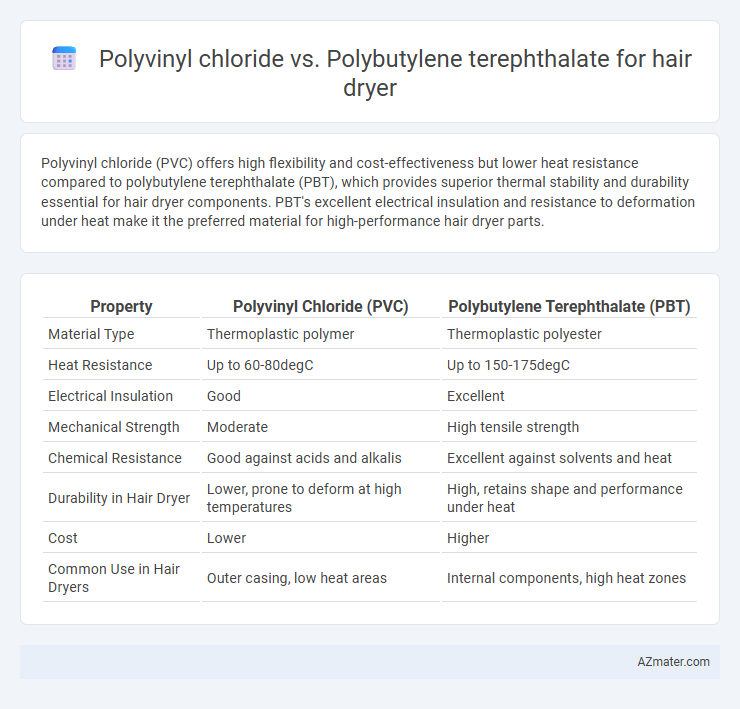
Polyvinyl chloride (PVC) offers high flexibility and cost-effectiveness but lower heat resistance compared to polybutylene terephthalate (PBT), which provides superior thermal stability and durability essential for hair dryer components. PBT's excellent electrical insulation and resistance to deformation under heat make it the preferred material for high-performance hair dryer parts.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Polyvinyl Chloride (PVC) | Polybutylene Terephthalate (PBT) |
|---|---|---|
| Material Type | Thermoplastic polymer | Thermoplastic polyester |
| Heat Resistance | Up to 60-80degC | Up to 150-175degC |
| Electrical Insulation | Good | Excellent |
| Mechanical Strength | Moderate | High tensile strength |
| Chemical Resistance | Good against acids and alkalis | Excellent against solvents and heat |
| Durability in Hair Dryer | Lower, prone to deform at high temperatures | High, retains shape and performance under heat |
| Cost | Lower | Higher |
| Common Use in Hair Dryers | Outer casing, low heat areas | Internal components, high heat zones |
Introduction to Polyvinyl Chloride (PVC) and Polybutylene Terephthalate (PBT)
Polyvinyl chloride (PVC) is a versatile thermoplastic widely used in hair dryer components due to its durability, chemical resistance, and flame-retardant properties, making it ideal for electrical insulation and flexible parts. Polybutylene terephthalate (PBT) is a high-performance engineering plastic valued for its excellent heat resistance, dimensional stability, and mechanical strength, often employed in hair dryer housings and structural elements exposed to high temperatures. Comparing PVC and PBT highlights PVC's flexibility and cost-effectiveness against PBT's superior thermal resistance and mechanical robustness in hair dryer applications.
Material Properties: PVC vs PBT
Polyvinyl chloride (PVC) offers high durability, chemical resistance, and cost-effectiveness, making it suitable for hair dryer casings but with limited heat resistance compared to polybutylene terephthalate (PBT). PBT provides superior thermal stability, electrical insulation, and mechanical strength, essential for internal components exposed to heat during hair dryer operation. The inherent flame retardancy and dimensional stability of PBT ensure enhanced safety and longevity in high-temperature conditions compared to PVC.
