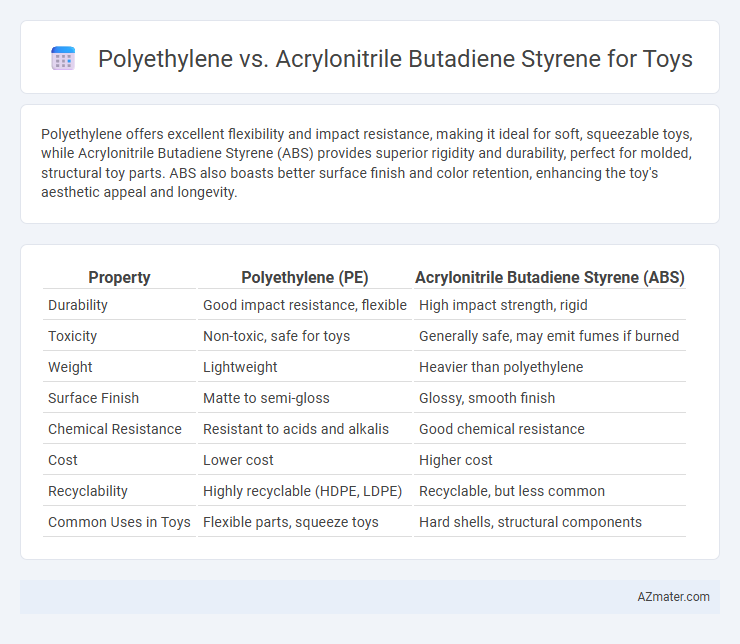
Polyethylene offers excellent flexibility and impact resistance, making it ideal for soft, squeezable toys, while Acrylonitrile Butadiene Styrene (ABS) provides superior rigidity and durability, perfect for molded, structural toy parts. ABS also boasts better surface finish and color retention, enhancing the toy's aesthetic appeal and longevity.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Polyethylene (PE) | Acrylonitrile Butadiene Styrene (ABS) |
|---|---|---|
| Durability | Good impact resistance, flexible | High impact strength, rigid |
| Toxicity | Non-toxic, safe for toys | Generally safe, may emit fumes if burned |
| Weight | Lightweight | Heavier than polyethylene |
| Surface Finish | Matte to semi-gloss | Glossy, smooth finish |
| Chemical Resistance | Resistant to acids and alkalis | Good chemical resistance |
| Cost | Lower cost | Higher cost |
| Recyclability | Highly recyclable (HDPE, LDPE) | Recyclable, but less common |
| Common Uses in Toys | Flexible parts, squeeze toys | Hard shells, structural components |
Introduction to Polyethylene and ABS Plastics
Polyethylene (PE) is a versatile thermoplastic known for its excellent chemical resistance, flexibility, and low cost, making it ideal for lightweight and durable toys. Acrylonitrile Butadiene Styrene (ABS) offers superior impact resistance, rigidity, and better surface finish, commonly used in high-quality, rigid toy construction. Both plastics provide unique benefits for toy manufacturing, with PE favored for soft, flexible parts and ABS preferred for structurally strong, detailed components.
Chemical Structure and Composition Differences
Polyethylene (PE) is a simple polymer composed of long chains of ethylene monomers, characterized by its linear or branched hydrocarbon structure, which results in excellent chemical resistance and flexibility. Acrylonitrile Butadiene Styrene (ABS) is a terpolymer consisting of acrylonitrile, butadiene, and styrene units, providing a more complex structure with high impact resistance, toughness, and rigidity due to the combination of polar and non-polar segments. The chemical composition difference between PE and ABS influences their mechanical properties and suitability for toys, with PE favored for soft, flexible parts and ABS preferred for durable, rigid components.
