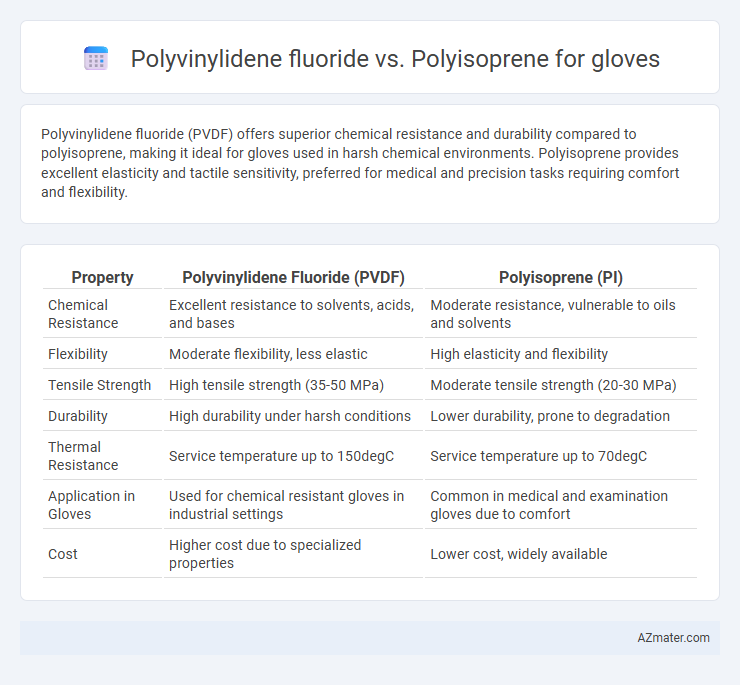
Polyvinylidene fluoride (PVDF) offers superior chemical resistance and durability compared to polyisoprene, making it ideal for gloves used in harsh chemical environments. Polyisoprene provides excellent elasticity and tactile sensitivity, preferred for medical and precision tasks requiring comfort and flexibility.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Polyvinylidene Fluoride (PVDF) | Polyisoprene (PI) |
|---|---|---|
| Chemical Resistance | Excellent resistance to solvents, acids, and bases | Moderate resistance, vulnerable to oils and solvents |
| Flexibility | Moderate flexibility, less elastic | High elasticity and flexibility |
| Tensile Strength | High tensile strength (35-50 MPa) | Moderate tensile strength (20-30 MPa) |
| Durability | High durability under harsh conditions | Lower durability, prone to degradation |
| Thermal Resistance | Service temperature up to 150degC | Service temperature up to 70degC |
| Application in Gloves | Used for chemical resistant gloves in industrial settings | Common in medical and examination gloves due to comfort |
| Cost | Higher cost due to specialized properties | Lower cost, widely available |
Introduction to Glove Materials: Polyvinylidene Fluoride vs Polyisoprene
Polyvinylidene fluoride (PVDF) gloves offer superior chemical resistance and durability, making them ideal for handling aggressive solvents and hazardous materials. Polyisoprene gloves provide excellent elasticity, comfort, and tactile sensitivity, closely mimicking natural rubber but without latex allergens. Selecting between PVDF and polyisoprene depends on specific application requirements such as chemical exposure, flexibility, and user sensitivity.
Chemical Composition and Structure Comparison
Polyvinylidene fluoride (PVDF) gloves consist of a semi-crystalline polymer featuring repeating vinylidene fluoride units (-CH2-CF2-) characterized by strong carbon-fluorine bonds, providing exceptional chemical resistance and thermal stability. In contrast, polyisoprene gloves are made from a natural or synthetic polymer composed of repeating isoprene units (-C5H8-) with cis-1,4 double bonds, resulting in high elasticity and flexibility but lower chemical resistance. The unique fluorinated backbone of PVDF grants superior durability against solvents and acids compared to the hydrocarbon-based, unsaturated structure of polyisoprene, which is more prone to chemical degradation.
