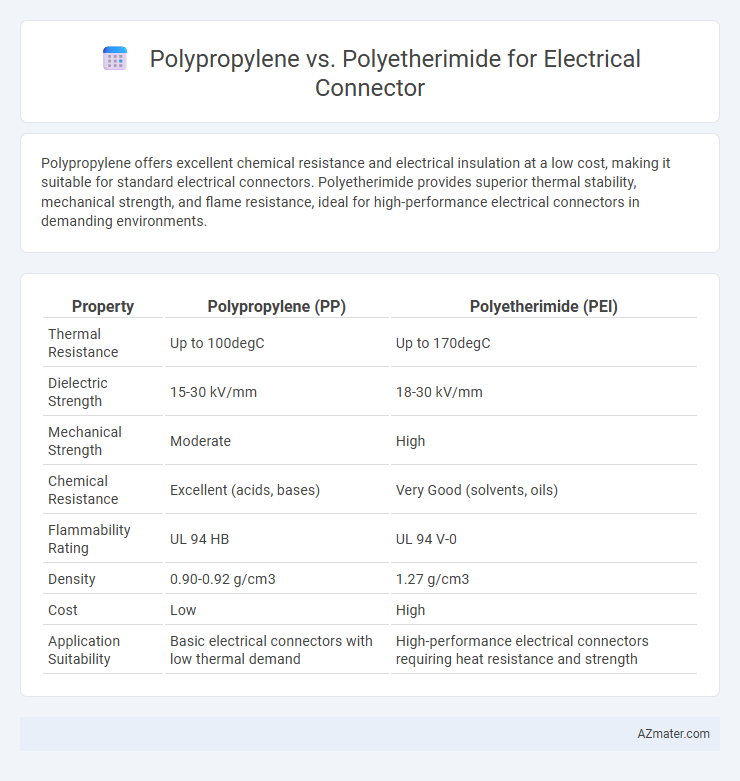
Polypropylene offers excellent chemical resistance and electrical insulation at a low cost, making it suitable for standard electrical connectors. Polyetherimide provides superior thermal stability, mechanical strength, and flame resistance, ideal for high-performance electrical connectors in demanding environments.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Polypropylene (PP) | Polyetherimide (PEI) |
|---|---|---|
| Thermal Resistance | Up to 100degC | Up to 170degC |
| Dielectric Strength | 15-30 kV/mm | 18-30 kV/mm |
| Mechanical Strength | Moderate | High |
| Chemical Resistance | Excellent (acids, bases) | Very Good (solvents, oils) |
| Flammability Rating | UL 94 HB | UL 94 V-0 |
| Density | 0.90-0.92 g/cm3 | 1.27 g/cm3 |
| Cost | Low | High |
| Application Suitability | Basic electrical connectors with low thermal demand | High-performance electrical connectors requiring heat resistance and strength |
Introduction to Polypropylene and Polyetherimide
Polypropylene is a thermoplastic polymer known for its excellent chemical resistance, low density, and good electrical insulating properties, making it a common choice in electrical connectors requiring cost-effective durability. Polyetherimide (PEI) is a high-performance engineering plastic characterized by superior thermal stability, mechanical strength, and flame retardancy, ideal for connectors exposed to high temperatures and demanding electrical environments. The selection between polypropylene and polyetherimide depends on specific application requirements such as temperature resistance, mechanical stress, and electrical insulation needs.
Key Material Properties Comparison
Polypropylene offers excellent chemical resistance, low moisture absorption, and good electrical insulation, making it suitable for basic electrical connectors in low-temperature environments. Polyetherimide (PEI) provides superior thermal stability with a continuous use temperature up to 170degC, higher mechanical strength, and better dimensional stability, ideal for demanding high-performance electrical connectors. While polypropylene is cost-effective and lightweight, PEI excels in flame retardancy, dielectric strength, and resistance to harsh environmental conditions, supporting advanced connector applications.
