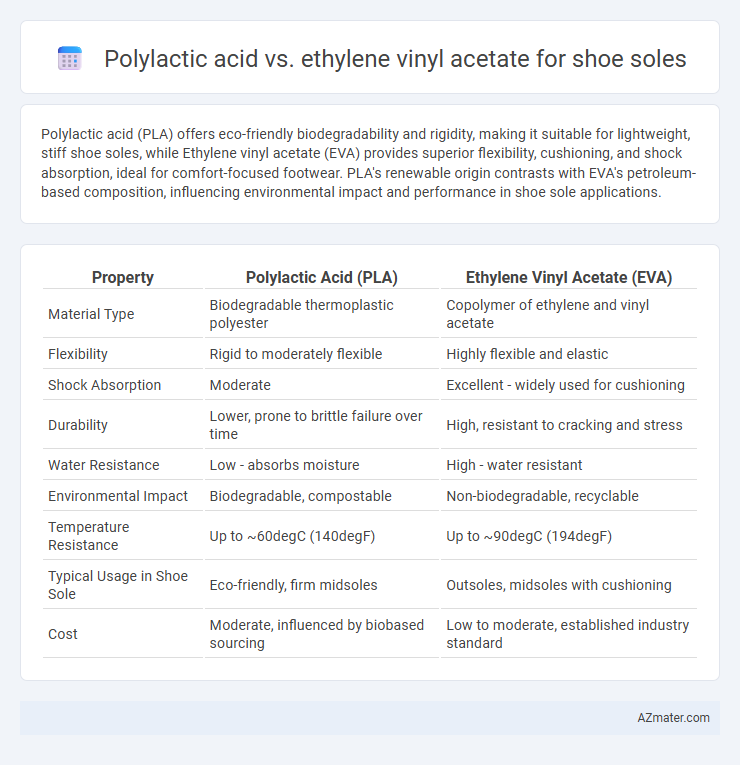
Polylactic acid (PLA) offers eco-friendly biodegradability and rigidity, making it suitable for lightweight, stiff shoe soles, while Ethylene vinyl acetate (EVA) provides superior flexibility, cushioning, and shock absorption, ideal for comfort-focused footwear. PLA's renewable origin contrasts with EVA's petroleum-based composition, influencing environmental impact and performance in shoe sole applications.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Polylactic Acid (PLA) | Ethylene Vinyl Acetate (EVA) |
|---|---|---|
| Material Type | Biodegradable thermoplastic polyester | Copolymer of ethylene and vinyl acetate |
| Flexibility | Rigid to moderately flexible | Highly flexible and elastic |
| Shock Absorption | Moderate | Excellent - widely used for cushioning |
| Durability | Lower, prone to brittle failure over time | High, resistant to cracking and stress |
| Water Resistance | Low - absorbs moisture | High - water resistant |
| Environmental Impact | Biodegradable, compostable | Non-biodegradable, recyclable |
| Temperature Resistance | Up to ~60degC (140degF) | Up to ~90degC (194degF) |
| Typical Usage in Shoe Sole | Eco-friendly, firm midsoles | Outsoles, midsoles with cushioning |
| Cost | Moderate, influenced by biobased sourcing | Low to moderate, established industry standard |
Introduction to Polylactic Acid (PLA) and Ethylene Vinyl Acetate (EVA)
Polylactic Acid (PLA) is a biodegradable thermoplastic derived from renewable resources such as corn starch or sugarcane, offering eco-friendly properties and biodegradability for sustainable shoe soles. Ethylene Vinyl Acetate (EVA), a copolymer of ethylene and vinyl acetate, provides excellent flexibility, cushioning, and shock absorption, making it a popular choice for lightweight, durable shoe midsoles and outsoles. PLA stands out for its environmental benefits while EVA excels in performance and comfort, serving distinct roles in footwear manufacturing.
Material Composition and Structure
Polylactic acid (PLA) is a biodegradable thermoplastic derived from renewable resources such as corn starch or sugarcane, featuring a semi-crystalline structure that provides rigidity and biodegradability suitable for eco-friendly shoe soles. Ethylene vinyl acetate (EVA) is a copolymer composed of ethylene and vinyl acetate monomers, known for its flexible, rubber-like properties and closed-cell foam structure that offers excellent cushioning and shock absorption in footwear applications. PLA's rigid and compostable nature contrasts with EVA's highly elastic and moisture-resistant composition, making material selection dependent on performance requirements such as durability and environmental impact.
