Biodegradable plastics for food containers reduce environmental impact through natural decomposition, while polypropylene offers superior durability, heat resistance, and cost-effectiveness. Choosing between them depends on balancing sustainability goals with functional performance and shelf life requirements.
Table of Comparison
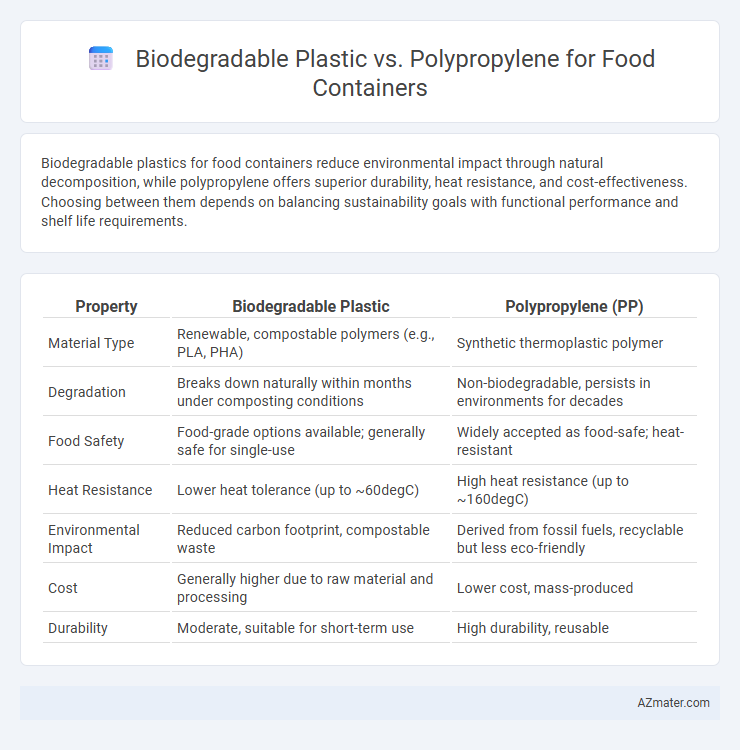
| Property | Biodegradable Plastic | Polypropylene (PP) |
|---|---|---|
| Material Type | Renewable, compostable polymers (e.g., PLA, PHA) | Synthetic thermoplastic polymer |
| Degradation | Breaks down naturally within months under composting conditions | Non-biodegradable, persists in environments for decades |
| Food Safety | Food-grade options available; generally safe for single-use | Widely accepted as food-safe; heat-resistant |
| Heat Resistance | Lower heat tolerance (up to ~60degC) | High heat resistance (up to ~160degC) |
| Environmental Impact | Reduced carbon footprint, compostable waste | Derived from fossil fuels, recyclable but less eco-friendly |
| Cost | Generally higher due to raw material and processing | Lower cost, mass-produced |
| Durability | Moderate, suitable for short-term use | High durability, reusable |
Introduction to Food Packaging Materials
Biodegradable plastics and polypropylene represent two key materials in food packaging, with polypropylene known for its durability, chemical resistance, and wide use in airtight food containers that preserve freshness. Biodegradable plastics, derived from renewable resources like cornstarch or sugarcane, offer environmental advantages by breaking down naturally, reducing plastic pollution associated with traditional polymers. Selecting the right material depends on factors such as product shelf life, sustainability goals, and regulatory compliance in food safety standards.
Overview of Biodegradable Plastics
Biodegradable plastics, derived from renewable biomass sources such as corn starch, sugarcane, and potato starch, offer an eco-friendly alternative to polypropylene in food container applications by breaking down more rapidly under composting conditions. These materials, including polylactic acid (PLA) and polyhydroxyalkanoates (PHA), reduce environmental impact by decomposing into natural elements within months, unlike conventional polypropylene that persists in landfills for decades. Their increasing use addresses growing consumer demand for sustainable packaging, though challenges remain in achieving comparable durability and heat resistance to polypropylene.
What is Polypropylene?
