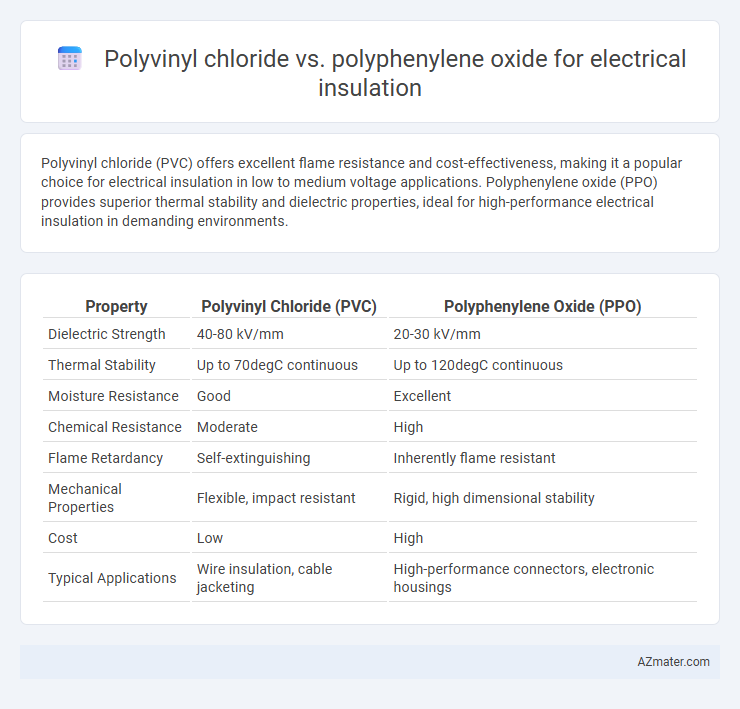
Polyvinyl chloride (PVC) offers excellent flame resistance and cost-effectiveness, making it a popular choice for electrical insulation in low to medium voltage applications. Polyphenylene oxide (PPO) provides superior thermal stability and dielectric properties, ideal for high-performance electrical insulation in demanding environments.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Polyvinyl Chloride (PVC) | Polyphenylene Oxide (PPO) |
|---|---|---|
| Dielectric Strength | 40-80 kV/mm | 20-30 kV/mm |
| Thermal Stability | Up to 70degC continuous | Up to 120degC continuous |
| Moisture Resistance | Good | Excellent |
| Chemical Resistance | Moderate | High |
| Flame Retardancy | Self-extinguishing | Inherently flame resistant |
| Mechanical Properties | Flexible, impact resistant | Rigid, high dimensional stability |
| Cost | Low | High |
| Typical Applications | Wire insulation, cable jacketing | High-performance connectors, electronic housings |
Introduction to Electrical Insulation Materials
Polyvinyl chloride (PVC) and Polyphenylene oxide (PPO) serve as crucial electrical insulation materials, each offering distinct advantages in dielectric strength and thermal stability. PVC is widely used due to its cost-effectiveness, flame retardancy, and flexibility, making it suitable for general-purpose cable insulation and consumer electronics. PPO provides superior heat resistance, dimensional stability, and higher dielectric constant, making it ideal for demanding applications in automotive and aerospace electrical systems.
Overview of Polyvinyl Chloride (PVC)
Polyvinyl chloride (PVC) is a widely used thermoplastic polymer known for its excellent electrical insulation properties, durability, and chemical resistance, making it ideal for coating and insulating electrical cables and wires. Its high dielectric strength and flame-retardant characteristics ensure safety and reliability in various electrical applications, from household wiring to industrial devices. PVC's cost-effectiveness and ease of processing contribute to its dominance as an electrical insulation material compared to specialized polymers like polyphenylene oxide (PPO).
