Polylactic acid (PLA) offers biodegradability and ease of 3D printing, making it ideal for eco-friendly button production, while Polyoxymethylene (POM) provides superior mechanical strength, chemical resistance, and durability for high-performance buttons. Selecting PLA suits environmentally conscious designs, whereas POM is preferred for long-lasting, wear-resistant applications.
Table of Comparison
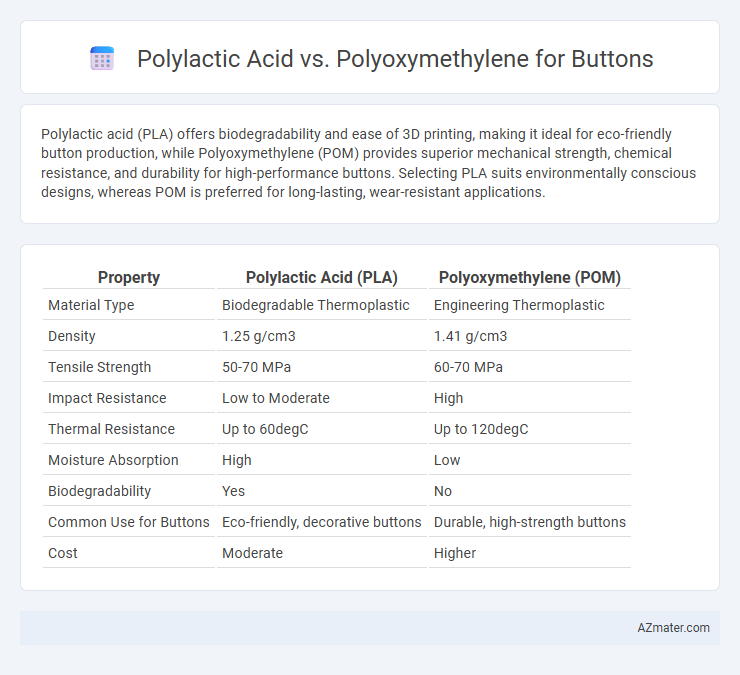
| Property | Polylactic Acid (PLA) | Polyoxymethylene (POM) |
|---|---|---|
| Material Type | Biodegradable Thermoplastic | Engineering Thermoplastic |
| Density | 1.25 g/cm3 | 1.41 g/cm3 |
| Tensile Strength | 50-70 MPa | 60-70 MPa |
| Impact Resistance | Low to Moderate | High |
| Thermal Resistance | Up to 60degC | Up to 120degC |
| Moisture Absorption | High | Low |
| Biodegradability | Yes | No |
| Common Use for Buttons | Eco-friendly, decorative buttons | Durable, high-strength buttons |
| Cost | Moderate | Higher |
Introduction to Polylactic Acid and Polyoxymethylene
Polylactic acid (PLA) is a biodegradable thermoplastic derived from renewable resources such as corn starch or sugarcane, widely used in eco-friendly applications due to its compostability and low environmental impact. Polyoxymethylene (POM), also known as acetal, is a high-strength engineering thermoplastic characterized by excellent mechanical properties, chemical resistance, and dimensional stability, making it suitable for durable button manufacturing. Comparing the two, PLA offers sustainability advantages while POM excels in structural integrity and wear resistance.
Material Composition and Sources
Polylactic acid (PLA) is a biodegradable thermoplastic derived primarily from renewable resources such as corn starch or sugarcane, featuring a composition based on lactic acid polymers. Polyoxymethylene (POM), also known as acetal, is a petroleum-based engineering thermoplastic composed of repeating formaldehyde units, valued for its high mechanical strength and dimensional stability. The choice between PLA and POM for buttons depends on the priority of sustainability, with PLA offering eco-friendly benefits and POM providing superior durability.
