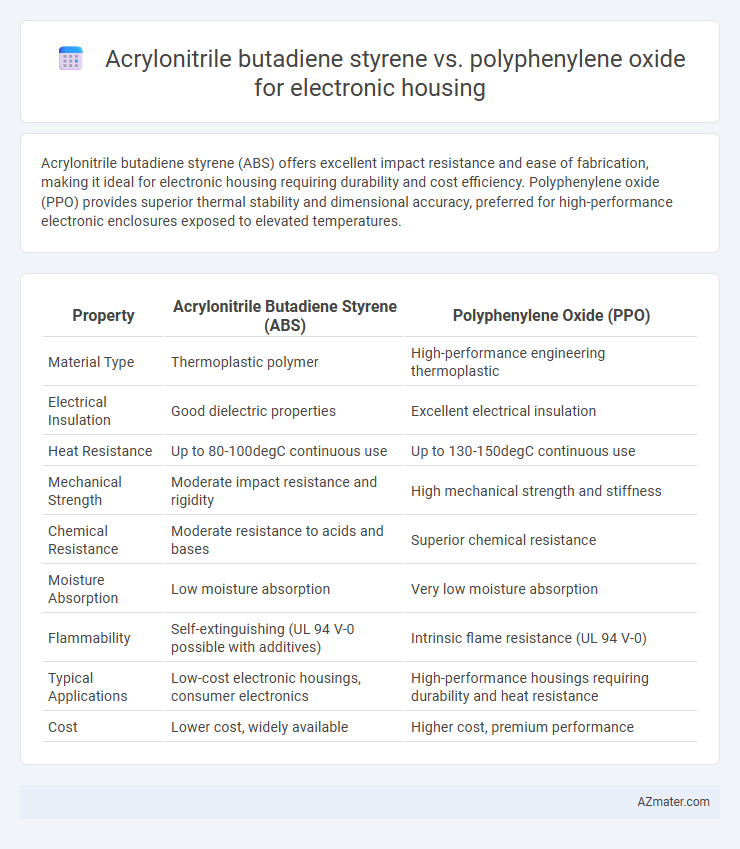
Acrylonitrile butadiene styrene (ABS) offers excellent impact resistance and ease of fabrication, making it ideal for electronic housing requiring durability and cost efficiency. Polyphenylene oxide (PPO) provides superior thermal stability and dimensional accuracy, preferred for high-performance electronic enclosures exposed to elevated temperatures.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Acrylonitrile Butadiene Styrene (ABS) | Polyphenylene Oxide (PPO) |
|---|---|---|
| Material Type | Thermoplastic polymer | High-performance engineering thermoplastic |
| Electrical Insulation | Good dielectric properties | Excellent electrical insulation |
| Heat Resistance | Up to 80-100degC continuous use | Up to 130-150degC continuous use |
| Mechanical Strength | Moderate impact resistance and rigidity | High mechanical strength and stiffness |
| Chemical Resistance | Moderate resistance to acids and bases | Superior chemical resistance |
| Moisture Absorption | Low moisture absorption | Very low moisture absorption |
| Flammability | Self-extinguishing (UL 94 V-0 possible with additives) | Intrinsic flame resistance (UL 94 V-0) |
| Typical Applications | Low-cost electronic housings, consumer electronics | High-performance housings requiring durability and heat resistance |
| Cost | Lower cost, widely available | Higher cost, premium performance |
Introduction to Electronic Housing Materials
Acrylonitrile butadiene styrene (ABS) and Polyphenylene oxide (PPO) are key materials used in electronic housing due to their durability and thermal stability. ABS offers excellent impact resistance and ease of molding, making it suitable for cost-effective enclosures, while PPO provides superior heat resistance and dimensional stability essential for high-performance applications. Selecting between ABS and PPO depends on the specific requirements of thermal management, mechanical strength, and environmental factors in electronic device design.
Overview of Acrylonitrile Butadiene Styrene (ABS)
Acrylonitrile Butadiene Styrene (ABS) is a widely used thermoplastic polymer renowned for its impact resistance, toughness, and ease of processing, making it an ideal choice for electronic housings. ABS exhibits excellent dimensional stability and good electrical insulation properties, essential for protecting sensitive electronic components. Its ability to withstand varying temperatures and exposure to chemicals enhances durability, distinguishing it in applications where Polyphenylene oxide (PPO) might offer higher heat resistance but at a greater cost.
