Polyethylene offers excellent chemical resistance and flexibility for medical devices, while polysulfone provides superior thermal stability and biocompatibility. Choosing between polyethylene and polysulfone depends on specific device requirements such as sterilization methods and mechanical strength.
Table of Comparison
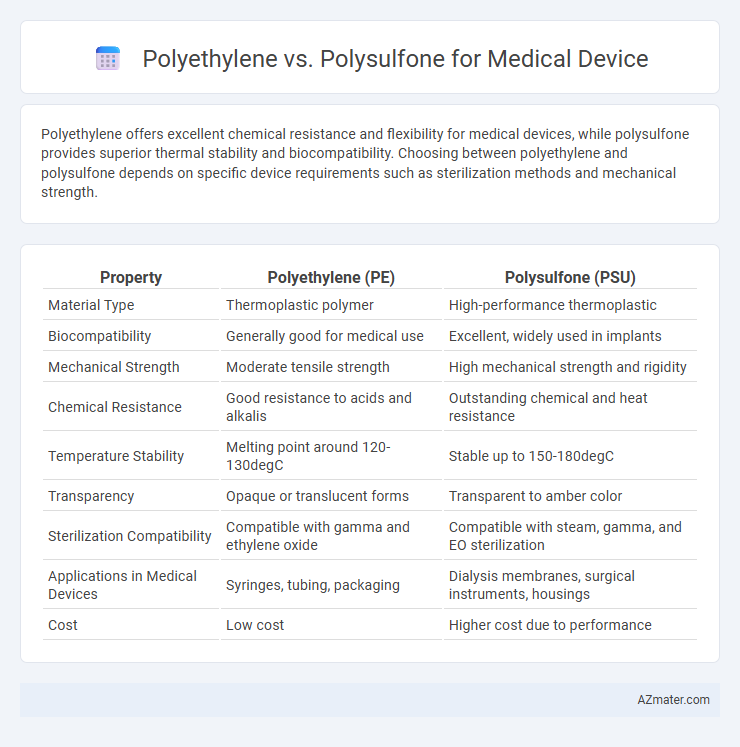
| Property | Polyethylene (PE) | Polysulfone (PSU) |
|---|---|---|
| Material Type | Thermoplastic polymer | High-performance thermoplastic |
| Biocompatibility | Generally good for medical use | Excellent, widely used in implants |
| Mechanical Strength | Moderate tensile strength | High mechanical strength and rigidity |
| Chemical Resistance | Good resistance to acids and alkalis | Outstanding chemical and heat resistance |
| Temperature Stability | Melting point around 120-130degC | Stable up to 150-180degC |
| Transparency | Opaque or translucent forms | Transparent to amber color |
| Sterilization Compatibility | Compatible with gamma and ethylene oxide | Compatible with steam, gamma, and EO sterilization |
| Applications in Medical Devices | Syringes, tubing, packaging | Dialysis membranes, surgical instruments, housings |
| Cost | Low cost | Higher cost due to performance |
Introduction to Polyethylene and Polysulfone in Medical Devices
Polyethylene is a widely used thermoplastic polymer in medical devices due to its excellent chemical resistance, biocompatibility, and flexibility, making it ideal for applications like tubing, containers, and prosthetics. Polysulfone offers superior thermal stability, high mechanical strength, and resistance to steam sterilization, which is essential for reusable medical devices such as surgical instruments, dialysis membranes, and sterilization trays. Both materials play pivotal roles in medical device manufacturing, with polyethylene favored for disposability and cost-efficiency, while polysulfone is preferred for durability and repeated sterilization cycles.
Material Composition and Chemical Structure
Polyethylene, a thermoplastic polymer composed of long chains of ethylene monomers, exhibits a simple hydrocarbon structure characterized by carbon-carbon and carbon-hydrogen bonds, providing excellent chemical resistance and flexibility for medical device applications. Polysulfone, an amorphous thermoplastic polymer consisting of aromatic rings linked by sulfone groups (-SO2-), offers superior thermal stability, rigidity, and resistance to hydrolysis and oxidative degradation. The distinct molecular structures influence material properties such as biocompatibility, sterilization tolerance, and mechanical performance, making polyethylene suitable for flexible components and polysulfone ideal for devices requiring high strength and chemical resistance.
