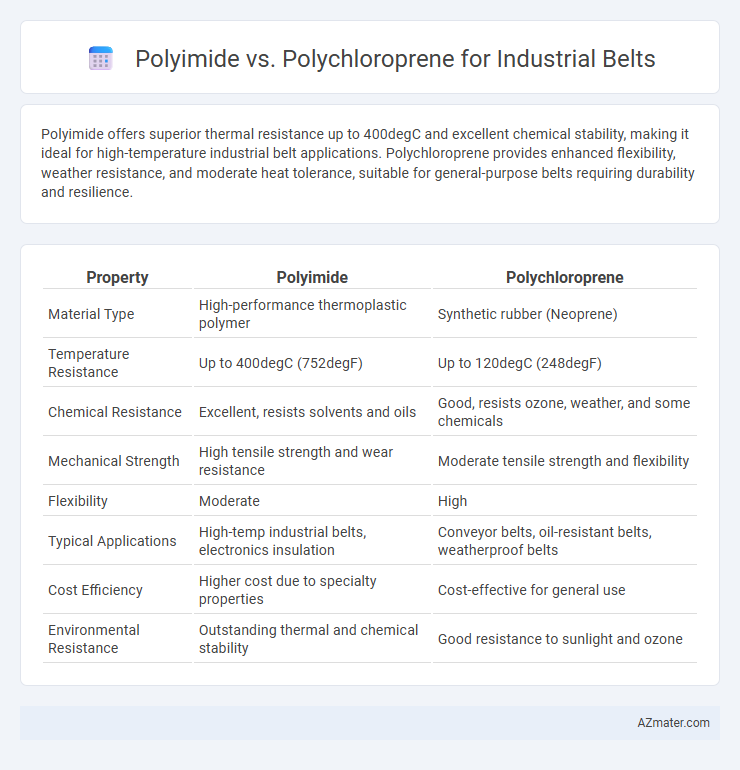
Polyimide offers superior thermal resistance up to 400degC and excellent chemical stability, making it ideal for high-temperature industrial belt applications. Polychloroprene provides enhanced flexibility, weather resistance, and moderate heat tolerance, suitable for general-purpose belts requiring durability and resilience.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Polyimide | Polychloroprene |
|---|---|---|
| Material Type | High-performance thermoplastic polymer | Synthetic rubber (Neoprene) |
| Temperature Resistance | Up to 400degC (752degF) | Up to 120degC (248degF) |
| Chemical Resistance | Excellent, resists solvents and oils | Good, resists ozone, weather, and some chemicals |
| Mechanical Strength | High tensile strength and wear resistance | Moderate tensile strength and flexibility |
| Flexibility | Moderate | High |
| Typical Applications | High-temp industrial belts, electronics insulation | Conveyor belts, oil-resistant belts, weatherproof belts |
| Cost Efficiency | Higher cost due to specialty properties | Cost-effective for general use |
| Environmental Resistance | Outstanding thermal and chemical stability | Good resistance to sunlight and ozone |
Introduction to Industrial Belt Materials
Polyimide Industrial Belts offer exceptional thermal stability, chemical resistance, and mechanical strength, making them ideal for high-temperature and precision applications in industries such as electronics and aerospace. Polychloroprene (Neoprene) Industrial Belts provide excellent abrasion resistance, flexibility, and moderate chemical resistance suitable for general-purpose conveyor and power transmission uses in manufacturing and automotive sectors. Selecting between polyimide and polychloroprene depends on specific operational conditions like temperature range, chemical exposure, and mechanical load requirements.
Overview of Polyimide Properties
Polyimide offers exceptional thermal stability, maintaining performance at temperatures up to 400degC, making it ideal for industrial belts exposed to high heat. Its chemical resistance to solvents, oils, and acids ensures durability in harsh environments, while excellent mechanical strength supports heavy-duty applications. Polyimide's low thermal expansion and electrical insulation properties further enhance its suitability for precision-driven industrial belt systems.
