Polybutylene terephthalate (PBT) offers superior chemical resistance and dimensional stability for display components compared to polymethyl methacrylate (PMMA), which provides higher optical clarity and better light transmission. PBT is ideal for structural display parts requiring heat resistance, while PMMA is preferred for screens and lenses due to its excellent transparency and scratch resistance.
Table of Comparison
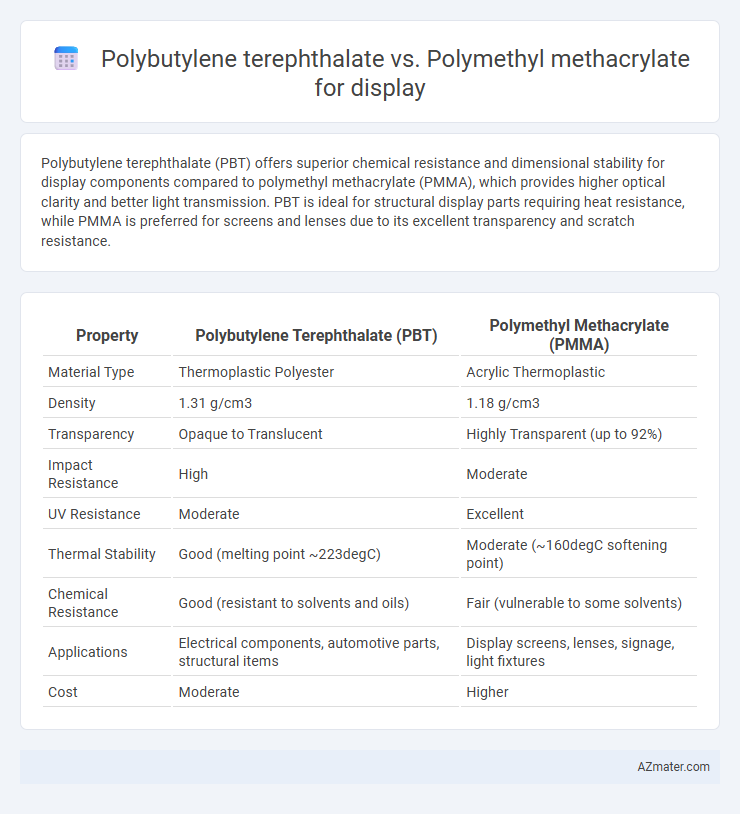
| Property | Polybutylene Terephthalate (PBT) | Polymethyl Methacrylate (PMMA) |
|---|---|---|
| Material Type | Thermoplastic Polyester | Acrylic Thermoplastic |
| Density | 1.31 g/cm3 | 1.18 g/cm3 |
| Transparency | Opaque to Translucent | Highly Transparent (up to 92%) |
| Impact Resistance | High | Moderate |
| UV Resistance | Moderate | Excellent |
| Thermal Stability | Good (melting point ~223degC) | Moderate (~160degC softening point) |
| Chemical Resistance | Good (resistant to solvents and oils) | Fair (vulnerable to some solvents) |
| Applications | Electrical components, automotive parts, structural items | Display screens, lenses, signage, light fixtures |
| Cost | Moderate | Higher |
Introduction to Polybutylene Terephthalate and Polymethyl Methacrylate
Polybutylene terephthalate (PBT) is a thermoplastic polyester known for its high mechanical strength, excellent electrical insulation properties, and resistance to moisture, making it suitable for durable display components. Polymethyl methacrylate (PMMA), commonly called acrylic or plexiglass, offers superior optical clarity, UV resistance, and weatherability, which are critical for transparent display panels and screens. While PBT excels in structural stability and impact resistance, PMMA is favored for applications requiring high light transmission and scratch resistance in display technology.
Chemical Structure and Properties Comparison
Polybutylene terephthalate (PBT) is a semi-crystalline thermoplastic polyester characterized by its aromatic terephthalate groups and flexible butylene segments, offering excellent chemical resistance, dimensional stability, and impact strength. Polymethyl methacrylate (PMMA), an amorphous thermoplastic acrylic polymer composed of methyl methacrylate monomers, provides superior optical clarity, high light transmittance up to 92%, and UV resistance, making it ideal for display applications. While PBT excels in mechanical toughness and thermal resistance due to its crystalline structure, PMMA's transparent amorphous nature ensures enhanced visual performance and weatherability in display technologies.
