Polyphenylene oxide offers excellent heat resistance and chemical stability, making it ideal for high-temperature food packaging films. Polyethylene naphthalate provides superior barrier properties against oxygen and moisture, ensuring extended shelf life for packaged foods.
Table of Comparison
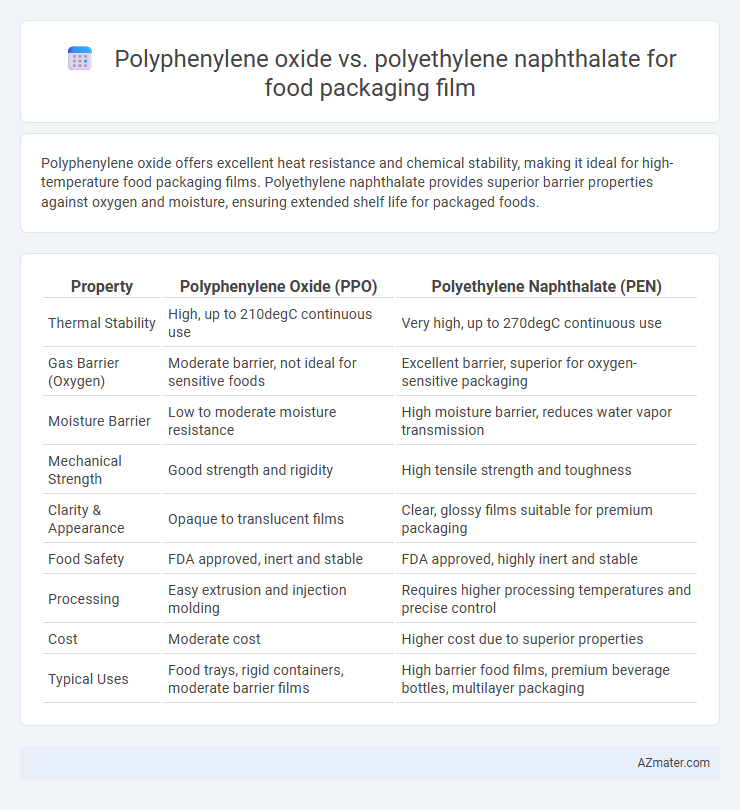
| Property | Polyphenylene Oxide (PPO) | Polyethylene Naphthalate (PEN) |
|---|---|---|
| Thermal Stability | High, up to 210degC continuous use | Very high, up to 270degC continuous use |
| Gas Barrier (Oxygen) | Moderate barrier, not ideal for sensitive foods | Excellent barrier, superior for oxygen-sensitive packaging |
| Moisture Barrier | Low to moderate moisture resistance | High moisture barrier, reduces water vapor transmission |
| Mechanical Strength | Good strength and rigidity | High tensile strength and toughness |
| Clarity & Appearance | Opaque to translucent films | Clear, glossy films suitable for premium packaging |
| Food Safety | FDA approved, inert and stable | FDA approved, highly inert and stable |
| Processing | Easy extrusion and injection molding | Requires higher processing temperatures and precise control |
| Cost | Moderate cost | Higher cost due to superior properties |
| Typical Uses | Food trays, rigid containers, moderate barrier films | High barrier food films, premium beverage bottles, multilayer packaging |
Introduction to Food Packaging Films
Polyphenylene oxide (PPO) and Polyethylene naphthalate (PEN) are advanced polymers used in food packaging films due to their excellent barrier properties and thermal stability. PPO offers superior oxygen barrier performance, making it ideal for preserving food freshness and extending shelf life, while PEN provides outstanding moisture and gas resistance alongside enhanced mechanical strength. Both materials contribute to improved packaging durability and food safety, with specific selection based on the required protection level and processing conditions in food packaging applications.
Overview of Polyphenylene Oxide (PPO)
Polyphenylene oxide (PPO) is a high-performance thermoplastic known for its excellent thermal stability, electrical insulation properties, and resistance to moisture and chemicals, making it suitable for food packaging films requiring durability and safety. PPO offers superior barrier properties against oxygen and water vapor compared to many conventional plastics, enhancing the shelf life and freshness of packaged food products. Its inherent dimensional stability and clarity allow it to maintain mechanical strength and visual appeal, which are critical factors in food packaging applications.
