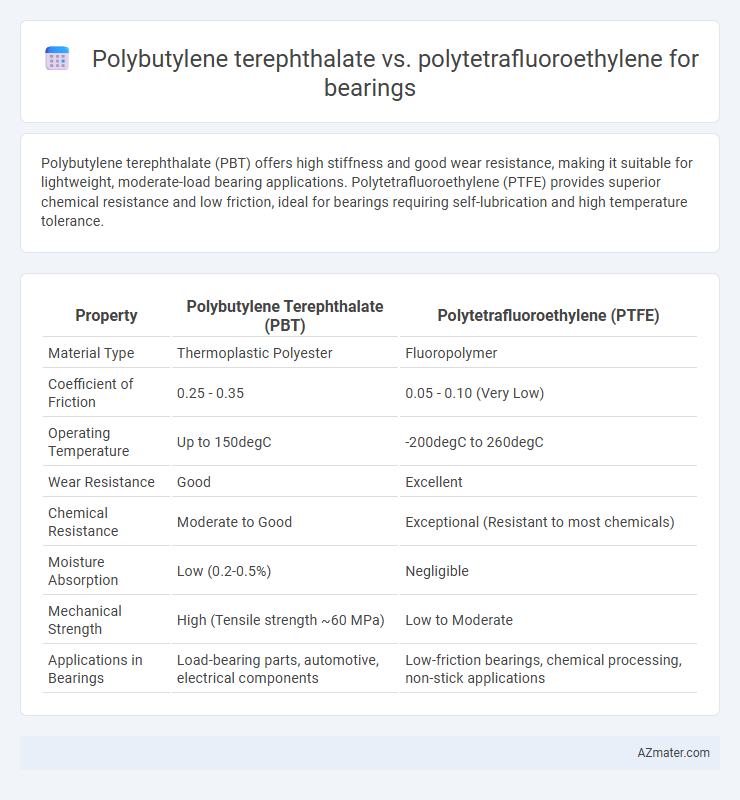
Polybutylene terephthalate (PBT) offers high stiffness and good wear resistance, making it suitable for lightweight, moderate-load bearing applications. Polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE) provides superior chemical resistance and low friction, ideal for bearings requiring self-lubrication and high temperature tolerance.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Polybutylene Terephthalate (PBT) | Polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE) |
|---|---|---|
| Material Type | Thermoplastic Polyester | Fluoropolymer |
| Coefficient of Friction | 0.25 - 0.35 | 0.05 - 0.10 (Very Low) |
| Operating Temperature | Up to 150degC | -200degC to 260degC |
| Wear Resistance | Good | Excellent |
| Chemical Resistance | Moderate to Good | Exceptional (Resistant to most chemicals) |
| Moisture Absorption | Low (0.2-0.5%) | Negligible |
| Mechanical Strength | High (Tensile strength ~60 MPa) | Low to Moderate |
| Applications in Bearings | Load-bearing parts, automotive, electrical components | Low-friction bearings, chemical processing, non-stick applications |
Introduction to Polybutylene Terephthalate and Polytetrafluoroethylene
Polybutylene terephthalate (PBT) is a semi-crystalline thermoplastic polyester known for its high mechanical strength, excellent dimensional stability, and resistance to abrasion, making it suitable for bearings in moderate-load applications. Polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE), a fluoropolymer with an extremely low coefficient of friction and excellent chemical resistance, is commonly used in bearings where lubrication is minimal or absent. The choice between PBT and PTFE for bearing applications depends on factors like load capacity, environmental exposure, and required frictional properties.
Material Properties Comparison: PBT vs PTFE
Polybutylene terephthalate (PBT) offers high mechanical strength, good dimensional stability, and excellent wear resistance, making it suitable for bearings requiring rigidity and durability under moderate loads. Polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE) exhibits superior chemical resistance, extremely low friction coefficient, and excellent self-lubricating properties, ideal for applications where minimal friction and high corrosion resistance are critical. The choice between PBT and PTFE for bearings depends on load capacity, operating temperature range, and environmental exposure to ensure optimal performance and longevity.