Mechanical Strength and Durability
Polybutylene terephthalate (PBT) offers superior mechanical strength and impact resistance compared to polymethyl methacrylate (PMMA), making it ideal for displays requiring enhanced durability and resistance to mechanical stress. PMMA provides excellent optical clarity but is more prone to scratching and brittle failure under mechanical strain, limiting its durability in high-impact environments. PBT's robust chemical resistance and better fatigue performance ensure longer-lasting display components in demanding applications.
Optical Clarity and Light Transmission
Polybutylene terephthalate (PBT) offers moderate optical clarity with some haze, making it less ideal for high-transparency display applications compared to polymethyl methacrylate (PMMA), which provides superior optical clarity and excellent light transmission rates exceeding 90%. PMMA's high light transmission minimizes distortion and enhances color brilliance, critical for advanced display technologies. In contrast, PBT's lower clarity and light transmission restrict its use to structural components rather than primary display surfaces.
Thermal Stability and Temperature Resistance
Polybutylene terephthalate (PBT) offers superior thermal stability with a high melting point around 223degC, making it suitable for display applications requiring moderate heat resistance and dimensional stability. Polymethyl methacrylate (PMMA), while transparent and UV resistant, has a lower glass transition temperature around 105degC, limiting its use in high-temperature environments. For displays subjected to elevated temperatures, PBT provides better performance by maintaining structural integrity and preventing deformation.
Ease of Fabrication and Processing
Polybutylene terephthalate (PBT) offers superior ease of fabrication and processing for display applications due to its excellent flow properties and compatibility with injection molding, enabling precise and efficient manufacturing of complex shapes. Polymethyl methacrylate (PMMA), while providing outstanding optical clarity, requires more careful handling during machining and thermoforming to avoid stress fractures and maintain surface quality. PBT's faster cycle times and better dimensional stability make it a preferred choice when production speed and structural integrity are critical factors in display fabrication.
Surface Finish and Aesthetic Qualities
Polybutylene terephthalate (PBT) offers a smooth, matte surface finish that enhances glare resistance and reduces fingerprint visibility, making it suitable for functional display components requiring durability and subtle aesthetics. Polymethyl methacrylate (PMMA), known for its superior optical clarity and glossy surface, provides vibrant color rendition and high light transmission, ideal for visually striking display applications. PMMA's excellent polishability results in a sleek, high-gloss finish that outperforms PBT in terms of aesthetic appeal and transparency.
Cost and Availability for Display Manufacturing
Polybutylene terephthalate (PBT) offers a cost-effective solution for display manufacturing due to its lower raw material price and ease of processing compared to polymethyl methacrylate (PMMA). PBT's widespread availability and excellent thermal stability make it a preferred choice for mass production in display components. PMMA, while providing superior optical clarity, generally incurs higher costs and limited supply, impacting large-scale display manufacturing budgets and availability.
Environmental Impact and Recyclability
Polybutylene terephthalate (PBT) offers superior environmental benefits compared to polymethyl methacrylate (PMMA) due to its higher recyclability rate and lower carbon footprint during production. PBT's chemical structure enables efficient mechanical recycling and energy recovery, reducing landfill waste and associated emissions. In contrast, PMMA presents challenges in recycling because of its thermoset nature, leading to more energy-intensive processes and higher environmental impact throughout its lifecycle in display applications.
Application Suitability: Choosing the Right Material for Displays
Polybutylene terephthalate (PBT) offers excellent mechanical strength, chemical resistance, and thermal stability, making it ideal for structural components in displays that require durability and heat resistance. Polymethyl methacrylate (PMMA), known for its outstanding optical clarity and light transmittance, is preferred for display covers and lenses where high transparency and scratch resistance are critical. For applications demanding both robust mechanical properties and superior visual performance, selecting between PBT and PMMA depends on whether structural integrity or optical quality is the primary requirement.
Infographic: Polybutylene terephthalate vs Polymethyl methacrylate for Display
 azmater.com
azmater.com