Polypropylene is a thermoplastic polymer widely used in food containers due to its durability, chemical resistance, and high melting point, making it safe for reheating and dishwasher use. Its non-biodegradable nature means it persists in the environment for hundreds of years, contributing to plastic pollution. In contrast, biodegradable plastics break down more rapidly under specific conditions but often lack the heat resistance and robustness of polypropylene for long-term or repeated use.
Environmental Impact: Biodegradable vs Polypropylene
Biodegradable plastics significantly reduce environmental impact by breaking down naturally within months, minimizing long-term pollution and landfill accumulation compared to polypropylene, which can take hundreds of years to decompose. Polypropylene, derived from fossil fuels, contributes to carbon emissions and microplastic pollution, posing challenges to marine and soil ecosystems. Choosing biodegradable containers supports circular economy goals by enhancing compostability and reducing carbon footprints in food packaging solutions.
Food Safety and Chemical Leaching Concerns
Biodegradable plastics, often made from plant-based materials like PLA, reduce chemical leaching risks compared to polypropylene, which can release additives such as stabilizers and plasticizers when exposed to heat. Polypropylene is generally recognized for its food safety due to its high melting point and resistance to chemical migration, but concerns arise when reused or heated, potentially leading to migration of residual monomers or additives. Choosing biodegradable plastics minimizes long-term chemical exposure but requires scrutiny of compostability standards and potential degradation byproducts impacting food safety.
Durability and Performance Comparison
Biodegradable plastics offer eco-friendly alternatives but typically have lower durability and heat resistance compared to polypropylene, which excels in strength and maintains integrity at high temperatures. Polypropylene food containers provide superior performance for repeated use, resisting cracking and warping, whereas biodegradable options may degrade faster under stress and exposure. For applications requiring long-term storage and microwave use, polypropylene remains preferred due to its robust mechanical properties and chemical stability.
Cost Analysis: Biodegradable Plastics vs Polypropylene
Biodegradable plastics typically incur higher production and raw material costs compared to polypropylene, impacting the overall price of food containers. Polypropylene benefits from large-scale manufacturing and well-established supply chains, resulting in lower unit costs and greater affordability. While biodegradable options may offer environmental advantages, polypropylene remains more cost-effective for mass-market food container applications.
Regulatory Requirements and Certifications
Biodegradable plastics used for food containers must comply with strict regulatory requirements such as ASTM D6400 and EN 13432 standards to ensure compostability and non-toxicity, while polypropylene (PP) often adheres to FDA 21 CFR 177.1520 for food safety and migration limits. Certifications like BPI, OK Compost, and TUV Austria validate the environmental claims of biodegradable plastics, whereas polypropylene containers typically receive FDA and NSF certifications confirming their suitability for direct food contact. Regulatory frameworks prioritize chemical safety, migration testing, and environmental impact assessments to guarantee consumer protection and ecological sustainability in both materials.
Consumer Perception and Market Trends
Consumers increasingly favor biodegradable plastics for food containers due to growing environmental awareness and demand for sustainable packaging solutions. Market trends reveal a steady rise in biodegradable plastic usage driven by regulations targeting single-use plastics, while polypropylene remains popular for its durability and low cost. Consumer perception highlights a trade-off between eco-friendliness and performance, with many willing to pay a premium for compostable options despite polypropylene's established presence.
Future Outlook for Food Container Materials
Biodegradable plastics offer an environmentally friendly alternative to polypropylene by reducing plastic waste and enhancing compostability in food containers, aligning with increasing regulatory demands for sustainability. Polypropylene remains widely used due to its durability, heat resistance, and versatility, but faces challenges from growing consumer preference for eco-friendly materials and stricter environmental policies. Advances in bioplastic technology and improved production scalability are expected to drive a gradual market shift toward biodegradable options, while polypropylene manufacturers invest in recycling innovations to maintain relevance in the evolving food container industry.
Infographic: Biodegradable plastic vs Polypropylene for Food container
 azmater.com
azmater.com