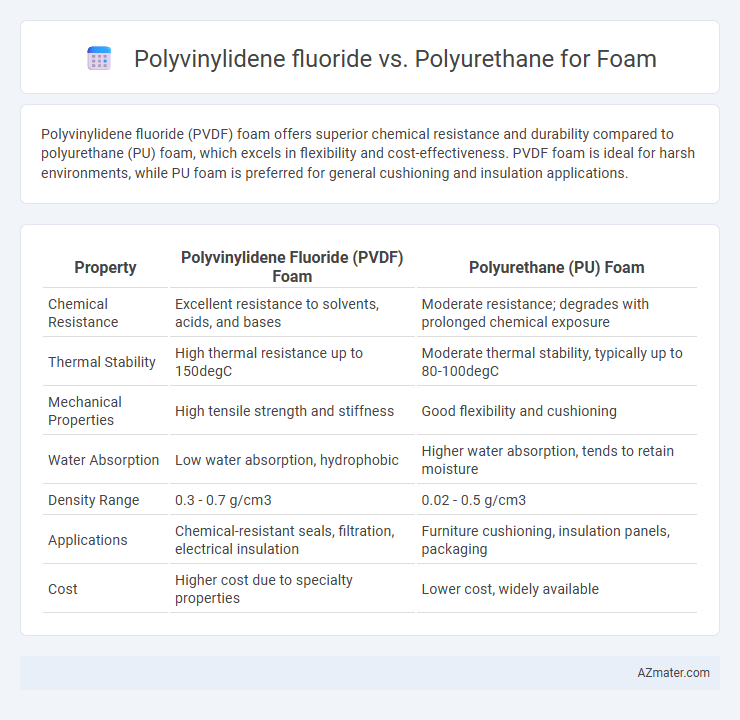
Polyvinylidene fluoride (PVDF) foam offers superior chemical resistance and durability compared to polyurethane (PU) foam, which excels in flexibility and cost-effectiveness. PVDF foam is ideal for harsh environments, while PU foam is preferred for general cushioning and insulation applications.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Polyvinylidene Fluoride (PVDF) Foam | Polyurethane (PU) Foam |
|---|---|---|
| Chemical Resistance | Excellent resistance to solvents, acids, and bases | Moderate resistance; degrades with prolonged chemical exposure |
| Thermal Stability | High thermal resistance up to 150degC | Moderate thermal stability, typically up to 80-100degC |
| Mechanical Properties | High tensile strength and stiffness | Good flexibility and cushioning |
| Water Absorption | Low water absorption, hydrophobic | Higher water absorption, tends to retain moisture |
| Density Range | 0.3 - 0.7 g/cm3 | 0.02 - 0.5 g/cm3 |
| Applications | Chemical-resistant seals, filtration, electrical insulation | Furniture cushioning, insulation panels, packaging |
| Cost | Higher cost due to specialty properties | Lower cost, widely available |
Introduction to Polyvinylidene Fluoride (PVDF) and Polyurethane (PU) Foams
Polyvinylidene Fluoride (PVDF) foam offers exceptional chemical resistance, high thermal stability, and excellent mechanical strength, making it ideal for harsh industrial environments. Polyurethane (PU) foam is known for its flexibility, lightweight properties, and superior cushioning, widely used in insulation, furniture, and automotive applications. Both PVDF and PU foams provide unique advantages depending on requirements such as durability, moisture resistance, and temperature tolerance.
Chemical Structure and Properties Comparison
Polyvinylidene fluoride (PVDF) features a highly crystalline structure with strong carbon-fluorine bonds that provide excellent chemical resistance, thermal stability, and UV durability, making it ideal for harsh environments. Polyurethane (PU), composed of soft and hard segments formed by urethane linkages, offers superior flexibility, elasticity, and abrasion resistance due to its segmented polymer chain structure. PVDF foams exhibit lower permeability and higher chemical inertness compared to polyurethane foams, which excel in impact absorption and cushioning applications because of their elastomeric nature.
