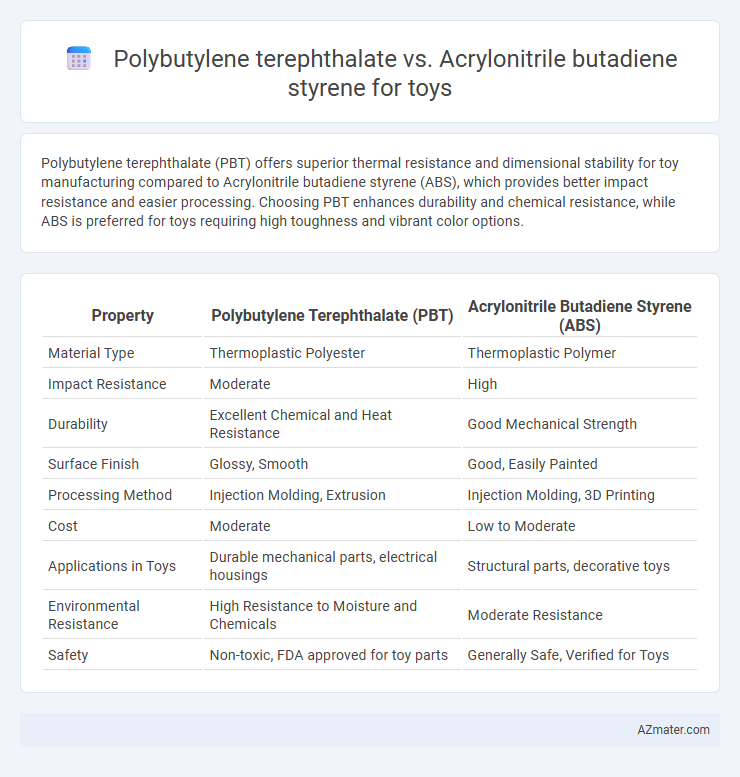
Polybutylene terephthalate (PBT) offers superior thermal resistance and dimensional stability for toy manufacturing compared to Acrylonitrile butadiene styrene (ABS), which provides better impact resistance and easier processing. Choosing PBT enhances durability and chemical resistance, while ABS is preferred for toys requiring high toughness and vibrant color options.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Polybutylene Terephthalate (PBT) | Acrylonitrile Butadiene Styrene (ABS) |
|---|---|---|
| Material Type | Thermoplastic Polyester | Thermoplastic Polymer |
| Impact Resistance | Moderate | High |
| Durability | Excellent Chemical and Heat Resistance | Good Mechanical Strength |
| Surface Finish | Glossy, Smooth | Good, Easily Painted |
| Processing Method | Injection Molding, Extrusion | Injection Molding, 3D Printing |
| Cost | Moderate | Low to Moderate |
| Applications in Toys | Durable mechanical parts, electrical housings | Structural parts, decorative toys |
| Environmental Resistance | High Resistance to Moisture and Chemicals | Moderate Resistance |
| Safety | Non-toxic, FDA approved for toy parts | Generally Safe, Verified for Toys |
Introduction to Toy-Grade Plastics
Toy-grade plastics like Polybutylene Terephthalate (PBT) and Acrylonitrile Butadiene Styrene (ABS) offer unique properties suited for durable, safe children's products. PBT provides excellent chemical resistance, dimensional stability, and high-impact strength, ideal for toys requiring sturdiness and heat resistance. ABS stands out for its toughness, ease of molding, and vibrant color retention, making it a popular choice for intricate, colorful toy components that endure rough play.
Key Properties of Polybutylene Terephthalate (PBT)
Polybutylene terephthalate (PBT) offers excellent mechanical strength, high dimensional stability, and superior resistance to heat and chemicals compared to acrylonitrile butadiene styrene (ABS), making it ideal for durable toy components. PBT's low moisture absorption enhances its electrical insulation properties, ensuring safety and reliability in electronic or interactive toys. Its resistance to wear and abrasion supports long-lasting toy usage, outperforming ABS in maintaining shape and performance under stress.
