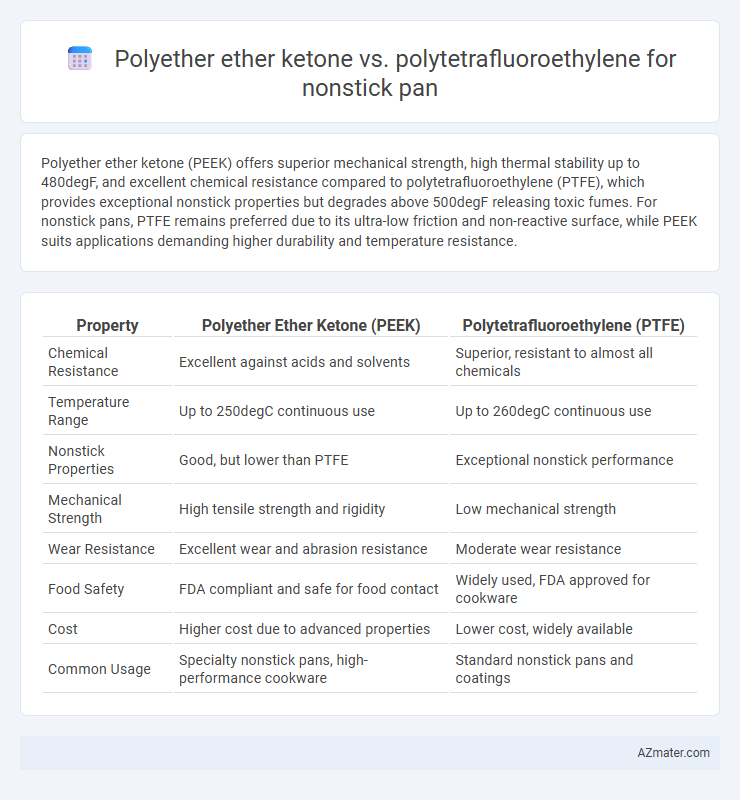
Polyether ether ketone (PEEK) offers superior mechanical strength, high thermal stability up to 480degF, and excellent chemical resistance compared to polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE), which provides exceptional nonstick properties but degrades above 500degF releasing toxic fumes. For nonstick pans, PTFE remains preferred due to its ultra-low friction and non-reactive surface, while PEEK suits applications demanding higher durability and temperature resistance.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Polyether Ether Ketone (PEEK) | Polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE) |
|---|---|---|
| Chemical Resistance | Excellent against acids and solvents | Superior, resistant to almost all chemicals |
| Temperature Range | Up to 250degC continuous use | Up to 260degC continuous use |
| Nonstick Properties | Good, but lower than PTFE | Exceptional nonstick performance |
| Mechanical Strength | High tensile strength and rigidity | Low mechanical strength |
| Wear Resistance | Excellent wear and abrasion resistance | Moderate wear resistance |
| Food Safety | FDA compliant and safe for food contact | Widely used, FDA approved for cookware |
| Cost | Higher cost due to advanced properties | Lower cost, widely available |
| Common Usage | Specialty nonstick pans, high-performance cookware | Standard nonstick pans and coatings |
Introduction to PEEK and PTFE in Nonstick Cookware
Polyether ether ketone (PEEK) and polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE) serve distinct roles in nonstick cookware due to their unique chemical properties. PTFE, known for its exceptional low friction and non-reactivity, has been the traditional choice for nonstick coatings, offering excellent food release and easy cleaning. PEEK, a high-performance thermoplastic with superior thermal stability and chemical resistance, is emerging as a durable alternative, potentially extending the lifespan of cookware under high-heat conditions.
Chemical Structure and Composition Comparison
Polyether ether ketone (PEEK) is a semi-crystalline thermoplastic polymer with a repeating unit containing aromatic rings linked by ketone and ether functional groups, providing high thermal stability and mechanical strength. Polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE) consists of a linear chain of carbon atoms fully fluorinated, resulting in strong C-F bonds that confer exceptional chemical resistance and nonstick properties. The key compositional difference lies in PEEK's aromatic ketone and ether linkages versus PTFE's fluorocarbon backbone, influencing their respective durability and nonstick performance in cookware applications.
