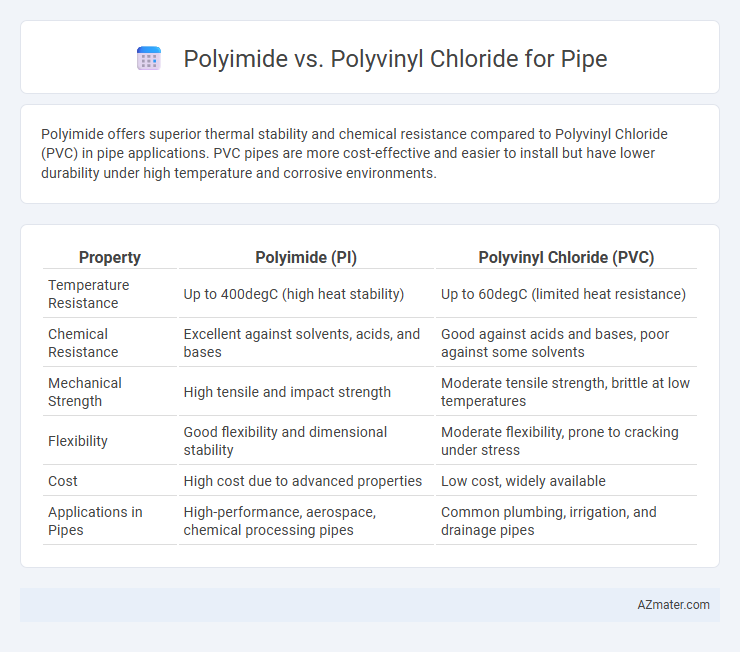
Polyimide offers superior thermal stability and chemical resistance compared to Polyvinyl Chloride (PVC) in pipe applications. PVC pipes are more cost-effective and easier to install but have lower durability under high temperature and corrosive environments.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Polyimide (PI) | Polyvinyl Chloride (PVC) |
|---|---|---|
| Temperature Resistance | Up to 400degC (high heat stability) | Up to 60degC (limited heat resistance) |
| Chemical Resistance | Excellent against solvents, acids, and bases | Good against acids and bases, poor against some solvents |
| Mechanical Strength | High tensile and impact strength | Moderate tensile strength, brittle at low temperatures |
| Flexibility | Good flexibility and dimensional stability | Moderate flexibility, prone to cracking under stress |
| Cost | High cost due to advanced properties | Low cost, widely available |
| Applications in Pipes | High-performance, aerospace, chemical processing pipes | Common plumbing, irrigation, and drainage pipes |
Introduction to Pipe Materials: Polyimide and Polyvinyl Chloride
Polyimide and Polyvinyl Chloride (PVC) are widely used materials in pipe manufacturing due to their distinct chemical and physical properties. Polyimide offers exceptional thermal stability, chemical resistance, and mechanical strength, making it suitable for high-temperature and corrosive environments. PVC is valued for its cost-effectiveness, good corrosion resistance, and ease of installation, making it a preferred choice in residential plumbing and irrigation systems.
Chemical Structure and Composition Differences
Polyimide pipes exhibit a robust chemical structure characterized by imide linkages, providing superior thermal stability and chemical resistance compared to Polyvinyl Chloride (PVC), which consists of repeating vinyl chloride units with chlorine atoms bound to a carbon backbone. The aromatic rings in polyimide's molecular chain contribute to its rigidity and resistance against solvents, acids, and high temperatures, while PVC's composition offers flexibility but lower thermal endurance and susceptibility to UV degradation. These compositional differences make polyimide ideal for high-performance applications requiring durability under harsh chemical and thermal conditions, whereas PVC suits cost-effective, moderate-use piping systems.
