Polycarbonate pipes offer superior impact resistance and thermal stability compared to polyvinyl chloride (PVC) pipes, which provide better chemical resistance and cost efficiency. Ideal applications for polycarbonate include high-pressure systems, while PVC is preferred for standard plumbing and drainage due to ease of installation and affordability.
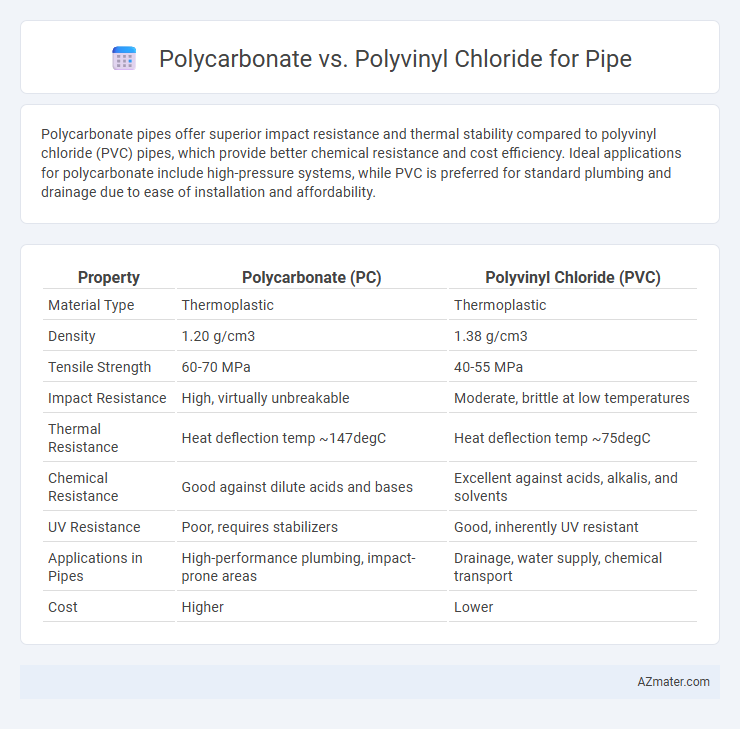
Table of Comparison
| Property | Polycarbonate (PC) | Polyvinyl Chloride (PVC) |
|---|---|---|
| Material Type | Thermoplastic | Thermoplastic |
| Density | 1.20 g/cm3 | 1.38 g/cm3 |
| Tensile Strength | 60-70 MPa | 40-55 MPa |
| Impact Resistance | High, virtually unbreakable | Moderate, brittle at low temperatures |
| Thermal Resistance | Heat deflection temp ~147degC | Heat deflection temp ~75degC |
| Chemical Resistance | Good against dilute acids and bases | Excellent against acids, alkalis, and solvents |
| UV Resistance | Poor, requires stabilizers | Good, inherently UV resistant |
| Applications in Pipes | High-performance plumbing, impact-prone areas | Drainage, water supply, chemical transport |
| Cost | Higher | Lower |
Introduction to Polycarbonate and Polyvinyl Chloride Pipes
Polycarbonate pipes are known for their exceptional impact resistance, transparency, and lightweight properties, making them ideal for applications requiring high durability and clarity in fluid transport. Polyvinyl chloride (PVC) pipes offer superior chemical resistance, affordability, and ease of installation, widely used in plumbing, irrigation, and industrial fluid conveyance. Both materials provide corrosion resistance, but PVC dominates the market due to its cost-effectiveness and extensive compatibility with various piping systems.
Chemical Composition and Material Properties
Polycarbonate pipes are composed of bisphenol A and carbonyl groups, providing high impact resistance, thermal stability, and transparency, making them suitable for applications requiring durability and clarity. Polyvinyl chloride (PVC) pipes consist of vinyl chloride monomers polymerized into a rigid, chemically resistant material with excellent corrosion resistance and low-cost production, widely used in plumbing and drainage. The chemical structure of polycarbonate offers superior toughness and heat resistance compared to PVC, which excels in chemical inertness and cost efficiency.