Overview of Polyethylene Naphthalate (PEN)
Polyethylene Naphthalate (PEN) is a high-performance polyester known for its exceptional barrier properties, thermal stability, and mechanical strength, making it ideal for food packaging films that require extended shelf life and protection against oxygen, moisture, and UV light. PEN exhibits superior chemical resistance and dimensional stability compared to conventional polyethylene terephthalate (PET), enabling enhanced preservation of food freshness and safety. Its excellent clarity and processability also contribute to its growing use in advanced packaging applications where durability and product visibility are critical.
Barrier Properties: PPO vs PEN
Polyphenylene oxide (PPO) exhibits excellent oxygen barrier properties, making it ideal for preserving food freshness by limiting oxygen permeability. Polyethylene naphthalate (PEN) offers superior moisture barrier performance, effectively protecting food products from water vapor transmission and maintaining package integrity. Combining PPO's low oxygen permeability with PEN's reduced water vapor transmission results in enhanced overall barrier performance for food packaging films.
Mechanical Strength and Durability Comparison
Polyphenylene oxide (PPO) offers superior mechanical strength with high impact resistance and dimensional stability compared to polyethylene naphthalate (PEN), making it ideal for durable food packaging films requiring toughness. PEN exhibits excellent tensile strength and barrier properties, but its mechanical rigidity is lower than PPO, impacting durability under mechanical stress. The enhanced thermal stability and chemical resistance of PPO contribute to longer-lasting packaging films in demanding food storage applications.
Thermal Stability in Food Packaging Applications
Polyphenylene oxide (PPO) demonstrates superior thermal stability with a high glass transition temperature around 215degC, making it highly suitable for food packaging films requiring heat resistance during sterilization processes. Polyethylene naphthalate (PEN) also offers excellent thermal stability, exhibiting a melting point near 270degC and better dimensional stability at elevated temperatures compared to conventional packaging polymers. The enhanced thermal properties of both PPO and PEN enable the production of food packaging films that maintain integrity and barrier performance under thermal stress, ensuring product safety and extended shelf life.
Chemical Resistance and Food Safety
Polyphenylene oxide (PPO) offers excellent chemical resistance against acids, bases, and hydrocarbons, making it highly suitable for food packaging films exposed to various substances. Polyethylene naphthalate (PEN) also provides strong chemical resistance with superior barrier properties against oxygen and moisture, enhancing food preservation. Regarding food safety, both polymers comply with FDA regulations, but PEN's enhanced barrier performance better maintains product freshness and extends shelf life in packaging applications.
Environmental Impact and Recyclability
Polyphenylene oxide (PPO) offers chemical resistance and thermal stability but presents challenges in recycling due to its complex polymer structure, which limits compatibility with conventional processing streams. Polyethylene naphthalate (PEN) provides superior barrier properties and greater recyclability, being more compatible with existing polyester recycling systems, thus reducing environmental impact through improved material recovery. PEN's biodegradability under certain conditions further enhances its sustainability profile compared to PPO, making it a more eco-friendly option for food packaging films.
Cost-Effectiveness Analysis
Polyphenylene oxide (PPO) offers high thermal stability and chemical resistance, making it suitable for durable food packaging films, but its production cost is relatively high compared to Polyethylene naphthalate (PEN). PEN provides excellent barrier properties against oxygen and moisture, enhancing shelf life in food packaging, while being more cost-effective due to lower raw material and processing expenses. Cost-effectiveness analysis favors PEN for scalable food packaging applications where barrier performance and moderate thermal resistance are critical, whereas PPO is justified in niche applications requiring superior chemical stability.
Conclusion: Selecting the Optimal Film for Food Packaging
Polyphenylene oxide (PPO) offers excellent thermal stability and moisture resistance, making it suitable for foods requiring temperature control and barrier protection. Polyethylene naphthalate (PEN) provides superior gas barrier properties and mechanical strength, ideal for extending shelf life and maintaining food freshness. Choosing between PPO and PEN depends on the specific packaging requirements, balancing thermal and barrier performance with durability to optimize food preservation.
Infographic: Polyphenylene oxide vs Polyethylene naphthalate for Food packaging film
 azmater.com
azmater.com