Mechanical Strength and Durability
Polyvinylidene fluoride (PVDF) foam outperforms polyurethane in mechanical strength, offering higher tensile strength and superior resistance to abrasion and chemical degradation. PVDF exhibits exceptional durability in harsh environments, maintaining structural integrity under UV exposure and extreme temperatures, unlike conventional polyurethane foams which tend to degrade more rapidly. The enhanced mechanical properties and long-term stability of PVDF foam make it ideal for demanding industrial applications requiring robust performance.
Thermal Resistance and Insulation Capabilities
Polyvinylidene fluoride (PVDF) foam offers superior thermal resistance with a melting point around 177degC and excellent chemical stability, making it ideal for high-temperature insulation applications. Polyurethane foam, known for its exceptional thermal insulation properties due to low thermal conductivity (typically 0.02-0.03 W/m*K), performs well in moderate temperature environments but degrades at temperatures above 80-90degC. PVDF's combination of thermal endurance and insulation effectiveness makes it suitable for harsh conditions, while polyurethane foam is preferred for efficient insulation in lower-temperature settings.
Water and Chemical Resistance
Polyvinylidene fluoride (PVDF) foam exhibits superior water and chemical resistance, making it ideal for harsh environments involving acids, bases, and solvents. Polyurethane foam, while offering flexibility and cushioning, is more susceptible to water absorption and chemical degradation, limiting its use in aggressive chemical settings. PVDF's molecular structure provides enhanced durability and longevity in moisture-rich and chemically active applications compared to polyurethane.
Flexibility and Compressibility
Polyvinylidene fluoride (PVDF) foam offers exceptional chemical resistance and moderate flexibility, making it less compressible compared to polyurethane foam. Polyurethane foam excels in both flexibility and compressibility due to its open-cell structure and elastomeric properties, providing superior cushioning and impact absorption. For applications requiring high flexibility and compressibility, polyurethane foam remains the preferred choice over PVDF foam.
Application Areas: PVDF vs PU Foam
Polyvinylidene fluoride (PVDF) foam excels in chemical resistance and high-temperature applications, making it ideal for use in harsh industrial environments such as chemical processing, aerospace, and electrical insulation. Polyurethane (PU) foam offers superior flexibility, cushioning, and cost-effectiveness, commonly applied in automotive seating, furniture, and packaging industries. The choice between PVDF and PU foam depends on performance requirements, with PVDF preferred for durability against corrosion and PU favored for comfort and versatility.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
Polyvinylidene fluoride (PVDF) foam offers superior chemical resistance and durability but is less biodegradable and more energy-intensive to produce compared to polyurethane (PU) foam. Polyurethane foam, derived largely from petrochemicals, tends to have a higher carbon footprint but offers more options for recycling and has formulations that incorporate bio-based polyols, enhancing its sustainability profile. The environmental impact of both materials depends significantly on end-of-life management and the potential for reuse or recycling within circular economy frameworks.
Cost Effectiveness and Availability
Polyvinylidene fluoride (PVDF) foam typically costs more than polyurethane foam due to its superior chemical resistance and durability, making it less cost-effective for budget-sensitive projects. Polyurethane foam is widely available and economical, favored in applications requiring large volumes and versatility. PVDF's limited availability and higher price point restrict its use primarily to specialized industries demanding high-performance materials.
Which Foam Material is Best for Your Project?
Polyvinylidene fluoride (PVDF) foam offers superior chemical resistance, UV stability, and durability, making it ideal for outdoor and industrial applications where long-term performance is critical. Polyurethane (PU) foam provides excellent flexibility, cushioning, and cost efficiency, often preferred for comfort-focused projects like furniture, mattresses, and automotive seating. Choosing the best foam depends on project requirements: select PVDF for harsh environments needing resistance to chemicals and weather, and PU for lightweight, soft, and cost-effective cushioning solutions.
Infographic: Polyvinylidene fluoride vs Polyurethane for Foam
 azmater.com
azmater.com