Mechanical Properties Comparison
Polyethylene and polysulfone exhibit distinct mechanical properties critical for medical device applications; polyethylene offers excellent flexibility and impact resistance, making it suitable for devices requiring durability and slight deformation. Polysulfone provides superior tensile strength, rigidity, and high-temperature resistance, ideal for devices exposed to sterilization processes or mechanical stress. The choice between polyethylene and polysulfone depends on balancing flexibility needs with temperature and chemical resistance in medical device design.
Biocompatibility and Safety
Polysulfone outperforms polyethylene in medical device applications due to its superior biocompatibility and chemical resistance, reducing the risk of adverse tissue reactions and ensuring patient safety. Polyethylene, while cost-effective and flexible, has limitations in sterilization methods and long-term stability that may compromise device performance. Polysulfone's high thermal stability and resistance to hydrolysis support repeated sterilization cycles, making it a safer choice for implants and critical medical components.
Sterilization Methods and Resistance
Polyethylene offers good chemical resistance but limited tolerance to high-temperature sterilization methods like autoclaving, making it suitable primarily for gamma or ethylene oxide sterilization. Polysulfone exhibits superior thermal stability, enabling repeated steam sterilization (autoclaving) without degradation, along with excellent resistance to radiation and chemical sterilants. The choice between polyethylene and polysulfone hinges on the sterilization protocol and the mechanical and chemical resistance requirements of the medical device.
Performance in Medical Applications
Polyethylene offers excellent chemical resistance and flexibility, making it suitable for various medical devices requiring durability and biocompatibility. Polysulfone demonstrates superior thermal stability and mechanical strength, ideal for applications demanding sterilization and high-temperature resistance. Both materials provide outstanding performance, with polyethylene favored for disposables and polysulfone preferred in reusable, high-performance medical components.
Cost-Effectiveness and Availability
Polyethylene offers superior cost-effectiveness and broader availability compared to polysulfone, making it a preferred choice for disposable medical devices and components requiring high-volume production. Polysulfone provides enhanced thermal stability and chemical resistance ideal for reusable medical equipment but comes with higher material costs and limited supplier options. Balancing budget constraints and performance requirements is crucial when selecting between polyethylene and polysulfone for specific medical device applications.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
Polyethylene exhibits lower environmental impact due to its high recyclability and widespread recycling infrastructure, making it a more sustainable choice for medical devices with lower carbon footprints. Polysulfone offers superior chemical resistance and sterilization durability but presents challenges in recycling and biodegradability, resulting in increased environmental persistence. Selecting polyethylene enables reduced medical waste accumulation and enhanced lifecycle sustainability, whereas polysulfone's performance benefits must be balanced against its environmental considerations.
Regulatory Considerations and Compliance
Polyethylene and polysulfone are both widely used polymers in medical devices, with regulatory considerations primarily driven by biocompatibility, sterilization compatibility, and FDA or ISO compliance standards. Polyethylene, often favored for disposables, must demonstrate compliance with FDA 21 CFR Part 177 for indirect food additives or USP Class VI biocompatibility for implantable devices. Polysulfone, known for high-temperature resistance and chemical stability, requires rigorous testing to meet ISO 10993 biological evaluation standards and is frequently used in devices demanding repeated sterilization cycles, necessitating strict adherence to regulatory guidelines for reusable medical equipment.
Choosing the Right Material for Medical Device Design
Polyethylene offers excellent chemical resistance, low cost, and biocompatibility, making it suitable for disposable medical devices such as tubing and containers. Polysulfone provides superior thermal stability, mechanical strength, and sterilization tolerance, ideal for reusable devices and components exposed to high temperatures. Selecting between polyethylene and polysulfone depends on the device's application requirements, expected sterilization methods, and longevity needs in medical environments.
Infographic: Polyethylene vs Polysulfone for Medical Device
 azmater.com
azmater.com