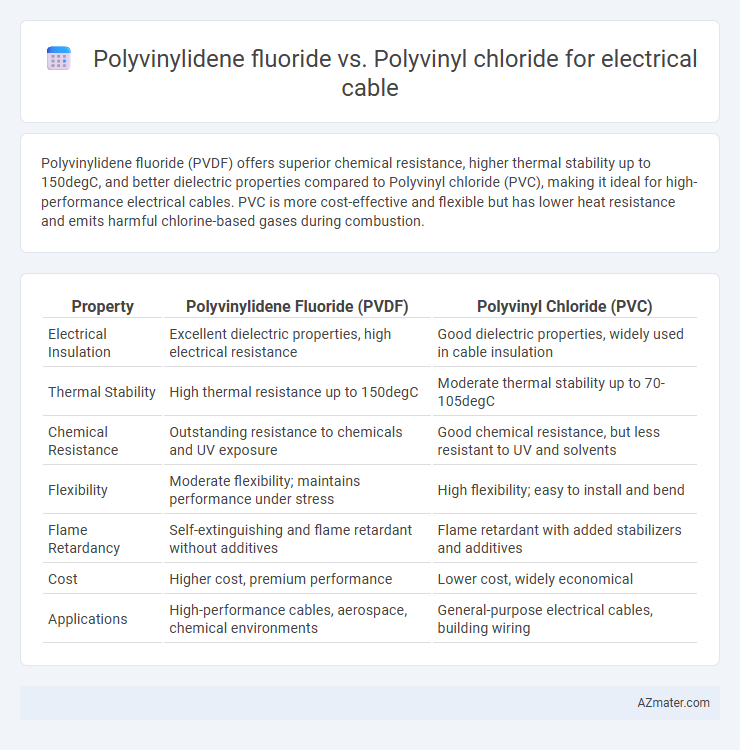
Polyvinylidene fluoride (PVDF) offers superior chemical resistance, higher thermal stability up to 150degC, and better dielectric properties compared to Polyvinyl chloride (PVC), making it ideal for high-performance electrical cables. PVC is more cost-effective and flexible but has lower heat resistance and emits harmful chlorine-based gases during combustion.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Polyvinylidene Fluoride (PVDF) | Polyvinyl Chloride (PVC) |
|---|---|---|
| Electrical Insulation | Excellent dielectric properties, high electrical resistance | Good dielectric properties, widely used in cable insulation |
| Thermal Stability | High thermal resistance up to 150degC | Moderate thermal stability up to 70-105degC |
| Chemical Resistance | Outstanding resistance to chemicals and UV exposure | Good chemical resistance, but less resistant to UV and solvents |
| Flexibility | Moderate flexibility; maintains performance under stress | High flexibility; easy to install and bend |
| Flame Retardancy | Self-extinguishing and flame retardant without additives | Flame retardant with added stabilizers and additives |
| Cost | Higher cost, premium performance | Lower cost, widely economical |
| Applications | High-performance cables, aerospace, chemical environments | General-purpose electrical cables, building wiring |
Introduction to Electrical Cable Insulation Materials
Polyvinylidene fluoride (PVDF) offers superior thermal stability, chemical resistance, and dielectric properties compared to polyvinyl chloride (PVC), making it ideal for high-performance electrical cable insulation. PVC remains popular due to its cost-effectiveness, flexibility, and good insulating characteristics, but its lower heat resistance and presence of plasticizers limit its use in extreme conditions. PVDF's ability to maintain insulation integrity under harsh environmental and electrical stresses positions it as a premium choice for specialized cable applications.
Overview of Polyvinylidene Fluoride (PVDF)
Polyvinylidene Fluoride (PVDF) is a highly non-reactive and pure thermoplastic fluoropolymer widely used in electrical cable insulation due to its excellent chemical resistance, high thermal stability up to 150degC, and superior dielectric properties. Compared to Polyvinyl Chloride (PVC), PVDF offers better flame retardancy and UV resistance, making it ideal for harsh environmental conditions and long-term outdoor applications. Its low smoke generation and minimal toxic gas emission during combustion enhance safety in electrical cable installations.
