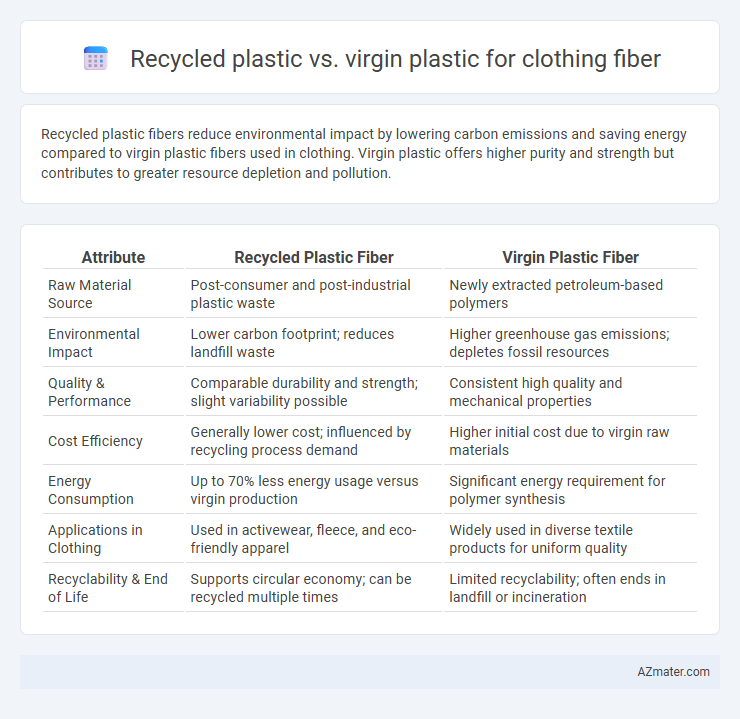
Recycled plastic fibers reduce environmental impact by lowering carbon emissions and saving energy compared to virgin plastic fibers used in clothing. Virgin plastic offers higher purity and strength but contributes to greater resource depletion and pollution.
Table of Comparison
| Attribute | Recycled Plastic Fiber | Virgin Plastic Fiber |
|---|---|---|
| Raw Material Source | Post-consumer and post-industrial plastic waste | Newly extracted petroleum-based polymers |
| Environmental Impact | Lower carbon footprint; reduces landfill waste | Higher greenhouse gas emissions; depletes fossil resources |
| Quality & Performance | Comparable durability and strength; slight variability possible | Consistent high quality and mechanical properties |
| Cost Efficiency | Generally lower cost; influenced by recycling process demand | Higher initial cost due to virgin raw materials |
| Energy Consumption | Up to 70% less energy usage versus virgin production | Significant energy requirement for polymer synthesis |
| Applications in Clothing | Used in activewear, fleece, and eco-friendly apparel | Widely used in diverse textile products for uniform quality |
| Recyclability & End of Life | Supports circular economy; can be recycled multiple times | Limited recyclability; often ends in landfill or incineration |
Introduction to Plastic Fibers in Clothing
Plastic fibers in clothing primarily consist of virgin and recycled plastics, where virgin plastic is newly manufactured from petrochemicals, offering consistent quality and performance. Recycled plastic fibers, often derived from post-consumer PET bottles, provide an eco-friendly alternative by reducing plastic waste and lowering carbon footprints. The choice between recycled and virgin plastic fibers impacts sustainability, material properties, and the environmental footprint of textile production.
Defining Recycled Plastic and Virgin Plastic
Recycled plastic for clothing fiber is made from post-consumer or post-industrial plastic waste that is cleaned, processed, and converted into usable textile fibers, significantly reducing environmental impact. Virgin plastic fibers originate from newly synthesized petrochemicals, offering consistent quality and performance but contributing to higher carbon emissions and resource depletion. The key differentiation lies in the source materials--recycled plastic prioritizes sustainability through waste reduction, while virgin plastic emphasizes purity and reliability in fiber production.
Environmental Impact: Recycled vs Virgin Plastic
Recycled plastic fibers significantly reduce environmental impact by lowering greenhouse gas emissions and conserving fossil fuel resources compared to virgin plastic fibers. The production of recycled plastic fibers emits up to 79% less carbon dioxide and uses 70% less energy, mitigating pollution and landfill waste. Utilizing recycled plastics in clothing fibers promotes a circular economy, reducing plastic waste accumulation in oceans and ecosystems.
Energy Consumption During Production
Recycled plastic fibers in clothing production consume up to 70% less energy compared to virgin plastic fibers, significantly reducing carbon emissions. The energy savings stem from bypassing the energy-intensive extraction and polymerization processes required for virgin plastics. Implementing recycled materials in textile manufacturing contributes substantially to lowering the overall environmental footprint of apparel production.
Quality and Durability of Fibers
Recycled plastic fibers often exhibit slightly lower tensile strength and consistency compared to virgin plastic fibers due to degradation during the recycling process, impacting overall fabric durability. Virgin plastic fibers, derived directly from petrochemical sources, maintain superior quality with uniform polymer chains that enhance fiber resilience and lifespan. Advances in recycling technology are narrowing the performance gap, but virgin plastic remains the benchmark for high-quality, durable clothing fibers.
Cost Analysis: Recycled Plastic vs Virgin Plastic
Recycled plastic fibers typically reduce raw material costs by up to 30% compared to virgin plastic, driven by lower energy requirements and reduced dependency on petroleum prices. Virgin plastic fibers, while offering more consistent quality, involve higher processing expenses and environmental compliance costs, elevating overall production expenses. Brands increasingly favor recycled fibers to optimize cost-efficiency and align with sustainability goals amidst rising plastic waste management regulations.
Consumer Perceptions and Market Trends
Consumer perceptions of recycled plastic fibers in clothing are increasingly positive, driven by growing environmental awareness and demand for sustainable fashion. Market trends indicate a significant rise in apparel brands adopting recycled polyester and nylon, reflecting a shift towards circular economy practices. Studies show that consumers value transparency and certifications, which enhance trust and willingness to pay a premium for recycled plastic-based garments.
Innovations in Plastic Fiber Technology
Innovations in plastic fiber technology have significantly advanced the use of recycled plastic over virgin plastic in clothing fibers, reducing environmental impact and resource consumption. Cutting-edge processes like chemical recycling and depolymerization enable higher quality recycled fibers with properties comparable to virgin polyester, enhancing durability and comfort. Brands leverage these technologies to create sustainable apparel lines, accelerating circular economy adoption in the fashion industry.
Challenges in Scaling Recycled Plastic Use
Scaling recycled plastic for clothing fiber faces challenges including inconsistent fiber quality, limited supply of high-grade recycled materials, and higher production costs compared to virgin plastic. Contamination and degradation during recycling processes reduce the performance of recycled fibers, hindering their appeal in high-performance apparel markets. Manufacturing infrastructure and consumer demand for sustainable textiles are growing but remain insufficient to meet global apparel fiber needs sustainably.
Future Outlook for Sustainable Clothing Fibers
Recycled plastic fibers contribute to reducing landfill waste and lowering carbon emissions compared to virgin plastic, which relies on fossil fuels and has a higher environmental footprint. Innovations in chemical recycling and biodegradable composites promise to enhance the quality and sustainability of recycled fibers, attracting major apparel brands aiming for circular fashion. Market trends forecast a significant increase in recycled plastic fiber adoption, driven by consumer demand for eco-friendly materials and stricter government regulations on plastics.
Infographic: Recycled plastic vs Virgin plastic for Clothing fiber
 azmater.com
azmater.com