Mechanical Strength Comparison
Polylactic acid (PLA) exhibits moderate mechanical strength with a tensile strength typically around 50-70 MPa, making it suitable for buttons requiring biodegradability and moderate durability. Polyoxymethylene (POM), also known as acetal, offers superior mechanical strength with tensile strength values ranging from 60-75 MPa and higher impact resistance, ensuring enhanced durability and wear resistance for high-stress button applications. For buttons subjected to frequent mechanical loading or friction, POM provides better performance in terms of mechanical longevity compared to PLA.
Durability and Wear Resistance
Polylactic acid (PLA) offers good initial stiffness but lacks long-term durability and wear resistance compared to polyoxymethylene (POM), which exhibits superior mechanical strength and excellent resistance to abrasion and wear. POM's high fatigue endurance and low friction characteristics make it ideal for buttons subjected to repeated use and mechanical stress. Durability testing confirms POM maintains performance under high-load conditions where PLA tends to degrade or deform.
Aesthetics and Finish Options
Polylactic acid (PLA) offers a matte, smooth finish with vibrant color options, making it ideal for buttons requiring a natural or eco-friendly aesthetic. Polyoxymethylene (POM) provides a polished, glossy finish with excellent dimensional stability, suitable for buttons needing a sleek and durable appearance. Both materials allow for fine detail in surface texture, but PLA favors customization in color variety while POM excels in a consistent high-gloss sheen.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
Polylactic acid (PLA) is a biodegradable polymer derived from renewable resources like corn starch, offering a lower carbon footprint and easier compostability compared to polyoxymethylene (POM), which is a petroleum-based plastic known for its durability but challenges in recyclability and environmental persistence. PLA's production results in reduced greenhouse gas emissions and supports circular economy principles, making it a more sustainable choice for button manufacturing. Conversely, POM's resistance to biodegradation contributes to long-term plastic pollution, raising concerns about its environmental impact in single-use or short-lifecycle applications.
Cost Analysis and Market Availability
Polylactic acid (PLA) offers a cost-effective solution for buttons due to its biodegradable nature and lower raw material expenses compared to polyoxymethylene (POM), which tends to be more expensive due to its engineering-grade properties and durability. Market availability of PLA buttons is expanding rapidly, driven by increasing demand for sustainable and eco-friendly materials, whereas POM buttons maintain steady demand in sectors requiring high mechanical strength and chemical resistance. Manufacturers favor PLA for cost-sensitive, environmentally conscious applications whereas POM dominates in industries prioritizing longevity and performance despite higher costs.
Processing and Manufacturing Methods
Polylactic acid (PLA) offers easier processing through injection molding and 3D printing due to its lower melting temperature and biodegradability, making it suitable for eco-friendly button manufacturing. Polyoxymethylene (POM), also known as acetal, requires higher processing temperatures and precise mold design in injection molding to achieve its superior mechanical strength and dimensional stability for durable buttons. Choosing between PLA and POM hinges on manufacturing equipment capabilities and desired product performance, with PLA favored for sustainable production and POM optimal for high-wear applications.
Suitability for Various Button Applications
Polylactic acid (PLA) offers biodegradability and a sustainable profile, making it ideal for eco-friendly buttons in fashion and disposable garments. Polyoxymethylene (POM) provides superior mechanical strength, wear resistance, and dimensional stability, optimizing its use in high-performance, durable buttons for heavy-duty applications like workwear and outdoor gear. Suitability depends on application demands: PLA suits sustainable and lightweight uses, while POM addresses longevity and mechanical stress requirements.
Conclusion: Selecting the Best Material for Buttons
Polylactic acid (PLA) offers biodegradability and ease of molding, making it ideal for eco-friendly button production with moderate durability. Polyoxymethylene (POM) provides superior mechanical strength, chemical resistance, and dimensional stability, suitable for high-stress button applications demanding long-term performance. Selecting the best material depends on the balance between environmental impact, durability requirements, and cost, with PLA favored for sustainability and POM for robustness.
Infographic: Polylactic acid vs Polyoxymethylene for Button
 azmater.com
azmater.com