Strength and Durability Comparison
Polycarbonate pipes exhibit superior impact resistance and higher tensile strength compared to polyvinyl chloride (PVC) pipes, making them more suitable for applications requiring enhanced mechanical durability. PVC pipes offer excellent chemical resistance and rigidity but may become brittle under prolonged UV exposure and extreme temperature fluctuations. The overall durability of polycarbonate supersedes PVC in dynamic environments due to its greater flexibility and resistance to cracking under stress.
Resistance to Chemicals and Corrosion
Polycarbonate pipes offer moderate resistance to chemicals but can degrade when exposed to strong acids or solvents, making them less ideal for harsh chemical environments. Polyvinyl chloride (PVC) pipes exhibit superior resistance to a wide range of acids, alkalis, and corrosive substances, maintaining integrity in aggressive chemical applications. PVC's enhanced corrosion resistance makes it the preferred choice for industrial piping systems requiring long-term durability against chemical exposure.
Temperature and Pressure Tolerance
Polycarbonate pipes exhibit high-temperature tolerance, typically withstanding continuous use up to 125degC, making them ideal for applications with fluctuating thermal conditions. Polyvinyl chloride (PVC) pipes generally handle temperatures up to 60degC but offer better resistance to chemical corrosion at lower temperatures, suitable for standard pressure systems. In terms of pressure tolerance, polycarbonate pipes maintain strength under high pressure environments, while PVC pipes are rated for moderate pressure and may require reinforcement for high-pressure applications.
Installation Process and Flexibility
Polycarbonate pipes offer greater flexibility compared to polyvinyl chloride (PVC), allowing easier bending and maneuvering during installation without the need for additional fittings. The installation process for polycarbonate is typically faster and less labor-intensive due to its lightweight and impact resistance, reducing the risk of cracking or breakage. In contrast, PVC pipes require precise cutting and solvent welding, making the installation more rigid and time-consuming, especially in complex plumbing layouts.
Cost Analysis: Polycarbonate vs PVC Pipes
Polyvinyl chloride (PVC) pipes generally offer a lower initial cost compared to polycarbonate pipes, making PVC the more budget-friendly choice for large-scale plumbing projects. Polycarbonate pipes, despite their higher price, provide superior impact resistance and durability, potentially reducing long-term maintenance expenses. Cost analysis should consider installation, longevity, and environmental factors, with PVC excelling in affordability and polycarbonate favored for high-stress applications.
Environmental Impact and Recyclability
Polycarbonate pipes exhibit lower environmental impact due to their durability and high resistance to chemical degradation, reducing the frequency of replacement and waste generation compared to polyvinyl chloride (PVC). PVC pipes, while widely used for their cost-effectiveness and rigidity, contain additives like phthalates and chlorine that pose greater environmental and health concerns during production and disposal. Recycling of polycarbonate is more challenging but yields higher-quality recycled material, whereas PVC recycling is more common yet often results in downcycled products, limiting long-term sustainability.
Common Applications in Industry and Construction
Polycarbonate pipes are commonly used in industrial applications requiring high impact resistance and transparency, such as in chemical processing and water treatment systems. Polyvinyl chloride (PVC) pipes dominate construction projects due to their cost-effectiveness, chemical resistance, and durability for plumbing, irrigation, and drainage systems. Both materials offer unique advantages: polycarbonate excels in environments needing toughness and visibility, while PVC is preferred for large-scale infrastructure and residential piping solutions.
Choosing the Right Pipe Material for Your Project
Polycarbonate offers superior impact resistance and flexibility, making it ideal for applications requiring durability and transparency, whereas polyvinyl chloride (PVC) is favored for its chemical resistance, affordability, and ease of installation in plumbing and drainage systems. Selecting the right pipe material depends on project-specific factors such as environmental exposure, pressure requirements, and budget constraints. For high-impact or UV-exposed environments, polycarbonate pipes are preferable, while PVC pipes are optimal for standard water supply and waste management due to their corrosion resistance and cost-effectiveness.
Infographic: Polycarbonate vs Polyvinyl chloride for Pipe
 azmater.com
azmater.com