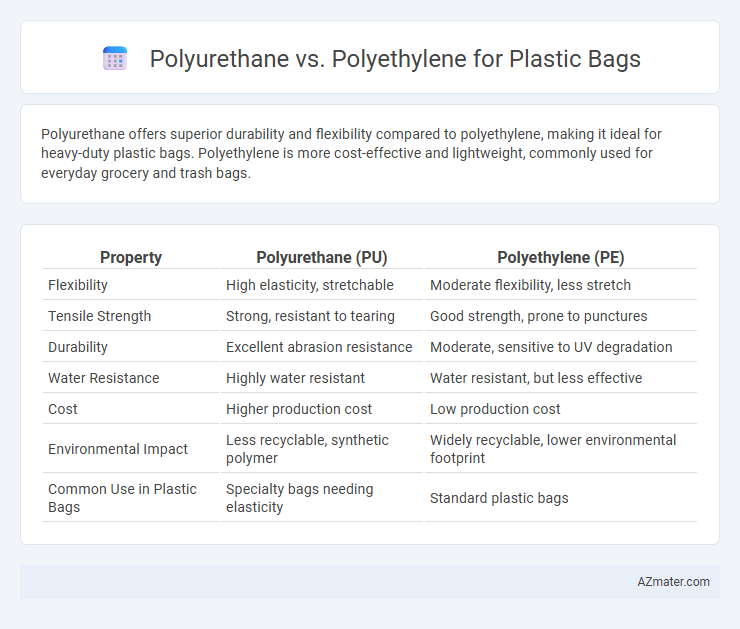
Polyurethane offers superior durability and flexibility compared to polyethylene, making it ideal for heavy-duty plastic bags. Polyethylene is more cost-effective and lightweight, commonly used for everyday grocery and trash bags.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Polyurethane (PU) | Polyethylene (PE) |
|---|---|---|
| Flexibility | High elasticity, stretchable | Moderate flexibility, less stretch |
| Tensile Strength | Strong, resistant to tearing | Good strength, prone to punctures |
| Durability | Excellent abrasion resistance | Moderate, sensitive to UV degradation |
| Water Resistance | Highly water resistant | Water resistant, but less effective |
| Cost | Higher production cost | Low production cost |
| Environmental Impact | Less recyclable, synthetic polymer | Widely recyclable, lower environmental footprint |
| Common Use in Plastic Bags | Specialty bags needing elasticity | Standard plastic bags |
Introduction to Polyurethane and Polyethylene
Polyurethane is a versatile polymer known for its elasticity, durability, and resistance to abrasion, making it suitable for flexible plastic bags requiring strength and stretchability. Polyethylene, the most commonly used plastic for bags, is characterized by its lightweight nature, chemical resistance, and cost-effectiveness, with variations like high-density polyethylene (HDPE) and low-density polyethylene (LDPE) offering different levels of toughness and flexibility. Understanding the material properties of polyurethane and polyethylene is crucial for selecting the right plastic bag type based on performance requirements and environmental impact.
Chemical Structure Differences
Polyurethane is composed of repeating urethane linkages formed by the reaction between diisocyanates and polyols, resulting in a polymer with segmented hard and soft regions that provide elasticity and durability. Polyethylene consists of long chains of ethylene monomers linked by strong carbon-carbon single bonds, creating a simple, non-polar hydrocarbon polymer known for its chemical resistance and flexibility. The fundamental chemical structure difference lies in polyurethane's heteroatoms and urethane groups that enable diverse mechanical properties, whereas polyethylene's uniform hydrocarbon backbone yields inertness and cost-effective production for plastic bags.
Physical Properties Comparison
Polyurethane (PU) exhibits superior elasticity and abrasion resistance compared to polyethylene (PE), making it more durable for plastic bag applications requiring flexibility and wear tolerance. Polyethylene offers higher moisture resistance and chemical inertness, which benefits plastic bags used for packaging food and liquids. Both materials vary in tensile strength, with polyurethane typically showing enhanced toughness, while polyethylene is favored for lightweight and cost-effective solutions.
Durability and Strength
Polyurethane plastic bags exhibit superior durability and strength compared to polyethylene bags, offering enhanced resistance to tears, punctures, and abrasion. Polyurethane's elasticity provides better performance under tension and repeated use, making it ideal for heavy-duty applications. Polyethylene bags, while cost-effective and moisture-resistant, generally lack the tensile strength and durability required for high-stress environments.
Environmental Impact and Biodegradability
Polyurethane and polyethylene differ significantly in environmental impact and biodegradability when used for plastic bags. Polyethylene, commonly used in single-use bags, is derived from fossil fuels and is not biodegradable, contributing to long-lasting plastic pollution. Polyurethane offers potential advantages in durability and recyclability, but its environmental footprint depends on formulation, and it generally lacks rapid biodegradability compared to emerging bioplastics designed for eco-friendly disposal.
Common Applications of Polyurethane Bags
Polyurethane bags are widely used in applications requiring flexibility, durability, and waterproof properties, such as protective covers, medical packaging, and reusable shopping bags. Their elasticity and resistance to abrasion make them ideal for heavy-duty storage and transportation of goods sensitive to moisture and impact. Compared to polyethylene, polyurethane bags provide superior strength and comfort, especially in environments demanding extended use and high tensile resistance.
Common Applications of Polyethylene Bags
Polyethylene bags are widely used in packaging, grocery stores, and food storage due to their durability, flexibility, and moisture resistance. These bags come in various forms, including high-density polyethylene (HDPE) and low-density polyethylene (LDPE), each suited for specific tasks such as heavy-duty shipping or lightweight produce bags. Their cost-effectiveness and recyclability make them the preferred choice over polyurethane for everyday plastic bag applications.
Cost Considerations
Polyethylene plastic bags are significantly more cost-effective compared to polyurethane, with prices typically ranging from $0.02 to $0.10 per unit, depending on thickness and size. Polyurethane bags, while offering superior elasticity and durability, often cost up to three to four times more, making them less suitable for budget-sensitive applications. Manufacturing processes and material availability heavily influence these cost disparities, positioning polyethylene as the preferred choice for large-scale, low-cost plastic bag production.
Safety and Regulatory Compliance
Polyurethane and polyethylene plastic bags differ significantly in safety and regulatory compliance; polyethylene is widely accepted for food contact applications due to its inert nature and certification by agencies such as the FDA and EFSA. Polyurethane, while versatile, often contains additives and residual monomers that require careful evaluation to meet safety standards, limiting its use in direct food contact without specific regulatory approvals. Both materials must comply with regional regulations like REACH and RoHS, but polyethylene's established safety profile makes it the preferred choice for consumer safety and regulatory adherence in plastic bag manufacturing.
Choosing the Right Material for Your Plastic Bags
Polyethylene is the most common material for plastic bags due to its cost-effectiveness, flexibility, and moisture resistance, making it ideal for everyday carry and grocery bags. Polyurethane offers superior durability, elasticity, and tear resistance, suitable for heavy-duty applications requiring stretch and resilience. Choosing between polyurethane and polyethylene depends on the bag's intended use, with polyethylene preferred for lightweight convenience and polyurethane chosen for strength and longevity.
Infographic: Polyurethane vs Polyethylene for Plastic Bag
 azmater.com
azmater.com