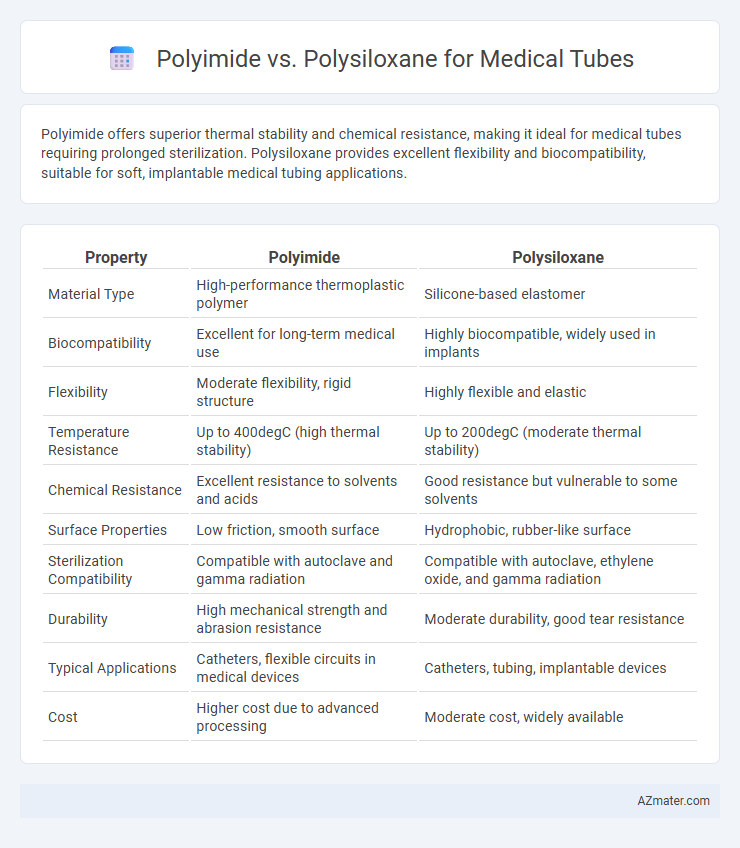
Polyimide offers superior thermal stability and chemical resistance, making it ideal for medical tubes requiring prolonged sterilization. Polysiloxane provides excellent flexibility and biocompatibility, suitable for soft, implantable medical tubing applications.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Polyimide | Polysiloxane |
|---|---|---|
| Material Type | High-performance thermoplastic polymer | Silicone-based elastomer |
| Biocompatibility | Excellent for long-term medical use | Highly biocompatible, widely used in implants |
| Flexibility | Moderate flexibility, rigid structure | Highly flexible and elastic |
| Temperature Resistance | Up to 400degC (high thermal stability) | Up to 200degC (moderate thermal stability) |
| Chemical Resistance | Excellent resistance to solvents and acids | Good resistance but vulnerable to some solvents |
| Surface Properties | Low friction, smooth surface | Hydrophobic, rubber-like surface |
| Sterilization Compatibility | Compatible with autoclave and gamma radiation | Compatible with autoclave, ethylene oxide, and gamma radiation |
| Durability | High mechanical strength and abrasion resistance | Moderate durability, good tear resistance |
| Typical Applications | Catheters, flexible circuits in medical devices | Catheters, tubing, implantable devices |
| Cost | Higher cost due to advanced processing | Moderate cost, widely available |
Introduction to Medical Tube Materials
Polyimide and polysiloxane are prominent materials used in medical tubes due to their unique chemical and mechanical properties. Polyimide offers high thermal stability, chemical resistance, and excellent mechanical strength, making it suitable for applications requiring durability and sterilization. Polysiloxane, or silicone, provides superior flexibility, biocompatibility, and resistance to bodily fluids, often preferred in applications demanding soft, elastic tubing with minimal tissue irritation.
Overview of Polyimide and Polysiloxane
Polyimide is a high-performance polymer known for its excellent thermal stability, chemical resistance, and mechanical strength, making it ideal for medical tubes requiring durability and sterilization compatibility. Polysiloxane, commonly referred to as silicone, offers superior flexibility, biocompatibility, and resistance to biofouling, which suits applications demanding softness and prolonged patient contact. Both materials provide distinct advantages in medical tubing, with polyimide excelling in structural integrity and polysiloxane prioritizing comfort and biocompatibility.
