Polyethylene terephthalate (PET) offers superior clarity, chemical resistance, and recyclability compared to Polyvinyl chloride (PVC) in food packaging applications. PET ensures safer food contact due to lower risk of harmful leachates, making it the preferred choice for sustainable and health-conscious packaging solutions.
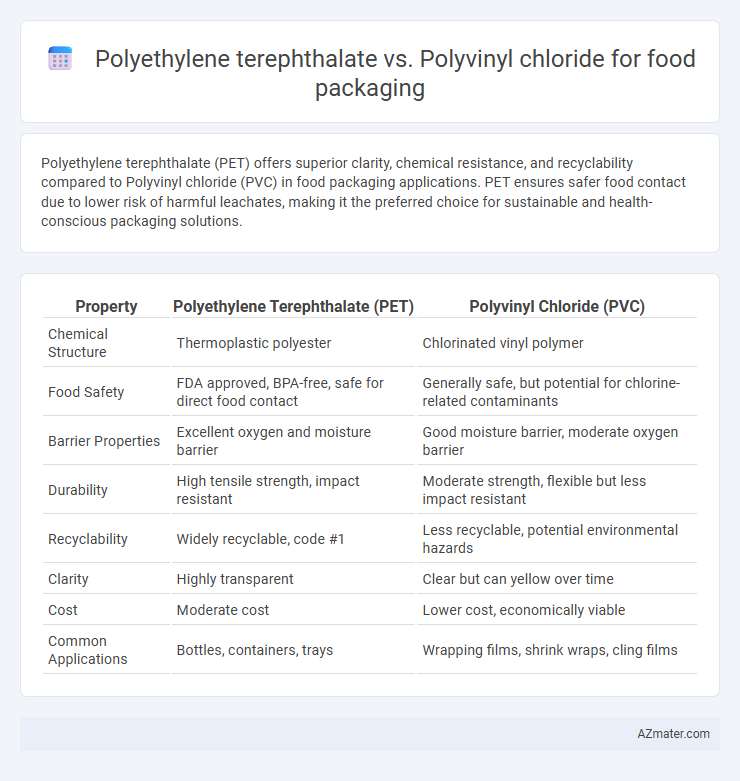
Table of Comparison
| Property | Polyethylene Terephthalate (PET) | Polyvinyl Chloride (PVC) |
|---|---|---|
| Chemical Structure | Thermoplastic polyester | Chlorinated vinyl polymer |
| Food Safety | FDA approved, BPA-free, safe for direct food contact | Generally safe, but potential for chlorine-related contaminants |
| Barrier Properties | Excellent oxygen and moisture barrier | Good moisture barrier, moderate oxygen barrier |
| Durability | High tensile strength, impact resistant | Moderate strength, flexible but less impact resistant |
| Recyclability | Widely recyclable, code #1 | Less recyclable, potential environmental hazards |
| Clarity | Highly transparent | Clear but can yellow over time |
| Cost | Moderate cost | Lower cost, economically viable |
| Common Applications | Bottles, containers, trays | Wrapping films, shrink wraps, cling films |
Introduction to Food Packaging Materials
Polyethylene terephthalate (PET) and polyvinyl chloride (PVC) are widely used polymers in food packaging due to their distinct properties. PET offers excellent clarity, high strength, and superior barrier properties against moisture and oxygen, making it ideal for beverages and perishable foods. PVC provides good chemical resistance and flexibility but has limitations related to potential plasticizer migration and lower transparency compared to PET.
Overview of Polyethylene Terephthalate (PET)
Polyethylene terephthalate (PET) is a thermoplastic polymer widely used in food packaging due to its excellent strength, clarity, and barrier properties against moisture and oxygen, which help extend shelf life. PET is lightweight, recyclable, and resistant to impact and chemicals, making it ideal for packaging beverages, salads, and ready-to-eat foods. Compared to polyvinyl chloride (PVC), PET offers superior safety and environmental benefits, as PVC contains chlorine and can release harmful additives during disposal or recycling.