Mechanical Strength and Durability Differences
Polyvinylidene fluoride (PVDF) gloves exhibit superior mechanical strength and chemical resistance compared to polyisoprene gloves, making them more durable in harsh environments. PVDF's high tensile strength and resistance to abrasion and tears enable prolonged usage in industrial settings, while polyisoprene offers excellent elasticity and comfort but lower overall durability under mechanical stress. The choice between PVDF and polyisoprene gloves should consider the specific application demands, prioritizing PVDF for heavy-duty protection and polyisoprene for flexible, delicate tasks.
Barrier Protection: Chemical and Biological Resistance
Polyvinylidene fluoride (PVDF) gloves offer superior chemical resistance, effectively shielding against strong acids, bases, and organic solvents, making them ideal for harsh chemical environments. Polyisoprene gloves provide excellent biological barrier protection with high elasticity and comfort, frequently used in medical settings for protection against bacteria and viruses. PVDF gloves outperform in aggressive chemical exposure, whereas polyisoprene excels in biological resistance and tactile sensitivity.
Comfort, Fit, and Tactile Sensitivity
Polyvinylidene fluoride (PVDF) gloves offer excellent chemical resistance but tend to be less flexible, impacting comfort and fit during prolonged use. Polyisoprene gloves provide superior elasticity and conform better to hand contours, enhancing comfort, fit, and tactile sensitivity essential for precision tasks. The softer texture and higher elasticity of polyisoprene significantly improve dexterity compared to the stiffer, more rigid PVDF material.
Allergenicity and Skin Compatibility
Polyvinylidene fluoride (PVDF) gloves offer superior chemical resistance and lower allergenicity compared to polyisoprene gloves, making them suitable for individuals with sensitive skin or latex allergies. Polyisoprene, while providing excellent elasticity and comfort similar to natural rubber, may still trigger allergic reactions in some users due to residual proteins. The non-latex composition of PVDF gloves reduces the risk of Type I hypersensitivity, enhancing skin compatibility for prolonged use in medical and industrial applications.
Applications in Healthcare and Laboratory Settings
Polyvinylidene fluoride (PVDF) gloves offer excellent chemical resistance and durability, making them ideal for handling aggressive solvents and acids in laboratory environments, while their strong barrier properties help prevent contamination in healthcare settings. Polyisoprene gloves provide superior elasticity, comfort, and tactile sensitivity, favored in medical examinations and surgical procedures where dexterity is crucial. Healthcare professionals and laboratory technicians select PVDF for protection during chemical exposure and Polyisoprene for tasks requiring flexibility and high sensitivity.
Cost-Effectiveness and Availability
Polyvinylidene fluoride (PVDF) gloves offer superior chemical resistance and durability but come at a higher cost compared to polyisoprene gloves, which are more affordable and widely available. Polyisoprene gloves provide excellent elasticity and comfort, making them a cost-effective choice for general use, while PVDF gloves are preferable in environments requiring enhanced protection despite limited availability. The balance between cost-effectiveness and availability positions polyisoprene as the more practical option for everyday applications, whereas PVDF suits specialized industrial settings.
Environmental Impact and Disposal Considerations
Polyvinylidene fluoride (PVDF) gloves exhibit higher chemical resistance and durability but pose significant environmental challenges due to their non-biodegradable nature and difficulty in recycling. Polyisoprene gloves, being a natural rubber derivative, offer superior biodegradability and lower ecological footprint, making them more environmentally friendly upon disposal. The disposal of PVDF gloves requires specialized waste management to mitigate long-term pollution, whereas polyisoprene gloves can degrade more readily in composting or landfill settings, reducing their environmental impact.
Choosing the Right Glove: Key Factors to Consider
Polyvinylidene fluoride (PVDF) gloves offer superior chemical resistance and durability, making them ideal for handling aggressive solvents and acids, whereas Polyisoprene gloves provide excellent elasticity, comfort, and tactile sensitivity, suitable for medical and laboratory use. Key factors to consider when choosing between PVDF and Polyisoprene gloves include the type of exposure, required barrier protection, and user dexterity needs. Evaluating chemical compatibility charts and examining glove thickness and fit are essential to ensure optimal safety and performance for specific applications.
Infographic: Polyvinylidene fluoride vs Polyisoprene for Glove
 azmater.com
azmater.com