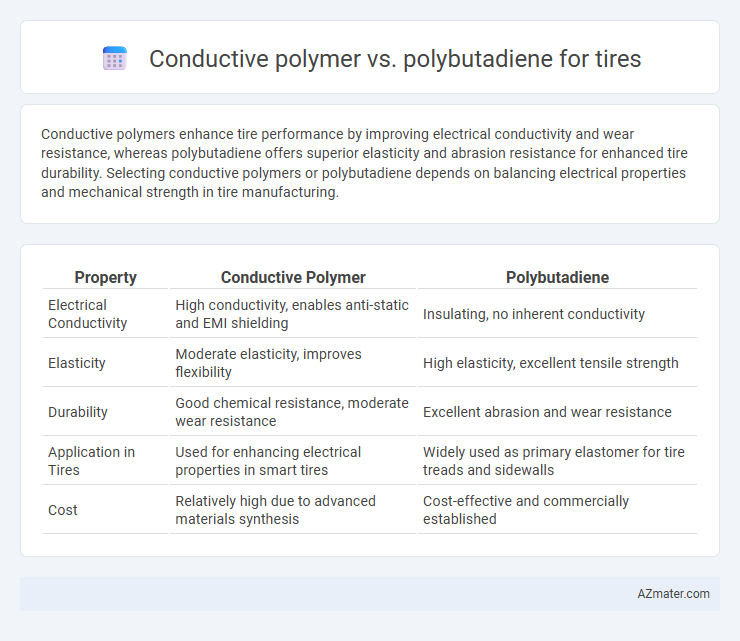
Conductive polymers enhance tire performance by improving electrical conductivity and wear resistance, whereas polybutadiene offers superior elasticity and abrasion resistance for enhanced tire durability. Selecting conductive polymers or polybutadiene depends on balancing electrical properties and mechanical strength in tire manufacturing.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Conductive Polymer | Polybutadiene |
|---|---|---|
| Electrical Conductivity | High conductivity, enables anti-static and EMI shielding | Insulating, no inherent conductivity |
| Elasticity | Moderate elasticity, improves flexibility | High elasticity, excellent tensile strength |
| Durability | Good chemical resistance, moderate wear resistance | Excellent abrasion and wear resistance |
| Application in Tires | Used for enhancing electrical properties in smart tires | Widely used as primary elastomer for tire treads and sidewalls |
| Cost | Relatively high due to advanced materials synthesis | Cost-effective and commercially established |
Introduction to Tire Materials
Conductive polymers offer enhanced electrical conductivity and durability, making them suitable for advanced tire applications that require improved wear resistance and static dissipation. Polybutadiene, a synthetic rubber known for its excellent abrasion resistance and low rolling resistance, remains a staple in tire manufacturing due to its superior elasticity and impact resilience. The integration of conductive polymers into tire compounds aims to combine the mechanical strength of polybutadiene with improved functional properties like conductivity and enhanced performance under diverse driving conditions.
Overview of Conductive Polymers
Conductive polymers, such as polyaniline and polypyrrole, are increasingly researched for tire applications due to their ability to enhance electrical conductivity and improve tire performance. Unlike polybutadiene, which primarily provides excellent wear resistance and elasticity, conductive polymers introduce anti-static and self-heating properties that can optimize traction and safety. These materials offer potential advancements in smart tire technology by enabling real-time monitoring of tire conditions and improving energy efficiency.
Understanding Polybutadiene
Polybutadiene is a synthetic rubber widely used in tire manufacturing due to its excellent wear resistance, high resilience, and low rolling resistance, which improve fuel efficiency and tire lifespan. Its molecular structure, characterized by a high cis-1,4 content, contributes to superior elasticity and impact strength compared to conductive polymers, which primarily focus on electrical conductivity rather than mechanical durability. The integration of polybutadiene in tire treads enhances traction and abrasion resistance, making it a preferred material for performance and long-lasting tires.
Electrical Properties: Conductivity Comparison
Conductive polymers exhibit significantly higher electrical conductivity compared to polybutadiene, making them ideal for applications requiring static dissipation and electromagnetic interference shielding in tires. Polybutadiene, a non-conductive elastomer, acts primarily as a high-performance rubber with excellent wear resistance and mechanical properties but lacks intrinsic conductivity. The contrast in electrical behavior underlines the suitability of conductive polymers for smart tire technologies, where real-time conductivity monitoring enhances safety and performance.
Durability and Wear Resistance
Conductive polymers in tires offer enhanced durability due to their ability to improve electrical conductivity and thermal stability, which reduces heat buildup and prolongs tire life. Polybutadiene, widely used in tire manufacturing, excels in wear resistance and abrasion performance, providing robust tread longevity under various driving conditions. Comparing both, polybutadiene's established rubber properties deliver superior wear resistance, while conductive polymers contribute to durability through improved heat dissipation and material stability.
Rolling Resistance and Fuel Efficiency
Conductive polymers in tires enhance electrical dissipation, reducing heat buildup and lowering rolling resistance compared to traditional polybutadiene compounds. Polybutadiene offers excellent wear resistance but generally contributes to higher rolling resistance, resulting in decreased fuel efficiency. Incorporating conductive polymers optimizes tire performance by improving energy conservation and extending vehicle range through reduced fuel consumption.
Traction and Performance on Roads
Conductive polymers enhance tire traction by improving electrical conductivity, which aids in dissipating static electricity and maintaining better contact with the road surface, especially in wet or slippery conditions. Polybutadiene, known for its high resilience and wear resistance, contributes significantly to tire performance by providing excellent grip and durability, particularly on dry roads. Tires combining conductive polymers and polybutadiene optimize road performance through balanced traction, improved handling, and increased lifespan under diverse driving conditions.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
Conductive polymers in tires enhance energy efficiency by improving electrical conductivity, which can reduce rolling resistance and lower fuel consumption, contributing to decreased greenhouse gas emissions. Polybutadiene, a synthetic rubber derived primarily from petroleum, presents environmental concerns due to its non-renewable origin and challenges in biodegradability. Implementing conductive polymers sourced from renewable materials offers a more sustainable alternative, promoting eco-friendly tire production while addressing the ecological footprint associated with traditional polybutadiene compounds.
Cost Considerations in Manufacturing
Conductive polymers generally incur higher manufacturing costs compared to polybutadiene due to the complexity of their synthesis and the need for specialized processing equipment. Polybutadiene offers a cost-effective solution with scalable production and lower raw material expenses, making it the preferred choice for large-scale tire manufacturing. Cost efficiency in polybutadiene also stems from its compatibility with existing tire production infrastructure, reducing the need for costly adjustments.
Future Trends in Tire Technology
Conductive polymers in tire manufacturing enhance electrical conductivity and improve durability, supporting the development of smart tires with integrated sensors for real-time performance monitoring. Polybutadiene remains essential for its exceptional wear resistance and elasticity, critical for maintaining safety and fuel efficiency in traditional tire models. Future tire technology trends emphasize blending conductive polymers with polybutadiene to create multifunctional tires that offer superior traction, self-healing properties, and adaptability to electric and autonomous vehicles.
Infographic: Conductive polymer vs Polybutadiene for Tire
 azmater.com
azmater.com