Key Properties of Acrylonitrile Butadiene Styrene (ABS)
Acrylonitrile Butadiene Styrene (ABS) offers excellent impact resistance, high tensile strength, and robust thermal stability, making it ideal for durable toy manufacturing. Its superior moldability and surface finish provide enhanced design flexibility and aesthetic appeal critical for complex toy shapes. ABS also exhibits good chemical resistance and toughness, ensuring long-lasting performance and safety in children's products compared to Polybutylene Terephthalate (PBT).
Mechanical Strength: PBT vs ABS
Polybutylene terephthalate (PBT) exhibits higher mechanical strength and rigidity compared to Acrylonitrile butadiene styrene (ABS), making it more resistant to deformation under stress in toy applications. ABS offers superior impact resistance and toughness, allowing it to absorb shocks without cracking, which is beneficial for toys subjected to rough handling. The choice between PBT and ABS depends on the balance required between stiffness for structural integrity and impact resistance for durability in toy manufacturing.
Safety and Non-Toxicity Considerations
Polybutylene terephthalate (PBT) offers superior chemical resistance and thermal stability, making it a safer choice for toys that require durability and exposure to high temperatures, while its low moisture absorption reduces the risk of microbial growth. Acrylonitrile butadiene styrene (ABS) is widely used in toy manufacturing due to its toughness and impact resistance, but it may release trace amounts of potentially harmful styrene, raising concerns about long-term safety and non-toxicity. Both materials comply with international toy safety standards like EN71 and ASTM F963, but PBT's inherent chemical stability often positions it as a more non-toxic and safer option for children's products.
Colorability and Surface Finish in Toy Manufacturing
Polybutylene terephthalate (PBT) offers excellent colorability with vibrant, consistent hues due to its high crystallinity and resistance to UV degradation, making it ideal for toys requiring durable, fade-resistant finishes. Acrylonitrile butadiene styrene (ABS) provides superior surface finish quality with a smooth, glossy appearance and easier post-processing options like painting and plating, enhancing aesthetic appeal in toy manufacturing. While PBT excels in color retention and chemical resistance, ABS is favored for intricate surface detailing and a premium tactile feel in consumer toys.
Durability and Impact Resistance Comparison
Polybutylene terephthalate (PBT) offers superior chemical resistance and high dimensional stability, making it highly durable for toy manufacturing. Acrylonitrile butadiene styrene (ABS) provides excellent impact resistance due to its tough, amorphous structure, ideal for toys subjected to rough handling. While PBT excels in heat resistance and rigidity, ABS outperforms in absorption of shocks and impact, crucial for safe and long-lasting toy applications.
Cost Implications for Toy Production
Polybutylene terephthalate (PBT) generally offers a lower material cost compared to acrylonitrile butadiene styrene (ABS), making it a cost-effective option for high-volume toy production. PBT's superior chemical resistance and dimensional stability can reduce expenses related to maintenance and product defects in manufacturing. However, ABS provides greater impact resistance and easier processing, which might justify its higher cost depending on toy design and safety requirements.
Environmental and Recycling Aspects
Polybutylene terephthalate (PBT) offers superior environmental benefits over acrylonitrile butadiene styrene (ABS) due to its better recyclability and lower carbon footprint during production. PBT can be efficiently recycled through thermal reprocessing without significant degradation, reducing landfill waste associated with toy manufacturing. ABS, while durable, poses challenges in recycling because of its complex polymer structure and higher emissions during incineration, making PBT a more sustainable choice for eco-conscious toy production.
Conclusion: Best Choice for Toy Applications
Polybutylene terephthalate (PBT) offers superior mechanical strength, excellent chemical resistance, and high thermal stability, making it ideal for durable and heat-resistant toy components. Acrylonitrile butadiene styrene (ABS) provides better impact resistance and ease of processing, suitable for intricate toy designs requiring toughness and aesthetic appeal. For toy applications demanding long-lasting performance and exposure to higher temperatures, PBT is the best choice, while ABS is preferred for cost-effective, impact-resistant, and visually appealing toys.
Infographic: Polybutylene terephthalate vs Acrylonitrile butadiene styrene for Toy
 azmater.com
azmater.com