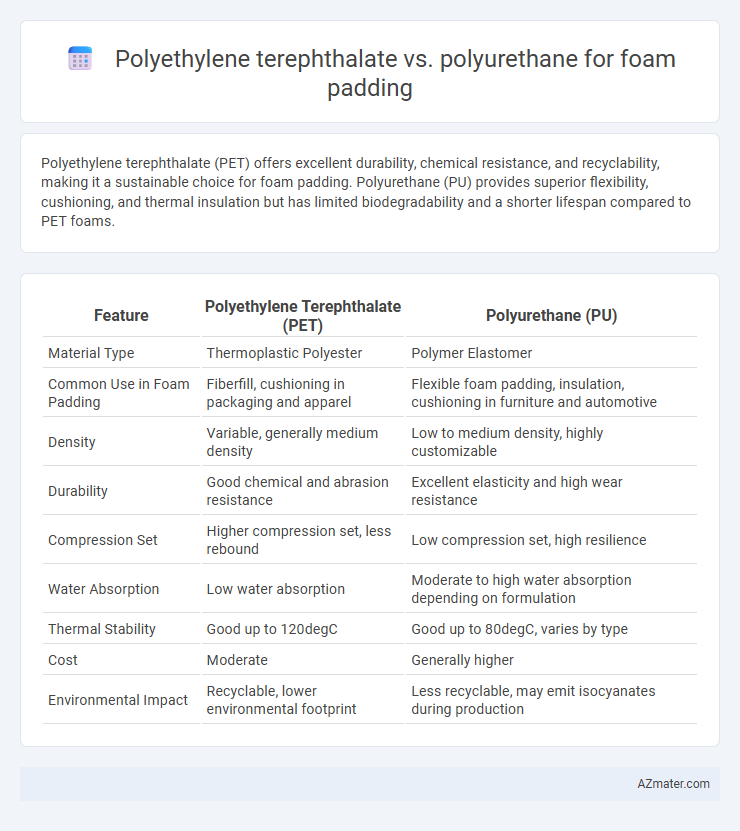
Polyethylene terephthalate (PET) offers excellent durability, chemical resistance, and recyclability, making it a sustainable choice for foam padding. Polyurethane (PU) provides superior flexibility, cushioning, and thermal insulation but has limited biodegradability and a shorter lifespan compared to PET foams.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Polyethylene Terephthalate (PET) | Polyurethane (PU) |
|---|---|---|
| Material Type | Thermoplastic Polyester | Polymer Elastomer |
| Common Use in Foam Padding | Fiberfill, cushioning in packaging and apparel | Flexible foam padding, insulation, cushioning in furniture and automotive |
| Density | Variable, generally medium density | Low to medium density, highly customizable |
| Durability | Good chemical and abrasion resistance | Excellent elasticity and high wear resistance |
| Compression Set | Higher compression set, less rebound | Low compression set, high resilience |
| Water Absorption | Low water absorption | Moderate to high water absorption depending on formulation |
| Thermal Stability | Good up to 120degC | Good up to 80degC, varies by type |
| Cost | Moderate | Generally higher |
| Environmental Impact | Recyclable, lower environmental footprint | Less recyclable, may emit isocyanates during production |
Overview of Polyethylene Terephthalate (PET) and Polyurethane
Polyethylene terephthalate (PET) is a durable, lightweight polyester commonly used in foam padding for its excellent dimensional stability, moisture resistance, and recyclability, making it an eco-friendly choice in various applications. Polyurethane foam is a versatile, flexible material known for its superior cushioning, high resilience, and shock absorption properties, widely utilized in furniture, automotive seating, and mattress production. While PET offers enhanced environmental benefits and structural strength, polyurethane provides greater comfort and adaptability in foam padding solutions.
Chemical Structure and Material Properties
Polyethylene terephthalate (PET) is a thermoplastic polymer characterized by its repeating ester functional groups formed from terephthalic acid and ethylene glycol, providing high tensile strength, rigidity, and chemical resistance ideal for durable foam padding. In contrast, polyurethane consists of urethane linkages created from the reaction between polyols and isocyanates, offering exceptional flexibility, abrasion resistance, and cushioning properties for foam applications. PET foams exhibit superior dimensional stability and thermal resistance, whereas polyurethane foams excel in compressibility and energy absorption, making material selection dependent on specific performance requirements.
