industry, especially in sectors prioritizing budget and sustainability.
Consumer Safety and Health Concerns
Polypropylene (PP) is favored for disposable cups due to its high heat resistance and low chemical leaching, making it safer for hot beverages compared to polystyrene (PS), which can release styrene monomers linked to potential carcinogenic effects. Polystyrene cups pose higher risks of chemical migration when in contact with hot or acidic liquids, raising consumer health concerns. Choosing PP reduces exposure to harmful substances, ensuring greater consumer safety in disposable cup use.
Applications in the Food and Beverage Industry
Polypropylene (PP) offers high heat resistance and durability, making it ideal for hot beverages and microwave-safe disposable cups in the food and beverage industry. Polystyrene (PS), known for its rigidity and clarity, is commonly used for cold drink cups and food containers where transparency and cost-effectiveness are priorities. Both materials provide distinct benefits: PP excels in thermal stability and chemical resistance, while PS is favored for its insulation properties and lightweight structure.
Choosing the Right Material for Disposable Cups
Polypropylene offers high heat resistance and flexibility, making it ideal for hot beverage cups, while polystyrene provides excellent rigidity and clarity, suitable for cold drink containers. Polypropylene's chemical resistance and lower environmental impact often result in better performance for reusable and recyclable disposable cups. Selecting the right material depends on temperature requirements, durability, and sustainability goals in disposable cup production.
Infographic: Polypropylene vs Polystyrene for Disposable Cup
 azmater.com
azmater.com