Mechanical Strength and Durability Comparison
Polyimide pipes exhibit superior mechanical strength compared to polyvinyl chloride (PVC), offering higher tensile resistance and excellent impact toughness under extreme conditions. Polyimide materials demonstrate outstanding durability, with exceptional thermal stability and chemical resistance that significantly outlast PVC in harsh environments. PVC pipes, while cost-effective and corrosion-resistant, have lower fatigue resistance and are more prone to brittleness and degradation over time compared to polyimide alternatives.
Thermal Resistance: Polyimide vs Polyvinyl Chloride
Polyimide exhibits exceptional thermal resistance, maintaining stability at temperatures up to 400degC, which significantly surpasses the maximum operating temperature of polyvinyl chloride (PVC), typically around 60-80degC. This makes polyimide highly suitable for applications involving extreme heat exposure, while PVC is more commonly used in environments with moderate thermal demands. The superior thermal resistance of polyimide results from its aromatic backbone and imide linkages, providing durability and mechanical strength under high-temperature conditions.
Chemical and Corrosion Resistance
Polyimide pipes exhibit exceptional chemical resistance, effectively withstanding aggressive solvents, acids, and alkalis without degradation, making them ideal for highly corrosive environments. In contrast, polyvinyl chloride (PVC) pipes offer moderate chemical resistance but are more susceptible to damage from hydrocarbons and strong solvents over time. The superior thermal stability and corrosion resistance of polyimide ensure long-term durability in harsh chemical applications where PVC may fail.
Flexibility and Installation Ease
Polyimide pipes offer superior flexibility compared to polyvinyl chloride (PVC), allowing easier bending and maneuvering during complex installations without the risk of cracking. PVC pipes, while rigid and less flexible, provide straightforward handling for standard, linear installations but may require additional fittings for bends. The enhanced flexibility of polyimide reduces labor time and installation costs, making it optimal for applications demanding dynamic pipe routing.
Cost Analysis and Economic Considerations
Polyvinyl Chloride (PVC) pipes offer lower initial costs and widespread availability, making them a cost-effective choice for many plumbing applications. Polyimide pipes, though significantly more expensive upfront due to advanced material properties like thermal resistance and chemical stability, provide long-term economic benefits through enhanced durability and reduced maintenance needs. Selecting between Polyimide and PVC requires balancing immediate budget constraints with lifecycle cost savings and performance demands.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
Polyimide pipes demonstrate superior environmental sustainability due to their high thermal stability, long service life, and recyclability compared to polyvinyl chloride (PVC) pipes, which often release harmful chlorine-based compounds during production and disposal. PVC manufacturing involves the use of toxic additives and generates dioxins, posing significant environmental and health risks. Polyimide's resistance to chemical degradation reduces landfill waste and environmental contamination, making it a more eco-friendly choice for sustainable piping systems.
Industry Applications for Polyimide and PVC Pipes
Polyimide pipes excel in aerospace and electronics industries due to their exceptional thermal stability, chemical resistance, and flexibility, making them ideal for high-temperature fluid transport and insulating sensitive wiring. Polyvinyl chloride (PVC) pipes dominate construction, plumbing, and water distribution sectors because of their affordability, corrosion resistance, and ease of installation in low to medium temperature applications. The choice between polyimide and PVC pipes depends on operational environment demands, with polyimide suited for harsh, high-performance conditions and PVC favored for cost-effective, general-purpose uses.
Choosing the Right Material: Key Factors to Consider
Polyimide pipes offer exceptional thermal stability and chemical resistance, making them ideal for high-temperature and corrosive environments, whereas polyvinyl chloride (PVC) pipes are favored for their affordability, ease of installation, and widespread availability in standard plumbing and drainage applications. Key factors to consider when choosing between polyimide and PVC include temperature tolerance, chemical exposure, mechanical strength, and budget constraints. Evaluating project-specific requirements such as operating pressure, environmental conditions, and longevity will ensure the selection of the most suitable pipe material.
Infographic: Polyimide vs Polyvinyl Chloride for Pipe
 azmater.com
azmater.com