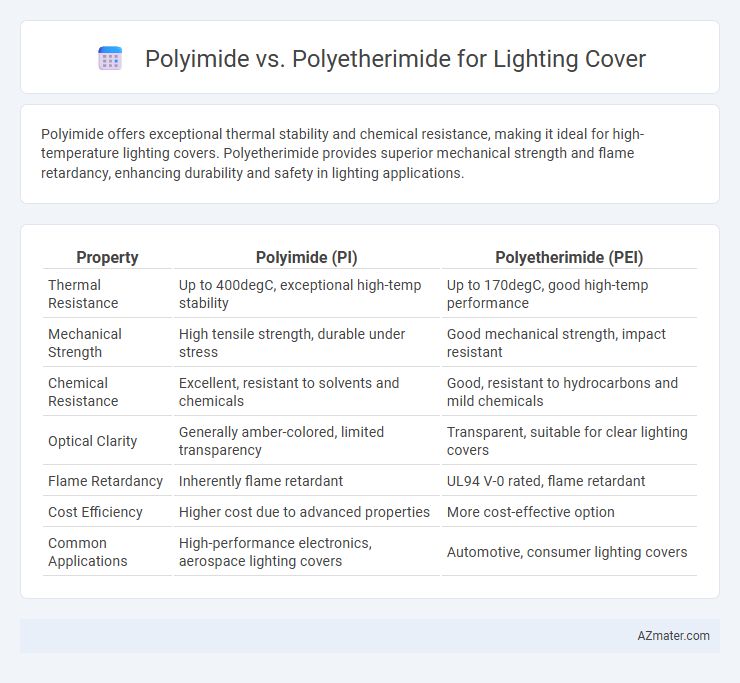
Polyimide offers exceptional thermal stability and chemical resistance, making it ideal for high-temperature lighting covers. Polyetherimide provides superior mechanical strength and flame retardancy, enhancing durability and safety in lighting applications.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Polyimide (PI) | Polyetherimide (PEI) |
|---|---|---|
| Thermal Resistance | Up to 400degC, exceptional high-temp stability | Up to 170degC, good high-temp performance |
| Mechanical Strength | High tensile strength, durable under stress | Good mechanical strength, impact resistant |
| Chemical Resistance | Excellent, resistant to solvents and chemicals | Good, resistant to hydrocarbons and mild chemicals |
| Optical Clarity | Generally amber-colored, limited transparency | Transparent, suitable for clear lighting covers |
| Flame Retardancy | Inherently flame retardant | UL94 V-0 rated, flame retardant |
| Cost Efficiency | Higher cost due to advanced properties | More cost-effective option |
| Common Applications | High-performance electronics, aerospace lighting covers | Automotive, consumer lighting covers |
Introduction to Polyimide and Polyetherimide
Polyimide (PI) is a high-performance polymer known for its exceptional thermal stability, chemical resistance, and excellent mechanical properties, making it suitable for demanding lighting cover applications. Polyetherimide (PEI) offers a unique combination of high heat resistance, transparency, and dimensional stability, providing a lightweight and durable alternative for lighting covers. Both materials deliver superior insulation and maintain optical clarity under prolonged exposure to heat and UV radiation, essential for enhancing the lifespan and efficiency of lighting fixtures.
Chemical Structure Comparison
Polyimide and polyetherimide differ significantly in their chemical structures, impacting performance in lighting cover applications. Polyimide features an imide ring directly attached to the aromatic backbone, providing exceptional thermal stability and chemical resistance. Polyetherimide incorporates an ether linkage between the aromatic rings and imide groups, which enhances impact resistance and dimensional stability while retaining high heat resistance, making it suitable for durable, lightweight lighting covers.
Thermal Resistance: Which Performs Better?
Polyimide exhibits superior thermal resistance with a continuous service temperature often exceeding 250degC, making it ideal for high-heat lighting cover applications. Polyetherimide (PEI), while offering good thermal stability up to around 170-200degC, falls short compared to polyimide under extreme heat conditions. The higher glass transition temperature (Tg) of polyimide ensures better dimensional stability and durability in demanding thermal environments for lighting covers.
Mechanical Strength and Flexibility
Polyimide exhibits superior mechanical strength with excellent tensile and impact resistance, making it ideal for demanding lighting cover applications requiring durability. Polyetherimide offers enhanced flexibility and toughness, allowing for better performance under bending or thermal cycling conditions. Both materials provide high thermal stability, but the choice depends on whether maximum rigidity or adaptability to mechanical stress is prioritized in the lighting cover design.
Optical Clarity and Light Transmission
Polyimide offers excellent thermal stability and mechanical strength but typically exhibits lower optical clarity and light transmission compared to polyetherimide, making it less ideal for lighting covers requiring high transparency. Polyetherimide provides superior optical clarity and higher light transmission rates, ensuring more efficient illumination and better color rendering in lighting applications. Its combination of high heat resistance and optical performance makes polyetherimide a preferred choice for transparent lighting covers.
Flame Retardancy and Electrical Insulation
Polyimide exhibits exceptional flame retardancy with a high limiting oxygen index (LOI) typically above 30%, making it ideal for harsh lighting cover environments requiring superior fire resistance. Polyetherimide (PEI) balances flame retardancy and electrical insulation, offering UL94 V-0 flame classification and dielectric strength around 20 kV/mm, ensuring reliable performance in electrical insulation applications. For lighting covers demanding stringent flame resistance and stable electrical insulation properties, polyimide generally outperforms PEI in thermal stability, while PEI offers cost-effective processing with adequate flame retardant and insulating capabilities.
Durability in Harsh Environments
Polyetherimide (PEI) offers superior durability compared to polyimide when used as lighting covers in harsh environments due to its higher impact resistance and excellent thermal stability up to 170degC. PEI's resistance to hydrolytic degradation, UV radiation, and chemical exposure ensures longer service life under extreme conditions, outperforming traditional polyimides that may become brittle or discolored over time. The intrinsic flame retardancy and dimensional stability of polyetherimide make it the preferred material for lighting applications demanding robust performance and reliability.
Weight and Design Versatility
Polyimide offers exceptional thermal stability and lightweight properties, making it ideal for high-performance lighting covers where weight reduction is critical. Polyetherimide balances high strength with increased design versatility due to its excellent moldability and dimensional stability, enabling complex shapes and intricate designs. Weight-wise, polyimide is generally lighter, while polyetherimide provides more flexibility in form, allowing manufacturers to tailor lighting covers to diverse applications.
Cost Analysis and Availability
Polyetherimide (PEI) generally incurs higher upfront costs compared to polyimide due to its superior mechanical properties and thermal stability, making it a premium choice for high-performance lighting covers. Polyimide, while offering excellent thermal resistance, is more readily available and cost-effective, catering to budget-sensitive lighting applications without significant compromise in durability. Availability of polyimide is broader across global suppliers, lowering lead times and procurement expenses, whereas polyetherimide may require sourcing from specialized providers, impacting overall project timelines and budget.
Best Applications for Lighting Cover
Polyimide offers exceptional thermal stability and excellent electrical insulation, making it ideal for high-temperature lighting covers in industrial and automotive applications. Polyetherimide provides superior impact resistance and flame retardancy, best suited for LED lighting covers requiring durability and compliance with fire safety standards. Both materials ensure transparency and UV resistance, but the choice depends on specific performance needs like operating temperature and mechanical strength.
Infographic: Polyimide vs Polyetherimide for Lighting Cover
 azmater.com
azmater.com