Overview of Polyvinyl Chloride (PVC)
Polyvinyl chloride (PVC) is a widely used plastic in food packaging due to its excellent clarity, chemical resistance, and flexibility. PVC offers strong barrier properties against moisture and gases, enhancing the shelf life of perishable products. However, concerns about potential plasticizer migration and environmental impact have led to increased scrutiny compared to polyethylene terephthalate (PET).
Mechanical Properties Comparison: PET vs PVC
Polyethylene terephthalate (PET) exhibits superior tensile strength and stiffness compared to polyvinyl chloride (PVC), making it more resistant to deformation under mechanical stress in food packaging applications. PET's higher impact resistance and better elongation at break provide enhanced durability and flexibility, crucial for protecting food products during handling and transportation. In contrast, PVC offers greater hardness but lower flexibility, which can limit its effectiveness in packaging applications requiring significant mechanical resilience.
Barrier Properties: Oxygen and Moisture Protection
Polyethylene terephthalate (PET) exhibits superior oxygen barrier properties compared to polyvinyl chloride (PVC), making it more effective at preserving food freshness and extending shelf life. PET also offers excellent moisture resistance, preventing water vapor transmission that can compromise product quality. PVC, while commonly used, generally allows higher oxygen and moisture permeability, limiting its suitability for sensitive food packaging applications.
Safety and Food Contact Compliance
Polyethylene terephthalate (PET) is widely preferred for food packaging due to its excellent clarity, strong barrier properties, and compliance with FDA and EU food contact regulations, ensuring minimal risk of chemical migration into food products. Polyvinyl chloride (PVC) poses greater safety concerns, as it can release harmful additives, including phthalates and vinyl chloride monomers, which have been linked to health risks and stricter regulatory restrictions for food contact materials. Choosing PET over PVC enhances food safety by reducing potential contamination and meeting stringent global standards for direct food contact applications.
Environmental Impact: Recyclability and Sustainability
Polyethylene terephthalate (PET) offers superior recyclability in food packaging due to well-established recycling streams and high demand for recycled content, reducing overall environmental impact. Polyvinyl chloride (PVC) presents challenges in sustainability because of limited recycling options and the release of harmful chemicals during production and disposal. PET's lower carbon footprint and better compatibility with circular economy principles make it a more environmentally sustainable choice for food packaging.
Cost Effectiveness and Market Availability
Polyethylene terephthalate (PET) offers higher cost-effectiveness in food packaging due to its recyclability and lower production costs compared to polyvinyl chloride (PVC), which involves more expensive additives and environmental compliance expenses. PET dominates market availability with extensive global manufacturing infrastructure and widespread consumer acceptance, whereas PVC faces restricted use because of health concerns and regulatory limitations. The economic advantages and robust supply chain positioning PET as the preferred material in the food packaging industry.
Common Applications in Food Packaging
Polyethylene terephthalate (PET) is widely used for carbonated beverage bottles, salad trays, and microwaveable food containers due to its strength, clarity, and excellent barrier properties against moisture and gases. Polyvinyl chloride (PVC) is commonly found in cling films, meat packaging, and juice cartons because of its flexibility, durability, and resistance to oils and fats. Both materials play critical roles in food packaging, with PET favored for its recyclability and safety, while PVC is preferred for applications requiring high transparency and formability.
Choosing the Right Material: PET or PVC?
Polyethylene terephthalate (PET) offers superior clarity, higher resistance to impact, and better gas barrier properties, making it ideal for packaging carbonated drinks and perishable foods. Polyvinyl chloride (PVC) is commonly used for its excellent chemical resistance and flexibility but poses concerns regarding potential chemical leaching and lower environmental sustainability. Choosing PET over PVC for food packaging improves safety, recyclability, and consumer appeal while ensuring product freshness and shelf life.
Infographic: Polyethylene terephthalate vs Polyvinyl chloride for Food Packaging
 azmater.com
azmater.com