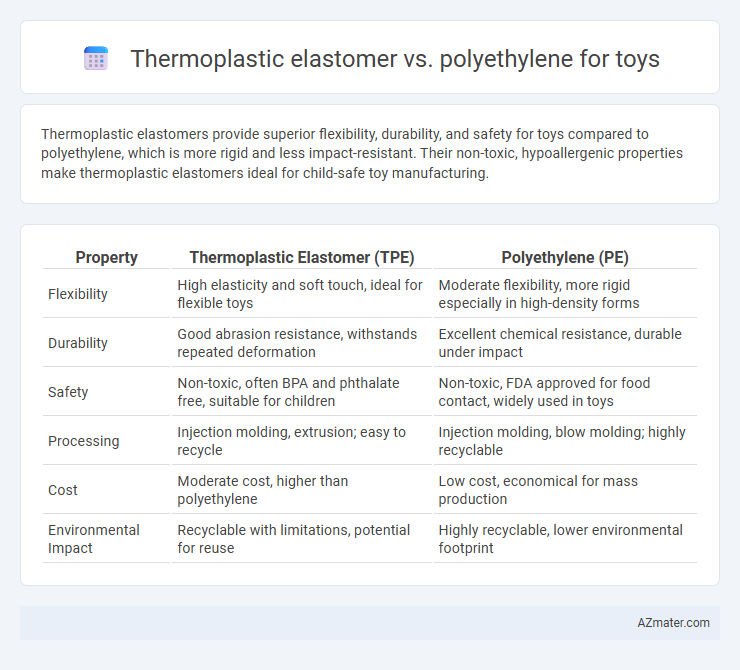
Thermoplastic elastomers provide superior flexibility, durability, and safety for toys compared to polyethylene, which is more rigid and less impact-resistant. Their non-toxic, hypoallergenic properties make thermoplastic elastomers ideal for child-safe toy manufacturing.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Thermoplastic Elastomer (TPE) | Polyethylene (PE) |
|---|---|---|
| Flexibility | High elasticity and soft touch, ideal for flexible toys | Moderate flexibility, more rigid especially in high-density forms |
| Durability | Good abrasion resistance, withstands repeated deformation | Excellent chemical resistance, durable under impact |
| Safety | Non-toxic, often BPA and phthalate free, suitable for children | Non-toxic, FDA approved for food contact, widely used in toys |
| Processing | Injection molding, extrusion; easy to recycle | Injection molding, blow molding; highly recyclable |
| Cost | Moderate cost, higher than polyethylene | Low cost, economical for mass production |
| Environmental Impact | Recyclable with limitations, potential for reuse | Highly recyclable, lower environmental footprint |
Introduction to Thermoplastic Elastomer and Polyethylene
Thermoplastic elastomers (TPE) are versatile materials combining the flexibility of rubber with the processability of plastics, making them ideal for safe, durable toy manufacturing. Polyethylene (PE), a widely used polymer, offers excellent impact resistance, chemical stability, and low cost, frequently utilized in rigid and flexible toy components. Both TPE and PE provide distinct advantages in toy applications, with TPE excelling in softness and elasticity, while PE stands out for toughness and lightweight properties.
Chemical Structure and Composition Comparison
Thermoplastic elastomers (TPE) exhibit a block copolymer structure combining hard thermoplastic segments with soft elastomeric domains, providing flexibility and resilience in toy applications. Polyethylene (PE), composed of long hydrocarbon chains with a linear or branched structure, offers rigidity and chemical resistance but lacks the elasticity found in TPE. The segmented chemical composition of TPE allows for enhanced mechanical performance and repeated deformation, whereas PE's homogeneous polyethylene chains result in a more crystalline material with higher stiffness but less flexibility.