Environmental Impact: Biodegradability and Sustainability
Polylactic acid (PLA) offers superior biodegradability compared to Ethylene vinyl acetate (EVA), breaking down more readily in industrial composting facilities and reducing long-term environmental pollution. PLA is derived from renewable biomass sources such as corn starch, enhancing its sustainability profile relative to EVA, which is petroleum-based and contributes to fossil fuel depletion. EVA soles, while durable and flexible, pose challenges in waste management due to their resistance to biodegradation and reliance on non-renewable resources.
Comfort and Cushioning Performance
Polylactic acid (PLA) offers biodegradability with moderate cushioning and stiffness, making it suitable for eco-friendly shoe soles but less optimal for maximum comfort. Ethylene vinyl acetate (EVA) provides superior cushioning and shock absorption due to its flexible, lightweight structure, enhancing overall comfort and performance in footwear applications. EVA's resilience and softness contribute to better energy return and prolonged comfort compared to the firmer, less elastic nature of PLA.
Durability and Wear Resistance
Polylactic acid (PLA) offers moderate durability and biodegradability but tends to have lower wear resistance compared to ethylene vinyl acetate (EVA), which is known for its exceptional flexibility and long-lasting wear properties. EVA provides superior impact absorption and maintains performance under repeated stress, making it ideal for high-durability shoe soles. PLA soles may degrade more quickly under abrasive conditions, whereas EVA soles deliver enhanced resilience and extended lifespan in footwear applications.
Flexibility and Shock Absorption
Polylactic acid (PLA) offers moderate flexibility but tends to be more rigid than ethylene vinyl acetate (EVA), which excels in providing superior cushioning and shock absorption essential for shoe soles. EVA's unique copolymer structure creates a lightweight,Rou Ruan shoe sole material that effectively disperses impact forces, enhancing comfort during prolonged wear. In contrast, PLA's biodegradability supports sustainability goals but may require blending with other materials to match EVA's performance in flexibility and impact resistance.
Manufacturing Processes and Costs
Polylactic acid (PLA) manufacturing involves fermentation of renewable resources like corn starch, followed by polymerization, which results in higher material costs and requires specialized processing equipment for shoe sole production. Ethylene vinyl acetate (EVA) is produced through the polymerization of ethylene and vinyl acetate monomers using well-established industrial methods, leading to lower raw material and processing costs. EVA's ease of molding and compatibility with conventional injection molding and extrusion techniques make it more cost-effective for large-scale shoe sole manufacturing compared to PLA.
Application Suitability for Different Footwear Types
Polylactic acid (PLA) offers excellent rigidity and biodegradability, making it suitable for casual or eco-friendly footwear focused on style rather than high impact resistance. Ethylene vinyl acetate (EVA) provides superior cushioning, flexibility, and durability, ideal for athletic, running, and hiking shoes requiring enhanced shock absorption and comfort. EVA outperforms PLA in applications where flexibility and repetitive stress resistance are critical for performance footwear.
Consumer Preferences and Market Trends
Polylactic acid (PLA) offers eco-conscious consumers a biodegradable alternative with a lower carbon footprint compared to traditional Ethylene vinyl acetate (EVA) used in shoe soles, appealing to the growing demand for sustainable footwear. Market trends reveal an increasing shift towards PLA-based soles driven by environmental awareness and regulatory pressures, although EVA remains favored for its superior cushioning and durability in performance footwear. Consumer preferences continue to evolve, balancing ecological impact with comfort and price, influencing manufacturers to innovate hybrid materials that integrate PLA's sustainability with EVA's functional benefits.
Future Prospects and Innovations in Shoe Sole Materials
Polylactic acid (PLA) offers promising sustainable alternatives in shoe sole materials due to its biodegradability and renewable bio-based origins, fostering innovations in eco-friendly footwear production. Ethylene vinyl acetate (EVA) remains favored for its superior flexibility, cushioning, and durability, but ongoing research aims to blend EVA with biodegradable polymers like PLA to enhance environmental impact without compromising performance. Future advancements are likely to concentrate on hybrid composites and bio-engineered polymers, pushing the boundaries of comfort, sustainability, and recyclability in shoe sole manufacturing.
Infographic: Polylactic acid vs Ethylene vinyl acetate for Shoe Sole
 azmater.com
azmater.com