Liquid crystal polymer (LCP) offers superior thermal stability, chemical resistance, and mechanical strength compared to polyvinyl chloride (PVC) for wire insulation. LCP's low dielectric constant and moisture resistance make it ideal for high-performance and high-frequency electrical applications, whereas PVC is more cost-effective but less durable in harsh environments.
Table of Comparison
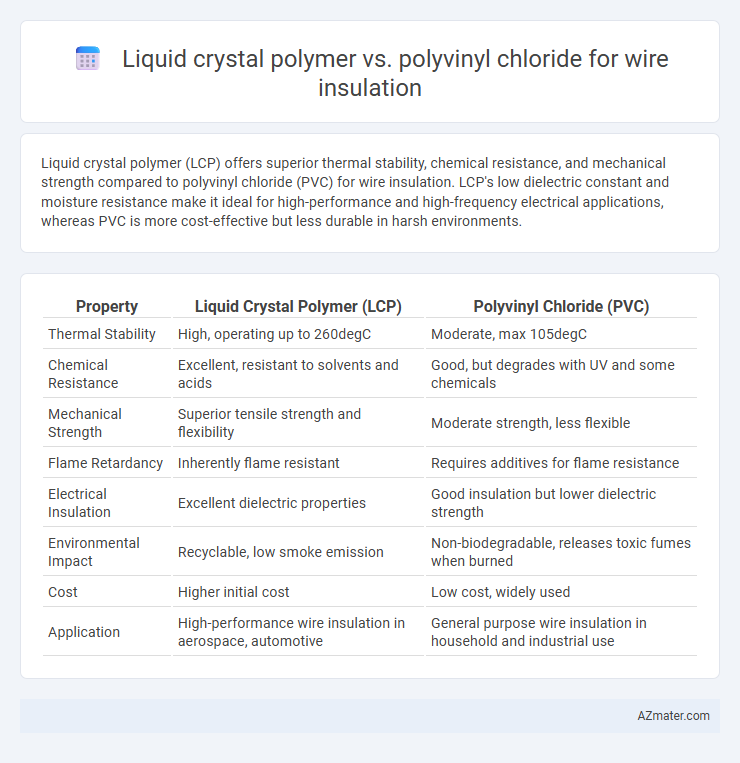
| Property | Liquid Crystal Polymer (LCP) | Polyvinyl Chloride (PVC) |
|---|---|---|
| Thermal Stability | High, operating up to 260degC | Moderate, max 105degC |
| Chemical Resistance | Excellent, resistant to solvents and acids | Good, but degrades with UV and some chemicals |
| Mechanical Strength | Superior tensile strength and flexibility | Moderate strength, less flexible |
| Flame Retardancy | Inherently flame resistant | Requires additives for flame resistance |
| Electrical Insulation | Excellent dielectric properties | Good insulation but lower dielectric strength |
| Environmental Impact | Recyclable, low smoke emission | Non-biodegradable, releases toxic fumes when burned |
| Cost | Higher initial cost | Low cost, widely used |
| Application | High-performance wire insulation in aerospace, automotive | General purpose wire insulation in household and industrial use |
Introduction to Wire Insulation Materials
Liquid crystal polymer (LCP) and polyvinyl chloride (PVC) serve distinct roles in wire insulation due to their unique material properties. LCP offers superior thermal stability, chemical resistance, and mechanical strength, making it ideal for high-performance or high-temperature applications. PVC is favored for its flexibility, cost-effectiveness, and flame retardant characteristics, widely used in standard electrical wiring and general consumer electronics.
Overview: Liquid Crystal Polymer (LCP)
Liquid Crystal Polymer (LCP) offers superior thermal stability, high mechanical strength, and excellent chemical resistance compared to Polyvinyl Chloride (PVC) for wire insulation, making it ideal for high-performance and high-temperature applications. LCP exhibits low dielectric constant and low dielectric loss, enhancing signal integrity in high-frequency electronic wiring systems. Its resistance to flame and environmental degradation surpasses PVC, contributing to longer service life and increased safety in demanding industrial and aerospace environments.
