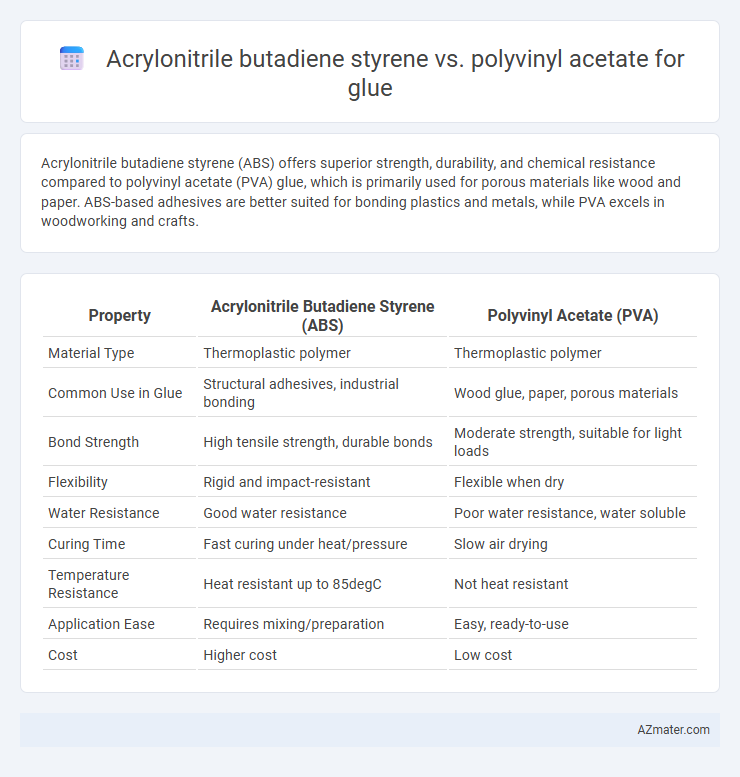
Acrylonitrile butadiene styrene (ABS) offers superior strength, durability, and chemical resistance compared to polyvinyl acetate (PVA) glue, which is primarily used for porous materials like wood and paper. ABS-based adhesives are better suited for bonding plastics and metals, while PVA excels in woodworking and crafts.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Acrylonitrile Butadiene Styrene (ABS) | Polyvinyl Acetate (PVA) |
|---|---|---|
| Material Type | Thermoplastic polymer | Thermoplastic polymer |
| Common Use in Glue | Structural adhesives, industrial bonding | Wood glue, paper, porous materials |
| Bond Strength | High tensile strength, durable bonds | Moderate strength, suitable for light loads |
| Flexibility | Rigid and impact-resistant | Flexible when dry |
| Water Resistance | Good water resistance | Poor water resistance, water soluble |
| Curing Time | Fast curing under heat/pressure | Slow air drying |
| Temperature Resistance | Heat resistant up to 85degC | Not heat resistant |
| Application Ease | Requires mixing/preparation | Easy, ready-to-use |
| Cost | Higher cost | Low cost |
Introduction to ABS and PVAc as Glue Options
Acrylonitrile butadiene styrene (ABS) offers strong adhesion, chemical resistance, and impact durability, making it ideal for bonding plastics and metal surfaces in industrial applications. Polyvinyl acetate (PVAc), commonly known as white glue, provides excellent adhesion for porous materials like wood, paper, and fabric, with easy water cleanup and fast drying times. While ABS glue is preferred for high-strength, abrasion-resistant bonds, PVAc remains popular for woodworking and crafts due to its flexibility and user-friendly application.
Chemical Composition: ABS vs PVAc
Acrylonitrile butadiene styrene (ABS) is a thermoplastic polymer composed of acrylonitrile, butadiene, and styrene monomers, offering high impact resistance and chemical stability. Polyvinyl acetate (PVAc) is a synthetic polymer derived from vinyl acetate monomers, primarily used in adhesives due to its strong bonding properties and flexibility. The chemical composition of ABS provides superior mechanical strength and durability, while PVAc excels in forming strong, flexible bonds ideal for wood and paper applications.
