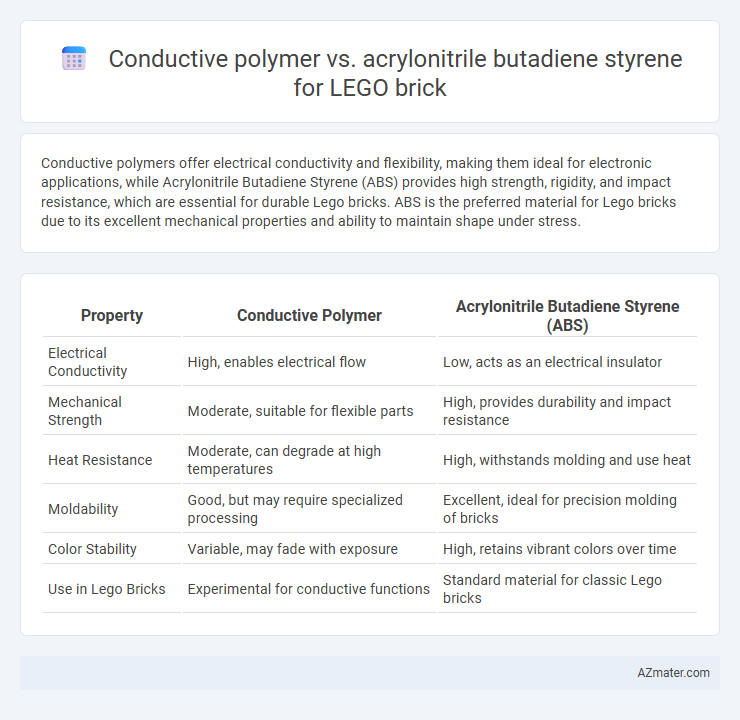
Conductive polymers offer electrical conductivity and flexibility, making them ideal for electronic applications, while Acrylonitrile Butadiene Styrene (ABS) provides high strength, rigidity, and impact resistance, which are essential for durable Lego bricks. ABS is the preferred material for Lego bricks due to its excellent mechanical properties and ability to maintain shape under stress.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Conductive Polymer | Acrylonitrile Butadiene Styrene (ABS) |
|---|---|---|
| Electrical Conductivity | High, enables electrical flow | Low, acts as an electrical insulator |
| Mechanical Strength | Moderate, suitable for flexible parts | High, provides durability and impact resistance |
| Heat Resistance | Moderate, can degrade at high temperatures | High, withstands molding and use heat |
| Moldability | Good, but may require specialized processing | Excellent, ideal for precision molding of bricks |
| Color Stability | Variable, may fade with exposure | High, retains vibrant colors over time |
| Use in Lego Bricks | Experimental for conductive functions | Standard material for classic Lego bricks |
Introduction to Material Selection in Lego Bricks
Conductive polymers offer electrical conductivity and flexibility, making them suitable for integrating electronic functions in Lego bricks, unlike Acrylonitrile Butadiene Styrene (ABS), which provides superior mechanical strength, durability, and easy molding. ABS is the standard material in Lego production due to its impact resistance and vibrant color retention, essential for maintaining the iconic look and feel of Lego bricks. Selecting between conductive polymers and ABS depends on intended functionality, with conductive polymers enhancing electronic interactivity and ABS ensuring structural integrity and longevity.
Overview of Conductive Polymers
Conductive polymers, such as polyaniline and polypyrrole, offer electrical conductivity while maintaining flexibility and lightweight properties, making them innovative materials for applications like electronic Lego bricks. Unlike Acrylonitrile Butadiene Styrene (ABS), which is primarily valued for its high mechanical strength, durability, and ease of molding, conductive polymers enable the integration of electronic functionalities directly into the plastic material. This unique combination of conductivity and processability positions conductive polymers as promising alternatives for advancing smart Lego bricks with embedded circuitry and sensing capabilities.