Overview of Polyphenylene Oxide (PPO)
Polyphenylene oxide (PPO) is a high-performance thermoplastic known for its excellent thermal stability, dimensional stability, and electrical insulating properties, making it suitable for electronic housing applications. Compared to acrylonitrile butadiene styrene (ABS), PPO offers superior heat resistance up to 190degC and better resistance to moisture and chemicals, enhancing the durability of electronic enclosures. Its inherent flame retardancy and low dielectric constant contribute to safer and more reliable electronic device protection.
Mechanical Strength: ABS vs PPO
Acrylonitrile butadiene styrene (ABS) offers excellent impact resistance and toughness, making it ideal for electronic housings requiring durability under mechanical stress. Polyphenylene oxide (PPO) provides superior stiffness and dimensional stability, ensuring long-term structural integrity in high-temperature environments. Comparing ABS vs PPO, ABS excels in impact strength, while PPO outperforms in rigidity and thermal resistance, influencing material selection based on specific mechanical demands.
Thermal Resistance and Stability Comparison
Acrylonitrile Butadiene Styrene (ABS) offers moderate thermal resistance with a heat deflection temperature around 90-100degC, making it suitable for electronic housings with standard heat exposure. Polyphenylene Oxide (PPO) demonstrates superior thermal stability, with heat deflection temperatures typically exceeding 130degC and excellent dimensional stability under prolonged heat stress. PPO's enhanced thermal resistance ensures greater reliability in high-temperature electronic applications compared to ABS, which may soften or deform under sustained thermal loads.
Electrical Insulation Properties
Acrylonitrile butadiene styrene (ABS) offers moderate electrical insulation suitable for electronic housings, providing good dielectric strength and resistance to electrical breakdown in standard applications. Polyphenylene oxide (PPO) excels with superior electrical insulation properties, including high dielectric constant and low dissipation factor, making it ideal for high-performance electronic enclosures requiring enhanced electrical safety and dimensional stability. The choice between ABS and PPO depends on specific insulation needs, with PPO favored for demanding electrical environments due to its excellent resistance to electrical tracking and insulation degradation.
Chemical Resistance and Environmental Durability
Acrylonitrile butadiene styrene (ABS) offers moderate chemical resistance suitable for many electronic housings but can degrade when exposed to strong acids, bases, and solvents. Polyphenylene oxide (PPO) provides superior chemical resistance, maintaining stability against a broader range of harsh chemicals, making it ideal for environments requiring high durability. Environmental durability of PPO surpasses ABS due to better resistance to heat, moisture, and UV radiation, ensuring prolonged performance in demanding electronic applications.
Processing and Manufacturing Differences
Acrylonitrile butadiene styrene (ABS) offers excellent impact resistance and ease of processing through injection molding, making it suitable for complex electronic housings with tight tolerances. Polyphenylene oxide (PPO) provides superior thermal stability and dimensional accuracy but requires higher processing temperatures and specialized drying to prevent moisture-related defects. Manufacturing electronic housings with PPO demands more precise temperature control compared to ABS, influencing cycle times and tool wear during mass production.
Cost Analysis and Economic Considerations
Acrylonitrile butadiene styrene (ABS) generally offers lower material and manufacturing costs compared to Polyphenylene oxide (PPO), making it a cost-effective choice for electronic housing applications. PPO provides superior thermal stability and electrical insulating properties, which can reduce long-term maintenance and failure costs but comes at a higher initial investment. Economic considerations favor ABS for budget-sensitive projects, while PPO suits applications where performance justifies greater upfront expenditure.
Application Suitability: ABS or PPO for Electronics Housing
Acrylonitrile butadiene styrene (ABS) is widely used in electronic housings due to its excellent impact resistance, ease of processing, and cost-effectiveness, making it suitable for consumer electronics, appliances, and enclosures requiring good mechanical durability. Polyphenylene oxide (PPO) offers superior thermal stability, dimensional stability, and electrical insulating properties, ideal for high-performance electronic housings in environments exposed to high temperatures or electrical stress. Choosing between ABS and PPO depends on the specific application requirements, with ABS favored for general-purpose housings and PPO preferred for demanding conditions requiring enhanced thermal and electrical performance.
Infographic: Acrylonitrile butadiene styrene vs Polyphenylene oxide for Electronic Housing
 azmater.com
azmater.com