Durability and Strength: Toy Longevity Compared
Polyethylene offers excellent impact resistance and flexibility, making it highly durable for toys that endure rough handling and repeated drops. Acrylonitrile Butadiene Styrene (ABS) provides superior rigidity and strength, resulting in toys that maintain structural integrity under stress and resist cracking. For toy longevity, ABS typically outperforms polyethylene in applications requiring hard, resilient surfaces, while polyethylene excels in flexible, impact-absorbing designs.
Safety and Non-Toxicity in Toy Manufacturing
Polyethylene offers excellent safety and non-toxicity profiles, making it a popular choice in toy manufacturing due to its chemical inertness and resistance to leaching harmful substances. Acrylonitrile Butadiene Styrene (ABS) provides durable, impact-resistant toys but requires careful formulation to meet stringent safety standards, as improper composition may release toxic compounds under stress. Regulatory compliance for both materials involves rigorous testing for heavy metals, phthalates, and other hazardous substances to ensure children's health and product safety.
Flexibility and Shape Retention in Toys
Polyethylene offers superior flexibility, making it ideal for toys that require bending and squeezing without permanent deformation. Acrylonitrile Butadiene Styrene (ABS) provides excellent shape retention due to its rigid and tough structure, ensuring toys maintain their form under stress and impact. For toys needing both durability and consistent shape, ABS is preferred, whereas polyethylene suits designs emphasizing soft, flexible play elements.
Color Vibrancy and Aesthetic Appeal
Polyethylene (PE) offers limited color vibrancy due to its semi-crystalline structure, resulting in a more muted and less glossy finish compared to Acrylonitrile Butadiene Styrene (ABS). ABS provides superior color retention and a glossy, smooth surface, enhancing the aesthetic appeal of toys with vibrant, long-lasting colors. The enhanced UV resistance in ABS ensures toys maintain their visual appeal over time, making it the preferred choice for color-intensive applications.
Cost-Effectiveness and Production Efficiency
Polyethylene offers superior cost-effectiveness for toy manufacturing due to its low raw material price and energy-efficient processing, making it ideal for high-volume, budget-sensitive production. Acrylonitrile Butadiene Styrene (ABS), while more expensive, provides enhanced durability and aesthetic appeal, justifying higher costs in premium or impact-resistant toy segments. Production efficiency favors polyethylene with quicker cycle times and easier molding, whereas ABS requires precise temperature control and longer cooling periods, affecting overall throughput.
Environmental Impact and Recyclability
Polyethylene (PE) exhibits a lower environmental impact compared to Acrylonitrile Butadiene Styrene (ABS) due to its simpler polymer structure, facilitating easier recycling and biodegradability under specific conditions. ABS, while offering superior strength and durability for toy manufacturing, poses greater challenges in recycling processes because of its complex chemical composition, which limits its recyclability and contributes to longer degradation times in landfills. Choosing PE for toys enhances sustainability through improved recyclability and reduced ecological footprint, aligning with environmental safety standards.
Common Toy Applications for Each Material
Polyethylene (PE) is widely used in the production of lightweight, flexible toys such as squeeze balls, doll accessories, and outdoor play equipment due to its excellent impact resistance and low-cost manufacturing. Acrylonitrile Butadiene Styrene (ABS) is favored for more rigid and durable toys like LEGO bricks, action figures, and electronic housings, offering superior strength, toughness, and surface finish. The choice between PE and ABS in toy manufacturing depends on factors such as desired durability, flexibility, and safety compliance for children's products.
Final Considerations: Choosing the Right Plastic for Toys
Polyethylene offers excellent impact resistance, flexibility, and chemical stability, making it ideal for soft, squeezable toys and components requiring durability and safety. Acrylonitrile Butadiene Styrene (ABS) provides superior rigidity, higher heat resistance, and better surface finish, suited for detailed, structural toys and parts needing strength and aesthetic appeal. Selecting the right plastic depends on the toy's functional requirements, safety standards, and desired texture, with polyethylene favored for pliability and ABS preferred for robust, finely molded designs.
Infographic: Polyethylene vs Acrylonitrile Butadiene Styrene for Toy
 azmater.com
azmater.com