Properties and Applications of Acrylonitrile Butadiene Styrene (ABS)
Acrylonitrile Butadiene Styrene (ABS) offers excellent impact resistance, toughness, and heat resistance, making it ideal for durable toys like Lego bricks. Its high dimensional stability and ease of molding ensure precise, consistent shapes essential for Lego's interlocking design. ABS is non-conductive, lightweight, and chemically resistant, supporting safe and long-lasting play applications.
Mechanical Strength Comparison: Conductive Polymer vs ABS
Conductive polymers used in Lego bricks exhibit lower mechanical strength compared to Acrylonitrile Butadiene Styrene (ABS), which provides superior impact resistance and durability under repeated stress. ABS's high tensile strength and toughness make it ideal for maintaining Lego brick integrity during toy assembly and play. The mechanical robustness of ABS ensures long-lasting performance, whereas conductive polymers often compromise structural rigidity for electrical conductivity.
Electrical Conductivity: Expanding Lego’s Potential
Conductive polymer offers significantly higher electrical conductivity compared to Acrylonitrile Butadiene Styrene (ABS), enabling innovative applications in Lego bricks such as embedded circuits and interactive components. ABS, traditionally used for Lego bricks, is an excellent insulator with negligible conductivity, limiting its use in electronic integrations. Utilizing conductive polymers in Lego bricks expands potential for smart, responsive builds that integrate seamless electrical pathways without compromising structural integrity.
Durability and Longevity in Play Environments
Conductive polymers in Lego bricks offer enhanced electrical properties but typically exhibit lower mechanical durability compared to Acrylonitrile Butadiene Styrene (ABS), which is renowned for its robustness and resilience under repeated stress in play environments. ABS provides superior resistance to impact, wear, and environmental factors such as UV exposure and temperature variations, ensuring longer-lasting structural integrity in Lego constructions. Consequently, ABS remains the preferred material for durable, long-lasting Lego bricks designed for extensive handling and play.
Environmental Impact: Sustainability of Both Materials
Conductive polymers in Lego bricks offer enhanced recyclability and lower carbon footprints due to their potential for electrical functionality recycling, contrasting with acrylonitrile butadiene styrene (ABS), which is petroleum-based and less biodegradable. ABS's production emits higher greenhouse gases and contributes more to plastic pollution, challenging sustainability efforts compared to emerging conductive polymer composites. Innovations in conductive polymers aim to reduce environmental impact by enabling circular material use, supporting Lego's commitment to eco-friendly alternatives over traditional ABS plastics.
Cost Analysis: Manufacturing and Market Feasibility
Conductive polymers offer innovative properties for LEGO bricks, but their manufacturing costs remain significantly higher than traditional Acrylonitrile Butadiene Styrene (ABS), which benefits from established large-scale production and supply chains. ABS bricks provide consistent quality and cost-efficiency, making them more feasible for mass-market LEGO products. Market feasibility favors ABS due to its durability, lower price point, and widespread acceptance, while conductive polymers suit niche applications where electrical conductivity justifies premium pricing.
Innovations Enabled by Conductive Polymers in Lego
Conductive polymers in Lego bricks enable innovations such as interactive electronic components and embedded sensors that traditional acrylonitrile butadiene styrene (ABS) cannot achieve due to its insulating properties. These polymers facilitate the integration of touch-sensitive surfaces and light-up features, enhancing the play experience with responsive and programmable elements. The use of conductive polymers supports advancements in educational robotics and smart building sets, opening new avenues for STEM learning and interactive design.
Future Prospects: Choosing the Ideal Material for Next-Gen Lego Bricks
Conductive polymers offer promising future prospects for next-gen Lego bricks by enabling integrated electronic functions such as touch sensitivity and light emission, enhancing interactivity beyond traditional play. Acrylonitrile butadiene styrene (ABS) remains favored for its durability, precise molding capabilities, and color stability, ensuring lasting structural integrity and aesthetic appeal. Balancing the innovative electrical properties of conductive polymers with the proven robustness of ABS will guide the development of multifunctional, resilient Lego bricks tailored to evolving consumer demands.
Infographic: Conductive polymer vs Acrylonitrile butadiene styrene for Lego brick
 azmater.com
azmater.com