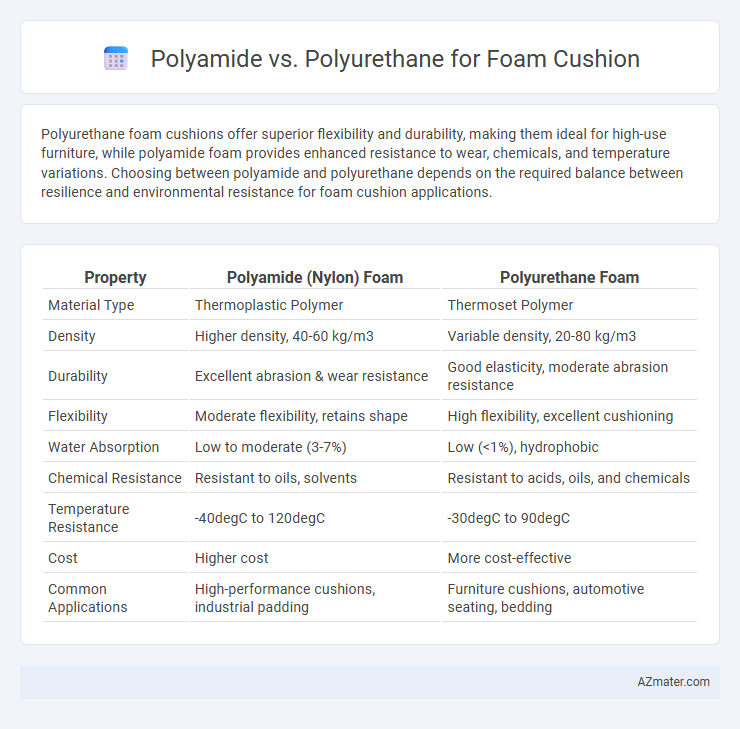
Polyurethane foam cushions offer superior flexibility and durability, making them ideal for high-use furniture, while polyamide foam provides enhanced resistance to wear, chemicals, and temperature variations. Choosing between polyamide and polyurethane depends on the required balance between resilience and environmental resistance for foam cushion applications.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Polyamide (Nylon) Foam | Polyurethane Foam |
|---|---|---|
| Material Type | Thermoplastic Polymer | Thermoset Polymer |
| Density | Higher density, 40-60 kg/m3 | Variable density, 20-80 kg/m3 |
| Durability | Excellent abrasion & wear resistance | Good elasticity, moderate abrasion resistance |
| Flexibility | Moderate flexibility, retains shape | High flexibility, excellent cushioning |
| Water Absorption | Low to moderate (3-7%) | Low (<1%), hydrophobic |
| Chemical Resistance | Resistant to oils, solvents | Resistant to acids, oils, and chemicals |
| Temperature Resistance | -40degC to 120degC | -30degC to 90degC |
| Cost | Higher cost | More cost-effective |
| Common Applications | High-performance cushions, industrial padding | Furniture cushions, automotive seating, bedding |
Introduction to Polyamide and Polyurethane Foam Cushions
Polyamide foam cushions offer high durability, excellent resistance to abrasion, and enhanced dimensional stability, making them ideal for long-lasting furniture and automotive seating. Polyurethane foam cushions provide superior cushioning comfort, flexibility, and are widely used for their lightweight properties and cost-effectiveness in upholstery and bedding. Both materials exhibit distinct performance traits, with polyamide excelling in toughness and polyurethane favored for softness and versatility.
Chemical Structure and Composition Differences
Polyamide foam cushions consist of long polymer chains with repeating amide groups (-CONH-) that provide high tensile strength and thermal stability. Polyurethane foams are formed from the reaction of polyols and diisocyanates, creating urethane linkages (-NHCOO-) that result in versatile elasticity and resilience. The key chemical difference lies in polyamide's strong hydrogen bonding versus polyurethane's flexible urethane bonds, affecting their durability and comfort in cushioning.
Manufacturing Processes Comparison
Polyamide foam cushions are primarily produced through a melt-blowing or spunbonding process, which results in a durable, resilient structure with superior mechanical properties and breathability. Polyurethane foam manufacturing involves a chemical reaction between polyols and diisocyanates, typically using a slabstock or molded foam process to create a soft, flexible, and highly customizable cushioning material. The polyamide process requires higher temperatures and complex equipment, while polyurethane foam production offers faster cycle times and greater versatility in density and firmness adjustment.
Mechanical Properties: Strength and Flexibility
Polyurethane foam cushions exhibit superior flexibility and high tensile strength, making them ideal for applications requiring significant deformation and shock absorption. Polyamide foams typically offer greater mechanical strength and abrasion resistance but have less elasticity compared to polyurethane, resulting in a stiffer feel. The balance between strength and flexibility positions polyurethane as the preferred material for dynamic cushioning, while polyamide suits environments demanding robust structural integrity.
Durability and Longevity in Cushion Applications
Polyurethane foam offers superior durability and longevity compared to polyamide foam due to its high resilience and resistance to compression set, making it ideal for long-term cushion applications. Polyamide foam, while providing excellent moisture resistance and elasticity, tends to degrade faster under continuous pressure and repeated use. In cushion manufacturing, polyurethane's ability to maintain shape and support over extended periods results in improved performance and extended product lifespan.
Comfort and Support: Performance Analysis
Polyamide foam cushions offer excellent durability and breathability, making them ideal for long-lasting comfort with moderate support. Polyurethane foam provides superior cushioning and higher support density, adapting better to body contours for enhanced pressure relief. Performance analysis indicates polyurethane excels in comfort for prolonged seating, while polyamide foam is preferred for applications requiring lightweight resilience and airflow.
Moisture Resistance and Breathability
Polyurethane foam cushions offer superior moisture resistance due to their closed-cell structure that repels water and prevents absorption, maintaining comfort and durability in humid environments. Polyamide foam cushions excel in breathability because their open-cell design allows better air circulation, reducing heat buildup and enhancing comfort during prolonged use. Choosing between polyamide and polyurethane foams depends on the balance needed between moisture resistance and airflow for specific cushioning applications.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
Polyamide foam cushions generally have a higher environmental footprint due to petroleum-based raw materials and energy-intensive production processes compared to polyurethane foams, which can incorporate bio-based polyols to reduce carbon emissions. Polyurethane offers enhanced recyclability and potential for closed-loop manufacturing, promoting sustainability through material recovery and reuse. Both materials require advancements in biodegradability and lifecycle management to minimize microplastic pollution and landfill waste in foam cushion applications.
Cost-Effectiveness and Market Availability
Polyurethane foam cushions generally offer superior cost-effectiveness due to lower raw material costs and widespread manufacturing, making them the dominant choice in furniture and automotive markets. Polyamide foams, while more expensive, provide enhanced durability and chemical resistance, appealing to specialized applications but limiting their market availability and increasing overall cost. The extensive supply chain and production scale of polyurethane ensure easier procurement and competitive pricing compared to the niche, high-performance polyamide alternatives.
Best Uses: Choosing the Right Foam for Your Needs
Polyamide foam offers superior durability and resistance to heat and chemicals, making it ideal for high-performance industrial cushions and automotive seating. Polyurethane foam provides excellent flexibility and cushioning, suitable for furniture, bedding, and soundproofing applications due to its softness and shock absorption. Selecting the right foam depends on whether durability or comfort is the priority, with polyamide excelling in longevity and polyurethane favored for ergonomic support.
Infographic: Polyamide vs Polyurethane for Foam Cushion
 azmater.com
azmater.com