Recycled plastic food containers reduce environmental impact by reusing waste materials, while polypropylene offers superior durability, heat resistance, and food safety compliance. Choosing between recycled plastic and polypropylene depends on prioritizing sustainability versus performance and chemical stability in food storage.
Table of Comparison
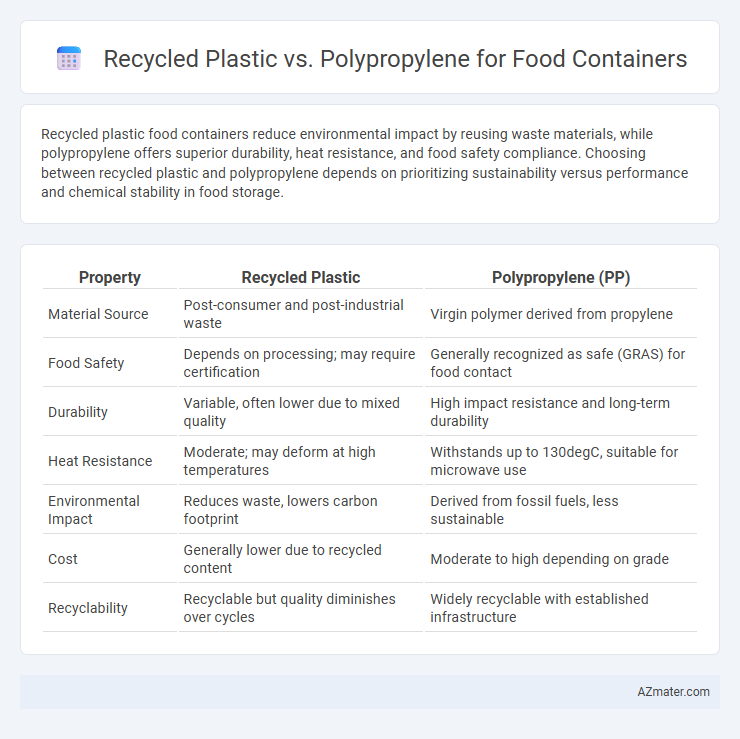
| Property | Recycled Plastic | Polypropylene (PP) |
|---|---|---|
| Material Source | Post-consumer and post-industrial waste | Virgin polymer derived from propylene |
| Food Safety | Depends on processing; may require certification | Generally recognized as safe (GRAS) for food contact |
| Durability | Variable, often lower due to mixed quality | High impact resistance and long-term durability |
| Heat Resistance | Moderate; may deform at high temperatures | Withstands up to 130degC, suitable for microwave use |
| Environmental Impact | Reduces waste, lowers carbon footprint | Derived from fossil fuels, less sustainable |
| Cost | Generally lower due to recycled content | Moderate to high depending on grade |
| Recyclability | Recyclable but quality diminishes over cycles | Widely recyclable with established infrastructure |
Introduction to Food Container Materials
Recycled plastic and polypropylene are widely used materials in food container manufacturing due to their durability and safety. Polypropylene, a thermoplastic polymer, offers high heat resistance and chemical stability, making it ideal for food storage and microwave-safe containers. Recycled plastic reduces environmental impact by reusing post-consumer waste while maintaining acceptable food-grade quality when processed with proper standards and certifications.
What is Recycled Plastic?
Recycled plastic refers to materials made by repurposing post-consumer or post-industrial plastic waste, reducing environmental impact and conserving resources. In food containers, recycled plastic maintains safety standards while lowering carbon footprint compared to virgin polypropylene, a thermoplastic polymer commonly used for its durability and chemical resistance. Choosing recycled plastic supports sustainable packaging solutions without compromising the functional benefits of polypropylene for food storage.
Overview of Polypropylene (PP)
Polypropylene (PP) is a thermoplastic polymer widely used for food containers due to its excellent chemical resistance, high melting point, and durability, ensuring food safety and extended shelf life. It is lightweight, moisture-resistant, and provides a strong barrier against contaminants, making it ideal for packaging perishable foods. PP is also recyclable, contributing to sustainable packaging solutions, though it is less frequently recycled than other plastics, which impacts the overall environmental footprint compared to recycled plastics.
Food Safety: Recycled Plastic vs Polypropylene
Polypropylene is widely preferred for food containers due to its strong resistance to chemicals, high melting point, and FDA approval for direct food contact, ensuring enhanced food safety. Recycled plastics may contain contaminants or residual chemicals that can potentially migrate into food, posing health risks if not properly processed and certified for food-grade use. Strict quality control and certification are essential for recycled plastic containers to meet the same food safety standards as virgin polypropylene containers.
Durability and Longevity Comparison
Recycled plastic food containers often exhibit slightly reduced durability compared to polypropylene due to potential degradation in polymer chains during the recycling process, which may affect impact resistance and structural integrity. Polypropylene containers are highly durable with excellent resistance to cracking, heat, and chemical exposure, ensuring longer longevity in typical food storage and microwave applications. Over time, polypropylene maintains its physical properties better, making it a more reliable choice for long-term food container use.
Environmental Impact: Recycled Plastic vs Polypropylene
Recycled plastic significantly reduces environmental impact by diverting waste from landfills and lowering energy consumption compared to virgin polypropylene production. Polypropylene, while durable and resistant to chemicals, relies on fossil fuels and generates higher greenhouse gas emissions during manufacturing. Choosing recycled plastic for food containers supports circular economy practices and decreases carbon footprint.
Cost Efficiency and Availability
Recycled plastic food containers often offer greater cost efficiency due to lower raw material expenses and reduced manufacturing energy consumption compared to polypropylene. Polypropylene containers, while slightly higher in price, benefit from widespread availability and consistent quality, making them a reliable choice for mass production. Both materials present distinct supply chain dynamics, with recycled plastics depending heavily on local recycling infrastructure and polypropylene sourced through well-established petrochemical markets.
Heat Resistance and Microwave Safety
Recycled plastic food containers often exhibit lower heat resistance compared to polypropylene, making them less suitable for high-temperature applications. Polypropylene is known for its superior heat tolerance, typically withstanding temperatures up to 120degC (248degF), which ensures microwave safety without deformation or leaching of harmful chemicals. Selecting polypropylene containers offers enhanced durability in microwave use, while recycled plastics may require careful temperature management to avoid compromising food safety.
Regulatory Standards and Certifications
Recycled plastic food containers must comply with FDA 21 CFR 177.1520 and EFSA Regulation (EU) No 10/2011 to ensure safety and prevent harmful chemical migration. Polypropylene containers also meet these standards, often achieving FDA food-contact certification and BfR compliance for durability and heat resistance. Both materials require rigorous testing for BPA, phthalates, and heavy metals to comply with global regulatory frameworks like the EU REACH regulation.
Best Choice for Food Containers: Final Analysis
Recycled plastic for food containers offers environmental benefits by reducing waste and conserving resources, but polypropylene (PP) remains the best choice due to its superior food safety, heat resistance, and durability. PP is FDA-approved for direct food contact, exhibits excellent chemical stability, and withstands high temperatures without leaching harmful substances, ensuring long-term food preservation. While recycled plastics promote sustainability, polypropylene's performance in maintaining food quality and safety makes it the optimal material for food container manufacturing.
Infographic: Recycled plastic vs Polypropylene for Food container
 azmater.com
azmater.com