Overview: Polyvinyl Chloride (PVC)
Polyvinyl chloride (PVC) is a widely used thermoplastic polymer for wire insulation known for its excellent electrical insulation properties, chemical resistance, and cost-effectiveness. PVC offers good flexibility and flame retardancy, making it suitable for a variety of residential, commercial, and industrial wiring applications. Compared to liquid crystal polymer (LCP), PVC has lower thermal stability and mechanical strength but remains a popular choice due to its ease of processing and versatility.
Electrical Performance Comparison
Liquid crystal polymer (LCP) exhibits superior electrical insulation properties compared to polyvinyl chloride (PVC), including higher dielectric strength and lower dielectric constant, which reduces signal loss and electromagnetic interference in wire applications. LCP's excellent thermal stability ensures consistent electrical performance under high temperature conditions, whereas PVC tends to degrade and lose insulating capability over time when exposed to heat. The enhanced electrical reliability of LCP makes it ideal for high-frequency, high-performance wiring in aerospace, automotive, and electronic industries where durability and minimal electrical resistance are critical.
Thermal Resistance and Heat Tolerance
Liquid crystal polymer (LCP) exhibits superior thermal resistance compared to polyvinyl chloride (PVC), with LCP sustaining continuous use temperatures above 260degC, whereas PVC typically degrades beyond 105degC. LCP's molecular arrangement provides excellent heat tolerance and dimensional stability under extreme thermal stress, making it ideal for high-performance wire insulation in demanding environments. In contrast, PVC's lower heat tolerance and risk of thermal degradation limit its application in high-temperature scenarios.
Mechanical Strength and Durability
Liquid crystal polymer (LCP) exhibits superior mechanical strength and durability compared to polyvinyl chloride (PVC) when used for wire insulation, due to its high tensile strength and excellent resistance to abrasion and deformation under stress. LCP maintains its structural integrity and performance in extreme temperatures and harsh chemical environments, whereas PVC tends to degrade, crack, and lose flexibility over time. This makes LCP ideal for high-performance applications requiring long-lasting, robust insulation in demanding electrical and industrial settings.
Chemical and Environmental Resistance
Liquid crystal polymer (LCP) exhibits superior chemical resistance compared to polyvinyl chloride (PVC), with exceptional stability against acids, bases, and solvents, making it ideal for harsh industrial environments. LCP also offers enhanced environmental resistance, including high thermal stability and resistance to UV degradation, which extends the lifespan of wire insulation under extreme conditions. PVC, while cost-effective and flexible, tends to degrade more rapidly when exposed to chemicals and UV radiation, leading to brittleness and potential insulation failure.
Flexibility and Processability in Manufacturing
Liquid crystal polymer (LCP) offers superior flexibility compared to polyvinyl chloride (PVC), enabling better performance in dynamic applications such as flexible cables and connectors. LCP's high thermal stability and low melt viscosity provide excellent processability in extrusion and injection molding, facilitating precise and consistent insulation layers. In contrast, PVC, while easier to process at lower temperatures and more cost-effective, tends to be less flexible and can become brittle under thermal stress, limiting its effectiveness in high-flexibility wire insulation applications.
Cost Analysis: LCP vs PVC
Liquid crystal polymer (LCP) wire insulation typically incurs higher upfront material costs compared to polyvinyl chloride (PVC) due to its advanced performance properties and thermal stability. However, LCP offers long-term cost benefits by reducing maintenance, enhancing durability, and allowing for thinner insulation layers that decrease overall weight and material usage. In contrast, PVC remains cost-effective for low-performance applications but may lead to higher replacement and environmental disposal expenses over time.
Application Suitability and Industry Trends
Liquid crystal polymer (LCP) offers superior thermal stability, chemical resistance, and dimensional stability compared to polyvinyl chloride (PVC), making it highly suitable for high-performance wire insulation in aerospace, automotive, and electronics industries. PVC remains widely used for general-purpose wire insulation due to its cost-effectiveness, flame retardancy, and flexibility, dominating applications in residential wiring and consumer electronics. Industry trends show increasing adoption of LCP in advanced electronics and automotive sectors driven by demand for miniaturization, higher operating temperatures, and improved reliability, while PVC maintains a strong presence in cost-sensitive, mass-market applications.
Infographic: Liquid crystal polymer vs Polyvinyl chloride for Wire insulation
 azmater.com
azmater.com