Electrical Insulation Performance
Polyetherimide (PEI) exhibits superior electrical insulation performance compared to polypropylene (PP) due to its higher dielectric strength and resistance to tracking and corona discharge. PEI maintains stable dielectric properties under elevated temperatures, making it ideal for high-performance electrical connectors subjected to thermal stress. In contrast, polypropylene offers moderate insulation with lower thermal stability, limiting its use in demanding electrical environments.
Mechanical Strength and Durability
Polyetherimide (PEI) offers superior mechanical strength and durability compared to polypropylene for electrical connectors, with a tensile strength above 110 MPa against polypropylene's typical 30-40 MPa. PEI also exhibits excellent thermal stability and resistance to creep, ensuring long-term performance in high-stress environments. Polypropylene, while lightweight and cost-effective, lacks the high-temperature resistance and mechanical robustness required for demanding electrical connector applications.
Thermal Stability and Heat Resistance
Polyetherimide (PEI) demonstrates superior thermal stability and heat resistance compared to polypropylene, sustaining continuous use temperatures up to 170degC versus polypropylene's limit around 100-110degC. PEI also has a higher glass transition temperature (Tg) near 217degC, ensuring dimensional stability and performance in high-heat electrical connector applications. Polypropylene's lower melting point and thermal endurance make it less suitable for connectors exposed to elevated temperatures or harsh thermal cycling conditions.
Chemical Resistance and Environmental Suitability
Polypropylene exhibits excellent chemical resistance against acids, bases, and many solvents, making it highly suitable for electrical connectors exposed to harsh chemical environments. Polyetherimide provides superior thermal stability and resists hydrolysis and oxidation better, ensuring reliability in electrical connectors operating in high-temperature or aggressive environmental conditions. For applications demanding long-term environmental durability and chemical resistance, polyetherimide outperforms polypropylene by maintaining mechanical integrity and electrical insulation properties under extreme conditions.
Ease of Processing and Manufacturing
Polypropylene offers excellent ease of processing due to its low melting point and high flow characteristics, making it ideal for injection molding electrical connectors with fast cycle times. In contrast, polyetherimide requires higher processing temperatures and more precise mold conditions, which can increase manufacturing complexity and costs. However, polyetherimide provides superior thermal stability and mechanical strength, often justifying the more demanding manufacturing process for high-performance electrical connector applications.
Cost Analysis: Polypropylene vs Polyetherimide
Polypropylene offers a significantly lower cost compared to polyetherimide, making it a budget-friendly choice for electrical connectors in applications with less demanding thermal and mechanical requirements. Polyetherimide, while more expensive, provides superior heat resistance, electrical insulation, and mechanical strength, which justify its higher price in high-performance or critical environments. Evaluating long-term durability and application-specific performance is essential when balancing initial material costs against overall value in electrical connector design.
Typical Applications in Electrical Connectors
Polypropylene is commonly used in electrical connectors for applications requiring excellent chemical resistance and insulation properties, such as consumer electronics and automotive wiring. Polyetherimide (PEI) is preferred in high-performance electrical connectors where superior thermal stability, mechanical strength, and flame retardance are critical, including aerospace and industrial equipment. Both polymers serve essential roles, with polypropylene favoring cost-effectiveness and chemical resistance, while polyetherimide excels in demanding electrical environments.
Choosing the Right Material for Your Electrical Connector
Polyetherimide (PEI) offers superior thermal stability and high dielectric strength, making it ideal for electrical connectors operating in high-temperature environments or requiring excellent electrical insulation. Polypropylene (PP) provides cost-effective, lightweight solutions with good chemical resistance but has lower heat resistance and mechanical strength compared to PEI. Selecting between PEI and PP depends on the specific performance needs of your electrical connector, such as operating temperature range, mechanical durability, and electrical insulation requirements.
Infographic: Polypropylene vs Polyetherimide for Electrical connector
 azmater.com
azmater.com