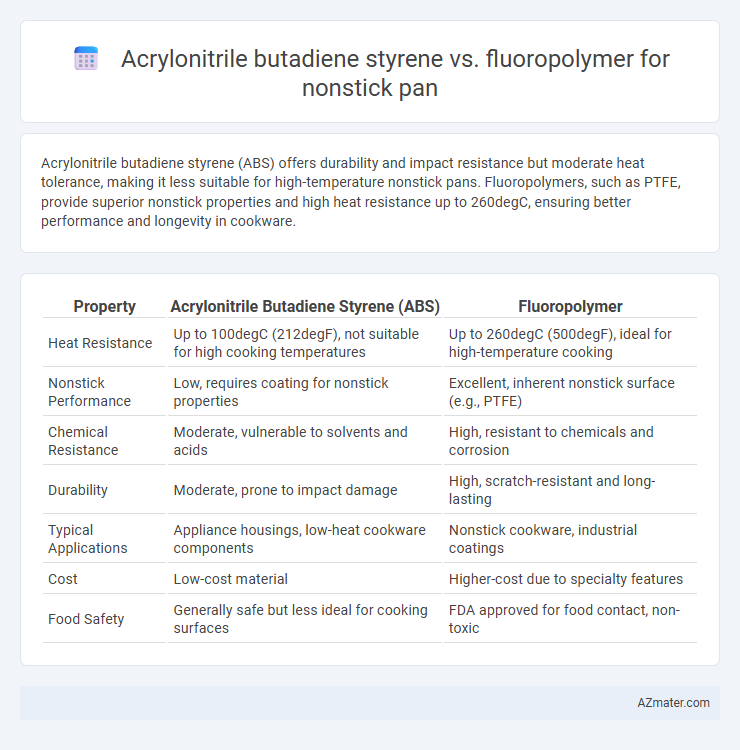
Acrylonitrile butadiene styrene (ABS) offers durability and impact resistance but moderate heat tolerance, making it less suitable for high-temperature nonstick pans. Fluoropolymers, such as PTFE, provide superior nonstick properties and high heat resistance up to 260degC, ensuring better performance and longevity in cookware.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Acrylonitrile Butadiene Styrene (ABS) | Fluoropolymer |
|---|---|---|
| Heat Resistance | Up to 100degC (212degF), not suitable for high cooking temperatures | Up to 260degC (500degF), ideal for high-temperature cooking |
| Nonstick Performance | Low, requires coating for nonstick properties | Excellent, inherent nonstick surface (e.g., PTFE) |
| Chemical Resistance | Moderate, vulnerable to solvents and acids | High, resistant to chemicals and corrosion |
| Durability | Moderate, prone to impact damage | High, scratch-resistant and long-lasting |
| Typical Applications | Appliance housings, low-heat cookware components | Nonstick cookware, industrial coatings |
| Cost | Low-cost material | Higher-cost due to specialty features |
| Food Safety | Generally safe but less ideal for cooking surfaces | FDA approved for food contact, non-toxic |
Introduction to Nonstick Cookware Materials
Nonstick cookware materials like Acrylonitrile Butadiene Styrene (ABS) and Fluoropolymers differ significantly in composition and performance. ABS is a thermoplastic polymer known for durability and impact resistance but lacks inherent nonstick properties, often requiring surface coatings. Fluoropolymers, such as polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE), provide superior nonstick performance due to their low friction coefficient and high chemical resistance, making them the preferred choice for high-quality nonstick pans.
Overview of Acrylonitrile Butadiene Styrene (ABS)
Acrylonitrile Butadiene Styrene (ABS) is a thermoplastic polymer known for its high impact resistance, toughness, and good heat resistance, making it a common material in various consumer goods. In nonstick pans, ABS is often used for handles or outer components rather than the cooking surface due to its moderate thermal stability and inability to withstand high cooking temperatures without deformation. Compared to fluoropolymers such as PTFE, which provide superior nonstick properties and heat resistance on the cooking surface, ABS serves a complementary structural role rather than a direct nonstick coating.