Foam Padding Applications: PET vs Polyurethane
Polyurethane foam padding offers superior cushioning and flexibility, making it ideal for furniture, automotive seats, and medical cushions due to its excellent shock absorption and durability. Polyethylene terephthalate (PET) foam padding excels in thermal insulation and moisture resistance, commonly used in packaging, sports equipment, and soundproofing applications. While polyurethane provides enhanced comfort and resilience, PET foam is preferred for eco-friendly and high-performance insulation solutions.
Comfort and Cushioning Performance Comparison
Polyethylene terephthalate (PET) foam padding offers superior breathability and moisture resistance, enhancing comfort during extended use, whereas polyurethane (PU) foam provides higher initial softness and better energy absorption for cushioning. PET foam maintains structural integrity and resilience over time, resulting in long-lasting support, while PU foam tends to compress and degrade faster under repeated stress, affecting its cushioning performance. For applications where durability and moisture management are critical, PET foam is preferable; PU foam excels in scenarios requiring immediate plushness and shock absorption.
Durability and Lifespan Analysis
Polyurethane foam padding offers superior durability and a longer lifespan compared to polyethylene terephthalate (PET) foam, maintaining cushioning properties under frequent compression and exposure to environmental factors. PET foam demonstrates moderate durability but tends to degrade faster due to lower resistance to heat, moisture, and mechanical stress. Choosing polyurethane is optimal for applications requiring extended use and consistent performance in foam padding.
Environmental Impact and Recyclability
Polyethylene terephthalate (PET) foam padding offers superior environmental benefits due to its high recyclability and widespread acceptance in recycling programs, significantly reducing landfill waste. Polyurethane foam padding, while durable and flexible, presents recycling challenges, often ending up in landfills due to limited recycling infrastructure and the release of harmful chemicals during degradation. Using PET foam padding supports a circular economy by enabling efficient reprocessing into new products, lowering the carbon footprint compared to the largely non-recyclable polyurethane alternatives.
Cost Considerations and Market Availability
Polyethylene terephthalate (PET) foam padding generally offers lower production costs due to its widespread use and efficient manufacturing processes compared to polyurethane (PU) foam. PU foam, while often providing superior cushioning and flexibility, tends to be more expensive due to higher raw material costs and specialized production techniques. Market availability favors PET foam in mass-produced applications, whereas PU foam is prevalent in specialized sectors requiring higher performance, impacting overall cost and accessibility.
Safety and Allergen Potential
Polyethylene terephthalate (PET) foam padding is generally considered hypoallergenic and resistant to mold and dust mites, making it a safer option for individuals with allergies or asthma. Polyurethane foam often contains chemical additives and off-gassing compounds such as isocyanates, which can trigger respiratory irritation and allergic reactions. PET foam's chemical stability and lower emission of volatile organic compounds (VOCs) enhance indoor air quality and reduce allergen potential compared to polyurethane foams.
Manufacturing Processes for Foam Padding
Polyethylene terephthalate (PET) foam padding is typically produced through a process of extrusion and expansion, where PET pellets are melted and expanded to create a lightweight, closed-cell foam structure, making it ideal for cushioning and insulation. Polyurethane (PU) foam padding is manufactured using a chemical reaction between polyols and diisocyanates, which creates an open or closed-cell foam with customizable density and flexibility, suitable for a wide range of applications including furniture and automotive seating. The manufacturing process of PET foam is generally more environmentally friendly with recyclability advantages, whereas PU foam production involves more complex chemical formulations and catalysts that impact cost and environmental considerations.
Choosing the Right Material for Your Foam Padding Needs
Polyethylene terephthalate (PET) foam offers excellent durability, chemical resistance, and recyclability, making it ideal for eco-friendly and long-lasting foam padding applications. Polyurethane foam provides superior cushioning, flexibility, and impact absorption, which is essential for comfort-focused uses such as upholstery and mattress padding. Selecting the right material depends on the specific requirements for performance, environmental impact, and cost-effectiveness in your foam padding project.
Infographic: Polyethylene terephthalate vs Polyurethane for Foam Padding
 azmater.com
azmater.com