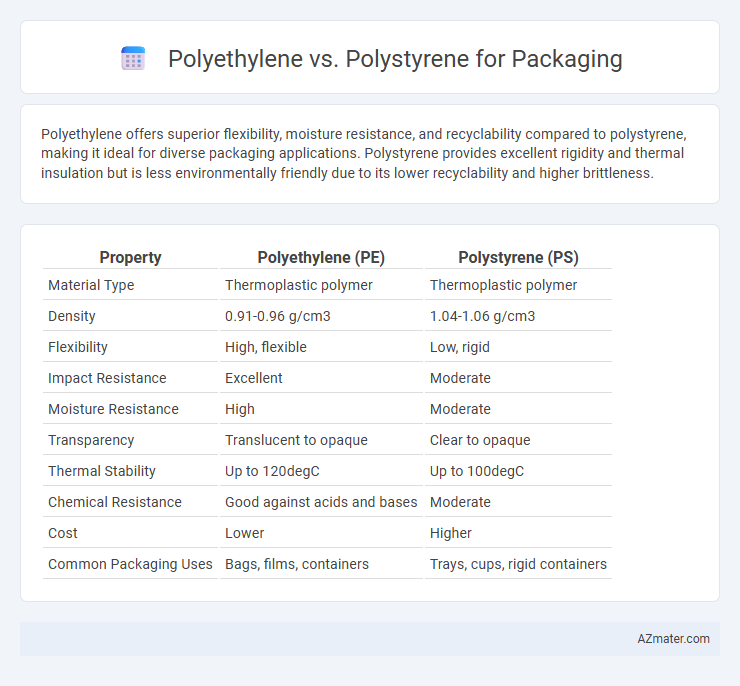
Polyethylene offers superior flexibility, moisture resistance, and recyclability compared to polystyrene, making it ideal for diverse packaging applications. Polystyrene provides excellent rigidity and thermal insulation but is less environmentally friendly due to its lower recyclability and higher brittleness.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Polyethylene (PE) | Polystyrene (PS) |
|---|---|---|
| Material Type | Thermoplastic polymer | Thermoplastic polymer |
| Density | 0.91-0.96 g/cm3 | 1.04-1.06 g/cm3 |
| Flexibility | High, flexible | Low, rigid |
| Impact Resistance | Excellent | Moderate |
| Moisture Resistance | High | Moderate |
| Transparency | Translucent to opaque | Clear to opaque |
| Thermal Stability | Up to 120degC | Up to 100degC |
| Chemical Resistance | Good against acids and bases | Moderate |
| Cost | Lower | Higher |
| Common Packaging Uses | Bags, films, containers | Trays, cups, rigid containers |
Introduction to Polyethylene and Polystyrene
Polyethylene, a versatile thermoplastic polymer, is widely used in packaging due to its excellent moisture resistance, flexibility, and durability. Polystyrene offers rigid, lightweight properties ideal for protective packaging and insulation, often found in disposable containers and foam applications. Selecting between polyethylene and polystyrene depends on specific packaging needs such as strength, weight, and environmental considerations.
Chemical Structure and Properties Comparison
Polyethylene consists of long chains of ethylene monomers with a simple, non-polar hydrocarbon structure, offering excellent flexibility, chemical resistance, and moisture barrier properties ideal for packaging. Polystyrene, composed of styrene monomers featuring aromatic phenyl groups attached to the carbon chain, provides rigidity, clarity, and thermal insulation but is more brittle and less resistant to chemicals compared to polyethylene. These molecular differences account for polyethylene's suitability in flexible films and bags, while polystyrene excels in rigid containers and protective foam applications.
Common Packaging Applications
Polyethylene is widely used in packaging applications such as plastic bags, shrink wraps, and flexible containers due to its excellent moisture barrier and flexibility. Polystyrene is commonly utilized for rigid packaging items like disposable cups, food trays, and protective foam inserts, offering good insulation and cushioning properties. Both materials serve distinct purposes in packaging, where polyethylene excels in flexibility and durability, while polystyrene provides structural rigidity and thermal insulation.
Strength and Durability Differences
Polyethylene offers superior impact resistance and flexibility, making it ideal for packaging requiring toughness and resilience under stress. Polystyrene, while rigid and excellent for maintaining shape, tends to be more brittle and prone to cracking under impact. These strength and durability differences influence their application, with polyethylene preferred for heavy-duty protection and polystyrene suited for lightweight, decorative packaging.
Flexibility and Versatility in Use
Polyethylene offers superior flexibility and durability, making it ideal for packaging products requiring stretchability or cushioning. Polystyrene provides rigidity and excellent shape retention but is less adaptable to varied packaging shapes and applications. The versatility of polyethylene in forms like films, bags, and containers outperforms polystyrene's more limited use primarily in rigid foam and packaging trays.
Barrier Properties: Moisture and Gas Resistance
Polyethylene offers excellent moisture resistance due to its low permeability, making it ideal for packaging products sensitive to water vapor. Polystyrene, while providing moderate moisture barrier properties, excels in gas resistance, particularly oxygen, which helps preserve the freshness of perishable goods. Selecting between polyethylene and polystyrene depends on the specific packaging requirements for moisture protection versus gas barrier performance.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
Polyethylene offers better recyclability and lower environmental toxicity compared to polystyrene, contributing to reduced landfill waste and lower carbon emissions. Polystyrene, while lightweight and insulating, presents significant challenges due to its non-biodegradable nature and difficulty in recycling, leading to persistent environmental pollution. Sustainable packaging solutions favor polyethylene's higher recycling rates and potential for reuse, advancing circular economy goals.
Cost Efficiency and Availability
Polyethylene offers superior cost efficiency due to its lower production expenses and widespread availability, making it a popular choice for large-scale packaging applications. Polystyrene, while providing better rigidity and insulation properties, tends to be more expensive and less readily available in bulk quantities. The balance between cost and functional requirements often drives manufacturers to prefer polyethylene for economical, high-volume packaging solutions.
Recycling and Waste Management Options
Polyethylene offers superior recycling options due to its widespread acceptance in curbside programs and higher recyclability rates compared to polystyrene, which is often excluded from standard recycling streams because of contamination risks. Polystyrene, especially expanded polystyrene (EPS), presents significant challenges in waste management due to its low density and propensity to fragment, making it less economically viable to recycle. Emphasizing polyethylene packaging can reduce landfill waste and improve circular economy outcomes, owing to established recycling technologies and infrastructure.
Choosing the Right Material for Packaging Needs
Polyethylene offers excellent flexibility, moisture resistance, and cost-effectiveness, making it ideal for flexible packaging such as bags and films. Polystyrene provides superior rigidity, impact resistance, and clarity, suitable for protective packaging, trays, and disposable containers. Selecting the right material depends on packaging requirements like durability, transparency, and environmental impact, with polyethylene favored for lightweight, moisture-proof solutions and polystyrene for rigid, shock-absorbing applications.
Infographic: Polyethylene vs Polystyrene for Packaging
 azmater.com
azmater.com