Overview of Fluoropolymer Coatings (e.g., PTFE, Teflon)
Fluoropolymer coatings such as PTFE (Polytetrafluoroethylene) and Teflon offer superior nonstick properties for cookware due to their low surface energy and excellent chemical inertness. These materials provide high resistance to heat up to approximately 260degC (500degF) and prevent food adhesion, enhancing cooking performance and ease of cleaning. Compared to Acrylonitrile Butadiene Styrene (ABS), which is primarily a structural polymer lacking inherent nonstick characteristics, fluoropolymers are specifically engineered for durability and nonstick functionality in cookware applications.
Nonstick Performance Comparison: ABS vs Fluoropolymer
Fluoropolymer coatings, such as PTFE, offer superior nonstick performance compared to Acrylonitrile Butadiene Styrene (ABS) due to their high chemical resistance and low surface energy, which prevents food adhesion effectively. ABS, primarily used as a structural material in cookware handles, lacks inherent nonstick properties and is not suitable for cooking surfaces. Fluoropolymer nonstick pans provide enhanced durability, easy food release, and higher temperature resistance, making them the preferred choice for nonstick cookware applications.
Durability and Scratch Resistance
Acrylonitrile butadiene styrene (ABS) offers moderate durability and scratch resistance but tends to degrade under high heat and abrasive utensils, limiting its lifespan in nonstick pans. Fluoropolymers, such as PTFE, exhibit superior durability and exceptional scratch resistance due to their chemical inertness and high thermal stability, making them the preferred choice for long-lasting nonstick cookware. The fluoropolymer's ability to maintain a smooth, intact surface under frequent use ensures consistent nonstick performance over time compared to ABS coatings.
Heat Resistance and Cooking Safety
Acrylonitrile butadiene styrene (ABS) offers moderate heat resistance up to around 105degC, suitable for handles but unsuitable for direct cooking surfaces due to potential deformation and toxic fume release. Fluoropolymers, such as PTFE, provide exceptional heat resistance up to approximately 260degC, enabling safe and effective nonstick cooking with minimal risk of harmful emissions under typical cooking temperatures. Choosing fluoropolymer coatings ensures superior cooking safety and durability compared to ABS in nonstick pan applications.
Chemical Reactivity and Food Safety
Acrylonitrile butadiene styrene (ABS) exhibits moderate chemical reactivity, potentially leaching harmful compounds when exposed to high heat, raising food safety concerns in nonstick pans. Fluoropolymers, such as polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE), offer superior chemical inertness and thermal stability, minimizing the risk of toxic substance release during cooking. The FDA recognizes fluoropolymer coatings as safe for food contact under normal cooking temperatures, whereas ABS lacks similar food-safe certification for culinary applications.
Cleaning and Maintenance Differences
Acrylonitrile butadiene styrene (ABS) nonstick pans often require gentle cleaning with non-abrasive sponges to prevent surface scratches and maintain coating integrity, as harsh scrubbing can degrade their finish over time. Fluoropolymer-coated pans, such as those using PTFE, offer superior resistance to staining and are easier to clean with mild detergents, minimizing the need for vigorous scrubbing and reducing the risk of damage during maintenance. Fluoropolymer coatings typically provide longer-lasting nonstick performance with less frequent reconditioning compared to ABS materials, making them a preferred option for low-maintenance cookware.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
Acrylonitrile butadiene styrene (ABS) is a petroleum-based plastic that poses environmental concerns due to its non-biodegradability and challenges in recycling, leading to long-term plastic pollution. Fluoropolymers, commonly used in nonstick pans, have greater chemical stability and can release harmful perfluorooctanoic acid (PFOA) during manufacturing or degradation, raising sustainability and toxicity issues. When comparing environmental impact, neither material is fully sustainable, but fluoropolymers often face greater scrutiny for persistence and bioaccumulation in ecosystems.
Conclusion: Best Choice for Nonstick Pans
Acrylonitrile butadiene styrene (ABS) offers durability and cost-effectiveness but lacks the high heat resistance and chemical inertness essential for premium nonstick pans. Fluoropolymers, such as PTFE, provide superior nonstick performance, high-temperature tolerance, and excellent chemical resistance, making them the preferred material for professional-grade cookware. For nonstick pan applications demanding longevity and optimal food release, fluoropolymers remain the best choice.
Infographic: Acrylonitrile butadiene styrene vs Fluoropolymer for Nonstick pan
 azmater.com
azmater.com