Heat Resistance and Thermal Stability
Polyvinyl chloride (PVC) offers moderate heat resistance suitable for standard hair dryer components but can degrade under prolonged high temperatures, leading to potential deformation. Polybutylene terephthalate (PBT) exhibits superior thermal stability with a higher melting point around 223degC, making it more resistant to heat and ideal for internal parts exposed to elevated temperatures. PBT's enhanced heat resistance reduces the risk of material breakdown and improves the durability and safety of hair dryer components compared to PVC.
Durability and Impact Resistance
Polyvinyl chloride (PVC) offers moderate durability and impact resistance for hair dryer components but tends to be less heat resistant compared to polybutylene terephthalate (PBT). Polybutylene terephthalate demonstrates superior impact resistance and thermal stability, making it more suitable for high-temperature applications such as hair dryer housings. PBT's enhanced durability under repeated thermal stress ensures longer lifespan and improved safety in hair dryer manufacturing.
Electrical Insulation Capabilities
Polyvinyl chloride (PVC) exhibits excellent electrical insulation properties with a high dielectric strength, making it ideal for preventing electrical hazards in hair dryers. Polybutylene terephthalate (PBT) also offers strong electrical insulation but with superior heat resistance and dimensional stability, ensuring consistent performance under prolonged thermal stress. The choice between PVC and PBT for hair dryer components depends on balancing electrical insulation quality with thermal durability requirements.
Weight and Design Flexibility
Polyvinyl chloride (PVC) offers a lightweight solution ideal for hair dryer housings, enhancing portability without compromising durability. Polybutylene terephthalate (PBT) provides superior design flexibility with excellent heat resistance and dimensional stability, supporting intricate molding and ergonomic shapes. Weight considerations favor PVC for reduced device mass, while PBT excels in complex design requirements and thermal performance.
Cost and Manufacturing Considerations
Polyvinyl chloride (PVC) offers low material costs and straightforward manufacturing processes, making it an economical choice for hair dryer housings. Polybutylene terephthalate (PBT), while more expensive, provides superior heat resistance and dimensional stability, benefiting components exposed to high temperatures during operation. Manufacturers often weigh PVC's affordability against PBT's performance advantages to optimize production costs and durability in hair dryer design.
Environmental Impact and Recyclability
Polyvinyl chloride (PVC) presents significant environmental concerns due to its production process releasing harmful dioxins and its difficulty in recycling, often ending up in landfills or incinerators. Polybutylene terephthalate (PBT) offers a more eco-friendly alternative with better recyclability and a lower carbon footprint during production, making it preferable for sustainable hair dryer manufacturing. The choice of PBT reduces hazardous waste and supports circular economy principles by enabling material recovery and reuse.
Suitability for Hair Dryer Components
Polyvinyl chloride (PVC) offers excellent electrical insulation and heat resistance, making it suitable for external hair dryer housings and flexible cords, but it can degrade under prolonged high temperatures. Polybutylene terephthalate (PBT) exhibits superior thermal stability, dimensional stability, and mechanical strength, ideal for internal hair dryer components such as fan blades and motor parts exposed to continuous heat. PBT's resistance to heat and wear enhances durability and performance, whereas PVC is more cost-effective but less mechanically robust for high-temperature internal applications.
Final Comparison: Which Material is Best for Hair Dryers?
Polybutylene terephthalate (PBT) offers superior thermal stability and mechanical strength compared to polyvinyl chloride (PVC), making it more suitable for hair dryers exposed to high heat. PBT's excellent electrical insulation properties reduce the risk of electrical hazards, enhancing user safety in hair dryer applications. While PVC is cost-effective, its lower heat resistance and potential for toxic gas emission under high temperatures render PBT the best overall material for durable, safe, and efficient hair dryers.
Infographic: Polyvinyl chloride vs Polybutylene terephthalate for Hair Dryer
 azmater.com
azmater.com