Adhesion Strength Comparison
Acrylonitrile butadiene styrene (ABS) exhibits significantly higher adhesion strength compared to polyvinyl acetate (PVA) when used as a glue, especially on non-porous surfaces like plastics and metals. ABS adhesive forms strong chemical bonds and offers excellent resistance to impact and temperature variations, whereas PVA glue primarily bonds well with porous materials such as wood and paper but lacks durability under stress. For applications requiring robust, long-lasting bonds, ABS-based adhesives outperform PVA by providing superior mechanical and environmental resilience.
Suitable Applications for ABS and PVAc Glues
Acrylonitrile butadiene styrene (ABS) glues exhibit strong adhesion, chemical resistance, and durability, making them ideal for bonding plastics in automotive, electronics, and household appliance assemblies. Polyvinyl acetate (PVAc) glues offer excellent adhesion to porous materials like wood, paper, and fabric, commonly used in woodworking, bookbinding, and general craft applications. ABS adhesives outperform PVAc in high-stress environments, while PVAc glues provide flexible, non-toxic bonding suitable for porous substrates.
Bonding Time and Curing Differences
Acrylonitrile butadiene styrene (ABS) glue offers faster bonding time and quicker curing, often solidifying within minutes, making it ideal for rapid assembly applications. In contrast, polyvinyl acetate (PVA) glue requires a longer bonding time, typically setting over several hours and reaching full cure in 24 hours, emphasizing durability over speed. The curing process of ABS adhesives relies on solvent evaporation and polymerization, while PVA adhesives cure through moisture evaporation and polymer cross-linking.
Water and Chemical Resistance
Acrylonitrile butadiene styrene (ABS) exhibits superior water and chemical resistance compared to polyvinyl acetate (PVA), making it more suitable for applications exposed to moisture or harsh chemicals. ABS maintains structural integrity and adhesion in wet environments, whereas PVA tends to degrade or lose bonding strength when exposed to water or solvents. The enhanced durability of ABS against water and chemical corrosion ensures longer-lasting adhesive performance in demanding conditions.
Temperature Tolerance and Durability
Acrylonitrile butadiene styrene (ABS) glue exhibits superior temperature tolerance, maintaining structural integrity in environments ranging from -20degC to 80degC, making it suitable for high-heat applications. Polyvinyl acetate (PVA) glue, however, has lower temperature resistance, typically softening above 40degC and degrading under extended heat exposure. In terms of durability, ABS adhesives offer enhanced resistance to impact and chemical exposure, whereas PVA glues are more prone to moisture damage and reduced long-term strength.
Safety and Environmental Impact
Acrylonitrile butadiene styrene (ABS) glue contains volatile organic compounds (VOCs) that pose inhalation hazards and contribute to air pollution, requiring adequate ventilation during use. Polyvinyl acetate (PVA) glue is water-based, non-toxic, and biodegradable, making it safer for indoor use and environmentally friendly. ABS adhesives have a higher environmental impact due to their petrochemical origin and difficulty in recycling, whereas PVA glues offer a more sustainable option with lower ecological footprint.
Cost and Availability Analysis
Acrylonitrile butadiene styrene (ABS) glue typically incurs higher costs due to its superior strength and durability, making it ideal for industrial applications, whereas polyvinyl acetate (PVA) glue is more economical and widely available for general-purpose use in woodworking and crafts. ABS adhesives often require specialized suppliers and have limited retail availability compared to PVA glue, which is mass-produced and accessible in most hardware stores worldwide. The cost-effectiveness and extensive distribution network of PVA glue make it the preferred choice for budget-conscious projects, while ABS glue's higher price reflects its enhanced mechanical properties and niche market presence.
Choosing the Right Glue: ABS or PVAc?
Acrylonitrile butadiene styrene (ABS) glue offers superior strength, chemical resistance, and durability, making it ideal for bonding plastics and materials exposed to stress or moisture. Polyvinyl acetate (PVAc) glue is best suited for porous materials like wood and paper due to its flexible, non-toxic, and easily sanded finish, but it lacks water resistance and bonding strength on plastics. Choosing the right glue depends on material compatibility and application requirements, with ABS glue preferred for synthetic materials and PVAc for woodworking and light crafts.
Infographic: Acrylonitrile butadiene styrene vs Polyvinyl acetate for Glue
 azmater.com
azmater.com