Polychloroprene: Key Features and Composition
Polychloroprene, commonly known as neoprene, is a synthetic rubber widely used in industrial belts for its excellent chemical stability and resistance to oils, heat, and weathering. Composed of chloroprene monomers, polychloroprene offers superior tensile strength, flexibility, and resilience compared to polyimide, making it ideal for heavy-duty applications requiring durability and abrasion resistance. Its inherent flame retardancy and resistance to degradation under harsh environmental conditions enhance its lifespan, ensuring consistent performance in industrial settings.
Mechanical Strength Comparison
Polyimide industrial belts exhibit superior mechanical strength with high tensile modulus and excellent resistance to abrasion, making them ideal for heavy-duty applications requiring durability under extreme conditions. Polychloroprene belts offer good elasticity and moderate tensile strength but tend to wear faster under continuous mechanical stress compared to polyimide. The enhanced thermal stability and fatigue resistance of polyimide belts provide a significant advantage in maintaining performance and extending service life in industrial machinery.
Heat and Chemical Resistance Analysis
Polyimide industrial belts exhibit superior heat resistance, maintaining structural integrity and performance at temperatures exceeding 300degC, compared to polychloroprene belts, which typically withstand up to 120degC. Chemically, polyimide resists a broad range of aggressive solvents, oils, and acids, making it ideal for harsh industrial environments, while polychloroprene offers moderate chemical resistance, effective primarily against oils and some refrigerants. The combination of high thermal stability and robust chemical resistance positions polyimide belts as the preferred choice for demanding applications involving extreme heat and exposure to corrosive substances.
Flexibility and Wear Performance
Polyimide industrial belts exhibit superior flexibility due to their high thermal stability and excellent mechanical properties, enabling them to perform well under demanding bending and flexing conditions. Polychloroprene belts offer good wear resistance with strong abrasion and chemical resistance, making them suitable for environments with moderate flexibility requirements. Compared to polychloroprene, polyimide belts provide enhanced wear performance in high-temperature and continuous flex applications, resulting in longer service life and reduced maintenance costs.
Application Suitability: Polyimide vs Polychloroprene
Polyimide belts excel in high-temperature environments and chemical resistance, making them ideal for precision industrial applications such as conveyor systems in electronics manufacturing and aerospace industries. Polychloroprene belts offer superior flexibility and resistance to oil, weathering, and abrasion, which suits heavy-duty conveyor operations in automotive and general manufacturing sectors. Choosing between polyimide and polychloroprene depends on the operational temperature, chemical exposure, and mechanical stress specific to the industrial application.
Cost and Availability Considerations
Polyimide industrial belts offer superior thermal stability and chemical resistance but come at a significantly higher cost and limited availability compared to polychloroprene belts. Polychloroprene, commonly known as neoprene, provides a more affordable and readily available option with good overall durability and flexibility for general industrial applications. Choosing between the two materials often depends on budget constraints and the specific environmental requirements of the operation.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
Polyimide industrial belts demonstrate superior environmental sustainability due to their high thermal stability and long lifecycle, which reduce the frequency of replacement and waste generation. Polychloroprene belts, while flexible and resistant to oil, pose greater environmental concerns because their production and disposal release chlorinated compounds that are harmful to ecosystems. Selecting polyimide belts supports greener manufacturing practices by minimizing volatile organic compound emissions and enhancing recyclability compared to polychloroprene alternatives.
Choosing the Right Material for Industrial Belts
Polyimide offers exceptional thermal stability, chemical resistance, and mechanical strength, making it ideal for high-temperature industrial belt applications requiring durability and precision. Polychloroprene, commonly known as neoprene, provides excellent flexibility, abrasion resistance, and good resistance to oils and weathering, suitable for general-purpose belts operating in moderate temperature environments. Selecting the right material depends on operational conditions, with polyimide preferred for extreme heat and chemical exposure, while polychloroprene fits well where elasticity and environmental resistance are priorities.
Infographic: Polyimide vs Polychloroprene for Industrial Belt
 azmater.com
azmater.com