Mechanical Properties Comparison
Polyimide exhibits superior tensile strength and high-temperature resistance compared to polysiloxane, making it ideal for medical tubes requiring mechanical durability and stability under sterilization processes. Polysiloxane offers excellent flexibility and elasticity with lower modulus of elasticity, enhancing patient comfort in long-term implants or catheters but compromises on abrasion resistance. The choice between polyimide and polysiloxane hinges on balancing rigidity and flexibility, where polyimide is favored for structural integrity and polysiloxane for compliance and softness.
Thermal Stability and Temperature Resistance
Polyimide exhibits superior thermal stability and can withstand continuous operating temperatures up to 400degC, making it ideal for high-temperature medical tubing applications. Polysiloxane offers excellent flexibility and biocompatibility but typically endures maximum temperatures around 200degC, limiting its use in extreme heat environments. The choice between Polyimide and Polysiloxane for medical tubes hinges on the required thermal resistance and operating conditions, with Polyimide preferred for high-temperature sterilization processes.
Chemical Resistance and Biocompatibility
Polyimide exhibits superior chemical resistance against solvents, acids, and bases, making it ideal for medical tubes exposed to aggressive sterilization processes and harsh chemicals. Polysiloxane offers excellent biocompatibility with low toxicity and high flexibility, ensuring minimal immune response and enhanced patient comfort during implantation. The choice between polyimide and polysiloxane hinges on the required balance between chemical durability and tissue compatibility in specific medical applications.
Flexibility and Handling Characteristics
Polyimide tubes offer exceptional chemical resistance and high-temperature stability but tend to be stiffer, limiting flexibility and maneuverability in delicate medical procedures. Polysiloxane tubes, characterized by their silicone-based elastomeric properties, provide superior flexibility and softness, enhancing patient comfort and ease of handling during insertion. The choice between polyimide and polysiloxane medical tubes largely depends on the required balance between mechanical rigidity and pliability for specific clinical applications.
Sterilization Compatibility
Polyimide medical tubes exhibit exceptional resistance to high-temperature sterilization methods such as autoclaving and ethylene oxide, maintaining structural integrity and chemical stability. Polysiloxane tubes offer superior compatibility with gamma irradiation and plasma sterilization due to their inherent flexibility and silicone-based composition. Selecting the appropriate material depends on the sterilization process, with polyimide favored for repeated thermal cycles and polysiloxane preferred for radiation-based sterilization protocols.
Applications in Medical Tubing
Polyimide offers exceptional thermal stability, chemical resistance, and biocompatibility, making it ideal for medical tubing used in high-temperature sterilization processes and long-term implantable devices. Polysiloxane, known for its excellent flexibility, kink resistance, and biocompatibility, is preferred in applications requiring soft, flexible tubing such as catheters and drug delivery systems. Both materials ensure safety and performance in medical tubing but differ in mechanical properties and sterilization compatibility, influencing their specific application choices.
Cost and Manufacturing Considerations
Polyimide medical tubes typically incur higher manufacturing costs due to complex curing processes and stringent quality control requirements, whereas polysiloxane tubes offer more cost-effective production with simpler molding and curing steps. The high thermal stability and chemical resistance of polyimide justify its premium price in specialized medical applications, while polysiloxane provides versatility and lower tooling costs suitable for higher-volume manufacturing. Manufacturers must consider the trade-off between polyimide's superior mechanical properties and polysiloxane's cost efficiency to optimize production budgets and meet specific medical device specifications.
Choosing the Right Material for Medical Tubes
Polyimide offers superior thermal stability and chemical resistance, making it ideal for medical tubes exposed to high temperatures and aggressive sterilization processes. Polysiloxane provides excellent flexibility and biocompatibility, which is crucial for patient comfort and long-term implantation. Selecting the right material depends on balancing the need for durability, flexibility, and biocompatibility based on the specific medical application.
Infographic: Polyimide vs Polysiloxane for Medical Tube
 azmater.com
azmater.com