Physical Properties Relevant to Toy Manufacturing
Thermoplastic elastomers (TPE) exhibit superior flexibility, impact resistance, and elasticity compared to polyethylene (PE), making them ideal for toys requiring soft touch and durability. PE offers excellent chemical resistance and tensile strength but lacks the compressive recovery and stress relaxation performance critical for safe, deformable toy components. TPEs' ability to withstand repeated bending and maintain shape enhances child safety and toy longevity, while PE's rigidity suits structural parts less exposed to mechanical stress.
Safety and Toxicity Concerns in Toys
Thermoplastic elastomers (TPE) offer superior safety for toys due to their non-toxic, phthalate-free composition and low allergenic potential compared to polyethylene (PE), which may contain additives raising toxicological concerns. TPE materials provide flexibility and durability without releasing harmful chemicals, whereas PE can degrade under certain conditions, potentially leaching additives harmful to children. Regulatory compliance such as CPSIA and EN71 standards favors TPE for safer toy manufacturing, minimizing risks associated with ingestion or prolonged skin contact.
Durability and Longevity in Play Environments
Thermoplastic elastomers (TPE) exhibit superior durability and resilience in dynamic play environments compared to polyethylene (PE), owing to their excellent flexibility and resistance to repeated stress and deformation. TPE materials maintain structural integrity and softness over extended periods, minimizing wear and tear even under rigorous handling and impact, whereas polyethylene tends to become brittle and prone to cracking after prolonged exposure to physical and environmental stressors. This inherent toughness and elasticity of TPE make it preferable for toys requiring long-lasting performance and child-safe safety standards.
Flexibility and Softness: Comfort for Children
Thermoplastic elastomers (TPE) offer superior flexibility and softness compared to polyethylene, making them ideal for children's toys that require a comfortable and safe tactile experience. TPE materials provide enhanced elasticity and a smooth, rubber-like feel, reducing the risk of injury during play. Polyethylene, while durable, tends to be stiffer and less cushioned, potentially compromising comfort and flexibility essential for child-friendly toy designs.
Coloring and Aesthetic Versatility
Thermoplastic elastomers (TPE) offer superior coloring and aesthetic versatility compared to polyethylene (PE) in toy manufacturing due to their enhanced dye absorption and ability to produce a wide range of vibrant, translucent, and rubber-like finishes. TPE materials support complex color gradients and custom textures, enabling designers to create visually appealing, tactile toys with varied surface properties. In contrast, polyethylene's limited color range and opacity reduce its effectiveness in applications requiring intricate color schemes or soft, flexible aesthetics.
Cost Efficiency for Toy Producers
Thermoplastic elastomers (TPE) offer greater cost efficiency for toy producers due to their recyclability and ease of processing, reducing manufacturing waste and energy consumption compared to polyethylene (PE). PE's lower raw material cost is offset by higher tooling expenses and limited customization options, leading to increased long-term production costs for complex toy designs. TPE's durability and flexibility enable longer-lasting toys, minimizing returns and enhancing overall production value.
Environmental Impact and Recyclability
Thermoplastic elastomers (TPEs) offer better recyclability compared to polyethylene (PE) due to their ability to be melted and reshaped multiple times without significant degradation, reducing environmental waste in toy manufacturing. Polyethylene, while widely recyclable, often contributes to persistent plastic pollution because of its slower degradation rate and challenges in recycling mixed-material toys. Selecting TPE for toy production enhances sustainability by minimizing landfill accumulation and facilitating closed-loop recycling processes.
Choosing the Right Material: Application-Based Recommendations
Thermoplastic elastomers (TPE) offer superior flexibility, impact resistance, and a softer touch, making them ideal for toys requiring safe, durable, and squeezable textures such as rattles and teething rings. Polyethylene (PE), known for its rigidity, chemical resistance, and ease of molding, suits toys that demand structural strength and lightweight characteristics like building blocks and outdoor playsets. Selecting the right material depends on the toy's functional requirements, safety standards, and tactile experience desired, with TPE favored for comfort and grip, and PE preferred for durability and shape retention.
Infographic: Thermoplastic elastomer vs Polyethylene for Toy
 azmater.com
azmater.com