Mechanical Strength and Durability
Polybutylene terephthalate (PBT) offers high mechanical strength with excellent dimensional stability and good impact resistance, making it suitable for bearing applications requiring stiffness and wear resistance. Polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE) exhibits superior chemical resistance and very low friction coefficient but has lower mechanical strength and is prone to cold flow under sustained loads, reducing its durability in high-stress bearing environments. PBT's enhanced load-bearing capacity and resistance to deformation generally provide longer service life in mechanical bearings compared to PTFE, which excels in low-friction applications where chemical inertness is critical.
Friction and Wear Performance in Bearings
Polybutylene terephthalate (PBT) exhibits moderate friction and wear performance in bearings, offering good dimensional stability and resistance to wear under typical load conditions. Polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE) provides significantly lower friction coefficients compared to PBT, enhancing self-lubricating properties and reducing wear in high-speed or low-load bearing applications. PTFE's superior chemical resistance and minimal adhesive wear make it preferable where reduced maintenance and extended bearing life are critical.
Chemical Resistance and Environmental Stability
Polybutylene terephthalate (PBT) offers good chemical resistance against oils, greases, and solvents but is susceptible to hydrolysis and degradation in harsh acidic or alkaline environments. Polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE) excels with exceptional chemical resistance across a broad spectrum, including strong acids and bases, maintaining stability in extreme temperatures and aggressive chemicals. PTFE's superior environmental stability and low friction make it more suitable than PBT for bearings exposed to corrosive chemicals and demanding operational conditions.
Thermal Stability and Operating Temperature Range
Polybutylene terephthalate (PBT) offers good thermal stability with an operating temperature range typically between -40degC to 150degC, making it suitable for moderate heat applications in bearings. Polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE) exhibits superior thermal stability and can operate continuously from -200degC up to 260degC, providing excellent performance in extreme temperature conditions. PTFE's high melting point and chemical inertness make it ideal for bearings requiring resistance to thermal degradation and harsh environments.
Ease of Machining and Fabrication
Polybutylene terephthalate (PBT) offers superior ease of machining due to its thermoplastic nature, allowing for precision cutting, drilling, and shaping with conventional tools, resulting in cost-effective fabrication and reduced lead times. Polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE), while chemically resistant and low-friction, presents challenges in machining because of its high ductility and tendency to deform under cutting forces, requiring specialized equipment and slower processing speeds. The dimensional stability of PBT during fabrication generally surpasses PTFE, making PBT a preferred choice for bearing components requiring tight tolerances and complex geometries.
Cost Analysis: PBT vs PTFE Bearings
Polybutylene terephthalate (PBT) bearings typically offer a lower upfront cost compared to polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE) bearings due to cheaper raw materials and simpler manufacturing processes. PTFE bearings, renowned for superior chemical resistance and low friction, carry higher expenses that reflect their enhanced performance in demanding applications. Cost analysis must balance PBT's economic advantage against PTFE's durability and reduced maintenance over the bearing lifecycle.
Common Applications in Bearing Design
Polybutylene terephthalate (PBT) is frequently used in bearing design for its excellent dimensional stability, low friction, and resistance to wear, making it ideal for applications requiring precision and durability, such as automotive and electrical components. Polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE) is preferred in bearing applications where extremely low friction and chemical resistance are critical, commonly utilized in industrial machinery and high-temperature environments. The choice between PBT and PTFE hinges on the specific demands of the bearing application, with PBT favored for mechanical strength and PTFE for superior lubrication and chemical inertness.
Choosing the Right Material for Bearing Solutions
Polybutylene terephthalate (PBT) offers excellent mechanical strength, chemical resistance, and dimensional stability, making it suitable for low to moderate load bearing applications with precision requirements. Polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE), known for its exceptional low friction coefficient and high temperature resistance, excels in applications demanding self-lubrication and minimal wear under harsh chemical environments. Selecting the right bearing material depends on load conditions, operating temperature, chemical exposure, and the necessity for low friction versus structural strength, with PBT favored for rigidity and PTFE for lubrication performance.
Infographic: Polybutylene terephthalate vs Polytetrafluoroethylene for Bearing
 azmater.com
azmater.com