Nonstick Performance: PEEK vs PTFE
Polyether ether ketone (PEEK) offers superior thermal stability and mechanical strength compared to polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE), enhancing its durability and resistance to wear in nonstick pan coatings. PTFE is known for its exceptional low friction coefficient, providing excellent initial nonstick performance but can degrade at higher temperatures above 260degC, limiting its longevity. PEEK maintains nonstick properties at elevated temperatures up to 300degC, making it more suitable for cookware requiring frequent high-heat cooking without compromising surface integrity.
Heat Resistance and Thermal Stability
Polyether ether ketone (PEEK) offers exceptional heat resistance with a continuous use temperature up to 250degC, vastly outperforming polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE), which typically degrades above 260degC under oxidative conditions but has a lower melting point around 327degC. PEEK's superior thermal stability ensures it maintains mechanical and chemical properties under prolonged high-temperature exposure, making it ideal for applications requiring durability beyond the thermal limits of PTFE. Despite PTFE's excellent nonstick properties, PEEK's robustness against thermal degradation provides enhanced safety and longevity in nonstick pan coatings exposed to intense heat.
Durability and Scratch Resistance
Polyether ether ketone (PEEK) offers superior durability and exceptional scratch resistance compared to polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE), making it ideal for high-performance nonstick pans that require long-lasting surface integrity. PEEK's high thermal stability and resistance to wear ensure that nonstick coatings retain their effectiveness over extended use without degradation or scratching. In contrast, PTFE tends to be more susceptible to surface damage and wear under abrasive cooking utensils, reducing the pan's nonstick lifespan and performance.
Food Safety and Health Implications
Polyether ether ketone (PEEK) offers superior thermal stability and chemical resistance compared to polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE), reducing the risk of toxic fumes when overheated during cooking. PTFE nonstick coatings, while popular for their low friction and ease of cleaning, can degrade at temperatures above 260degC, potentially releasing harmful perfluorooctanoic acid (PFOA) and other toxic compounds linked to respiratory issues and environmental persistence. Choosing PEEK-coated pans enhances long-term food safety by minimizing exposure to hazardous substances and ensuring durability under high-heat cooking conditions.
Ease of Cleaning and Maintenance
Polyether ether ketone (PEEK) offers superior thermal stability and chemical resistance compared to Polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE), making it more resilient during high-temperature cooking and less prone to degradation. PTFE's nonstick surface provides excellent release properties, simplifying cleaning by preventing food adhesion, but may require careful maintenance to avoid scratching or overheating. PEEK-coated pans generally demand less frequent replacement due to their durability, whereas PTFE coatings require cautious handling to preserve their nonstick efficacy over time.
Cost and Availability in Cookware Manufacturing
Polyether ether ketone (PEEK) offers superior thermal stability and chemical resistance but comes at a significantly higher cost compared to Polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE), making PTFE more prevalent in nonstick pan manufacturing. PTFE's widespread availability and cost-effectiveness drive its dominance in cookware production despite PEEK's enhanced durability and temperature tolerance. Manufacturers prioritize PTFE for large-scale production due to lower raw material expenses and established supply chains, whereas PEEK remains niche for high-end, specialty cookware.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
Polyether ether ketone (PEEK) offers superior thermal stability and durability compared to polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE), which often degrades and releases harmful perfluorinated compounds during high-heat cooking, posing environmental risks. PTFE's chemical inertness makes it persistent in ecosystems, contributing to microplastic pollution and bioaccumulation problems, whereas PEEK's polymer structure allows for better recyclability and longer lifespan, reducing waste. Choosing PEEK-based nonstick pans supports sustainability by minimizing toxic emissions and facilitating circular economy principles, while PTFE remains controversial due to its environmental footprint.
Final Verdict: Which is Better for Nonstick Pans?
Polyether ether ketone (PEEK) offers higher thermal stability and mechanical strength compared to polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE), making it more durable for nonstick pans subjected to frequent high-heat cooking. PTFE, commonly known as Teflon, provides superior nonstick properties and ease of cleaning but can degrade at temperatures above 260degC, releasing potentially harmful fumes. For long-term use and resistance to thermal and mechanical stress, PEEK surpasses PTFE, while PTFE remains preferred for flawless release and affordability in standard home cooking applications.
Infographic: Polyether ether ketone vs Polytetrafluoroethylene for Nonstick Pan
 azmater.com
azmater.com