Overview of Polyphenylene Oxide (PPO)
Polyphenylene oxide (PPO) is a high-performance thermoplastic widely used in electrical insulation due to its excellent thermal stability, dimensional stability, and inherent flame resistance. PPO exhibits superior dielectric properties, low moisture absorption, and maintains mechanical strength at elevated temperatures, making it ideal for demanding electrical applications. Compared to polyvinyl chloride (PVC), PPO offers enhanced thermal endurance and chemical resistance, contributing to longer lifespan and reliability in insulation systems.
Electrical Properties: PVC vs PPO
Polyvinyl chloride (PVC) exhibits moderate dielectric strength and good insulation resistance, making it widely used in electrical insulation applications with a dielectric constant typically around 3. Polymer phenylene oxide (PPO) offers superior electrical properties, including higher dielectric strength and lower dielectric loss, enhancing its performance in high-frequency and high-voltage environments. PPO's excellent thermal stability further supports consistent electrical insulation performance under elevated temperatures compared to PVC.
Thermal Stability Comparison
Polyphenylene oxide (PPO) exhibits superior thermal stability compared to polyvinyl chloride (PVC) in electrical insulation applications, maintaining structural integrity at temperatures up to 180degC, whereas PVC typically degrades around 140degC. PPO's high glass transition temperature and inherent flame resistance contribute to enhanced performance in high-heat environments. This thermal resilience makes PPO a preferred choice for electrical components requiring prolonged exposure to elevated temperatures without compromising insulation properties.
Mechanical Strength and Durability
Polyvinyl chloride (PVC) offers moderate mechanical strength and durability, making it suitable for flexible electrical insulation applications where cost-efficiency and chemical resistance are important. Polyphenylene oxide (PPO) provides superior mechanical strength and enhanced thermal stability, resulting in longer-lasting insulation performance under high-stress and high-temperature conditions. PPO's resistance to environmental degradation outperforms PVC, ensuring reliability in demanding electrical insulation scenarios.
Chemical Resistance and Environmental Factors
Polyvinyl chloride (PVC) offers strong chemical resistance to acids, alkalis, and oils, making it suitable for electrical insulation in harsh industrial environments. Polyphenylene oxide (PPO) provides superior resistance to oxidative degradation and higher thermal stability, enhancing performance in elevated temperature applications. Environmental factors favor PPO due to its better resistance to UV radiation and lower smoke emission during combustion, contributing to safer, longer-lasting electrical insulation.
Cost Effectiveness and Availability
Polyvinyl chloride (PVC) offers superior cost-effectiveness and widespread availability compared to polyphenylene oxide (PPO), making it the preferred choice for electrical insulation in budget-sensitive applications. PVC's lower raw material and processing costs contribute to its dominance in mass production and global supply chains. PPO, while providing excellent thermal stability and electrical properties, is more expensive and less readily available, limiting its use to specialized insulation needs where performance outweighs cost.
Application Suitability in Electrical Insulation
Polyvinyl chloride (PVC) offers excellent flexibility, flame resistance, and cost-effectiveness, making it widely suitable for general electrical insulation in household wiring and cable jacketing. Polyphenylene oxide (PPO) exhibits superior thermal stability, high dielectric strength, and low moisture absorption, which are critical for high-performance electrical insulation in demanding industrial and automotive applications. Selecting PVC is ideal for standard insulation tasks, whereas PPO excels in environments requiring enhanced mechanical and electrical durability under elevated temperatures.
Conclusion: Choosing the Right Material
Polyvinyl chloride (PVC) offers excellent electrical insulation with superior flame resistance and cost-effectiveness, making it suitable for general-purpose wiring and low-voltage applications. Polyphenylene oxide (PPO) provides higher thermal stability and mechanical strength, ideal for demanding environments with elevated temperatures and stringent performance requirements. Selecting the right material depends on specific application needs, balancing factors such as temperature tolerance, mechanical durability, and budget constraints.
Infographic: Polyvinyl chloride vs Polyphenylene oxide for Electrical Insulation
 azmater.com
azmater.com