Overview of Polyvinyl Chloride (PVC)
Polyvinyl Chloride (PVC) is a widely used thermoplastic polymer in electrical cable insulation due to its excellent electrical insulation properties, durability, and flame resistance. PVC offers chemical and weather resistance, making it suitable for indoor and outdoor cable applications while maintaining flexibility over a broad temperature range. Its cost-effectiveness and ease of processing contribute to its popularity in low to medium voltage electrical cables.
Thermal Stability: PVDF vs PVC
Polyvinylidene fluoride (PVDF) exhibits superior thermal stability compared to polyvinyl chloride (PVC), maintaining its mechanical and electrical properties at temperatures up to 150degC, whereas PVC typically degrades around 105degC. PVDF's high melting point and resistance to thermal oxidation make it ideal for applications requiring prolonged exposure to elevated temperatures in electrical cable insulation. This enhanced thermal stability ensures longer service life and improved safety performance in demanding electrical environments.
Electrical Properties and Dielectric Strength
Polyvinylidene fluoride (PVDF) exhibits superior dielectric strength and electrical properties compared to Polyvinyl chloride (PVC), making it ideal for high-performance electrical cable insulation. PVDF offers excellent resistance to electrical breakdown, with a dielectric strength typically around 40-50 kV/mm, whereas PVC's dielectric strength ranges between 20-40 kV/mm. The higher thermal stability and lower dielectric constant of PVDF enhance signal integrity and reduce energy losses in electrical applications relative to PVC.
Chemical Resistance Comparison
Polyvinylidene fluoride (PVDF) exhibits superior chemical resistance compared to polyvinyl chloride (PVC), particularly against acids, bases, and organic solvents, making it highly suitable for harsh environments in electrical cable applications. PVC offers moderate chemical resistance but tends to degrade when exposed to strong chemicals and UV radiation over time, limiting its durability. The enhanced chemical stability of PVDF ensures longer service life and reliability in cables used in industrial and corrosive settings.
Flame Retardancy and Fire Safety
Polyvinylidene fluoride (PVDF) surpasses polyvinyl chloride (PVC) in flame retardancy for electrical cables due to its intrinsic resistance to ignition and self-extinguishing properties. PVDF emits fewer toxic gases and produces less smoke when exposed to fire, enhancing overall fire safety in critical installations. In contrast, PVC releases harmful hydrochloric acid fumes and dense smoke, posing greater health risks during combustion.
Flexibility and Mechanical Strength
Polyvinylidene fluoride (PVDF) offers superior flexibility compared to polyvinyl chloride (PVC), making it ideal for applications requiring dynamic bending and movement in electrical cables. PVDF also exhibits enhanced mechanical strength, including higher tensile strength and better abrasion resistance, ensuring durability under mechanical stress. In contrast, PVC provides moderate flexibility and mechanical strength but is more prone to cracking and degradation over time in demanding environments.
Cost Considerations and Economic Impact
Polyvinylidene fluoride (PVDF) offers superior chemical resistance and thermal stability compared to polyvinyl chloride (PVC), resulting in higher initial material costs for electrical cables. PVC remains the more cost-effective option due to its lower production expenses and widespread availability, making it a preferred choice for budget-sensitive projects. The economic impact of choosing PVDF arises from its longer lifespan and reduced maintenance needs, potentially offsetting upfront costs through enhanced durability and reliability in demanding electrical applications.
Application Suitability: Choosing Between PVDF and PVC
Polyvinylidene fluoride (PVDF) offers superior chemical resistance, high thermal stability up to 150degC, and excellent electrical insulation, making it ideal for high-performance electrical cables in harsh industrial environments. Polyvinyl chloride (PVC) remains a cost-effective choice with good flame retardance and flexibility, suitable for general-purpose electrical wiring and residential installations. When selecting cable materials, PVDF is preferred for demanding applications requiring durability and resistance to solvents, while PVC is favored for budget-conscious projects with moderate performance demands.
Infographic: Polyvinylidene fluoride vs Polyvinyl chloride for Electrical cable
 azmater.com
azmater.com