Polybutylene terephthalate (PBT) offers superior thermal stability and mechanical strength compared to polyvinyl chloride (PVC) for cable insulation, enhancing durability in high-temperature environments. PVC provides excellent flexibility and cost-effectiveness but has lower heat resistance and emits harmful fumes when burned.
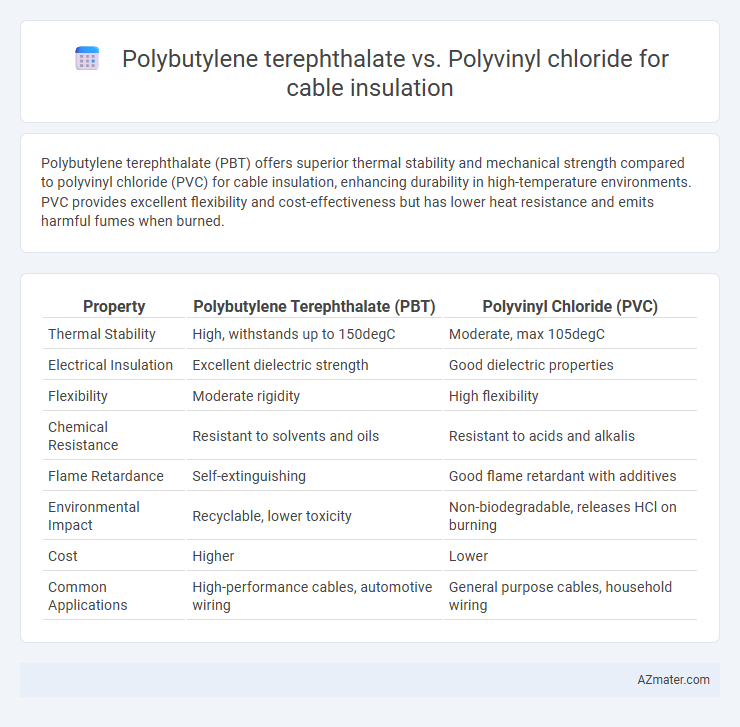
Table of Comparison
| Property | Polybutylene Terephthalate (PBT) | Polyvinyl Chloride (PVC) |
|---|---|---|
| Thermal Stability | High, withstands up to 150degC | Moderate, max 105degC |
| Electrical Insulation | Excellent dielectric strength | Good dielectric properties |
| Flexibility | Moderate rigidity | High flexibility |
| Chemical Resistance | Resistant to solvents and oils | Resistant to acids and alkalis |
| Flame Retardance | Self-extinguishing | Good flame retardant with additives |
| Environmental Impact | Recyclable, lower toxicity | Non-biodegradable, releases HCl on burning |
| Cost | Higher | Lower |
| Common Applications | High-performance cables, automotive wiring | General purpose cables, household wiring |
Introduction to Cable Insulation Materials
Polybutylene terephthalate (PBT) and polyvinyl chloride (PVC) are prominent materials used in cable insulation due to their distinct chemical and physical properties. PBT offers superior thermal stability and mechanical strength, making it ideal for high-performance and high-temperature applications in automotive and industrial wiring. PVC remains widely favored for general-purpose cables due to its excellent flame resistance, flexibility, and cost-effectiveness, which contribute to its extensive use in residential and commercial wiring systems.
Overview of Polybutylene Terephthalate (PBT)
Polybutylene Terephthalate (PBT) is a high-performance thermoplastic polymer known for its excellent electrical insulation properties, making it ideal for cable insulation applications. It offers superior mechanical strength, chemical resistance, and thermal stability compared to Polyvinyl Chloride (PVC), enhancing durability and safety in harsh environments. PBT's low moisture absorption and dimensional stability contribute to reliable long-term performance in electrical cables.
Overview of Polyvinyl Chloride (PVC)
Polyvinyl Chloride (PVC) is a widely used polymer in cable insulation due to its excellent electrical insulation properties, flexibility, and flame retardancy. It offers superior resistance to chemicals, abrasion, and weathering, making it suitable for both indoor and outdoor cable applications. PVC is also cost-effective and easy to process, ensuring durability and safety in cable manufacturing.
Mechanical Properties Comparison
Polybutylene terephthalate (PBT) exhibits superior mechanical properties compared to Polyvinyl chloride (PVC) for cable insulation, including higher tensile strength and better impact resistance. PBT's enhanced flexibility and abrasion resistance contribute to increased durability in demanding environments, while PVC tends to be more rigid and prone to cracking under mechanical stress. PBT also offers improved thermal stability, which maintains mechanical integrity over a wider temperature range, making it a preferred choice for applications requiring robust performance.
Thermal Stability and Heat Resistance
Polybutylene terephthalate (PBT) exhibits superior thermal stability and heat resistance compared to Polyvinyl chloride (PVC), with a melting point around 223degC and continuous use temperatures up to 150degC, making it ideal for high-temperature cable insulation applications. PVC, while cost-effective and flexible, degrades at lower temperatures, typically around 105degC to 140degC, and releases hazardous hydrochloric acid when overheated, posing safety risks. The enhanced thermal resilience of PBT results in improved performance and longevity in demanding electrical environments, especially where elevated temperatures are common.
Electrical Insulation Performance
Polybutylene terephthalate (PBT) offers superior electrical insulation performance compared to polyvinyl chloride (PVC) due to its higher dielectric strength and excellent thermal stability, which ensures consistent insulation properties under elevated temperatures. PBT's low dielectric constant and dissipation factor contribute to reduced electrical losses, making it ideal for high-frequency cable applications. PVC, while cost-effective and flexible, exhibits lower heat resistance and higher dielectric losses, limiting its use in demanding electrical environments.
Chemical and Environmental Resistance
Polybutylene terephthalate (PBT) exhibits superior chemical resistance compared to polyvinyl chloride (PVC), offering enhanced durability against solvents, oils, and acids commonly encountered in cable insulation environments. PBT demonstrates excellent resistance to hydrolysis and thermal degradation, making it more stable under high-temperature and moisture conditions, whereas PVC is more susceptible to plasticizer migration and environmental stress cracking. Environmentally, PBT is considered more sustainable due to its better recyclability and lower emission of hazardous substances during production and disposal, while PVC raises concerns related to chlorine content and dioxin formation in incineration processes.
Flexibility and Processability
Polybutylene terephthalate (PBT) offers superior flexibility compared to polyvinyl chloride (PVC), making it ideal for applications requiring dynamic bending and repeated flexing in cable insulation. PBT's enhanced processability is due to its excellent melt flow characteristics, allowing precise extrusion and molding with minimal defects. PVC, while versatile and cost-effective, tends to be stiffer and less adaptable during complex processing, limiting its use in high-flexibility cable insulation applications.
Cost Analysis and Availability
Polybutylene terephthalate (PBT) offers moderate cost efficiency with a price range typically higher than polyvinyl chloride (PVC), which remains the most cost-effective option for cable insulation due to its widespread production. PVC benefits from extensive global availability and established manufacturing infrastructure, ensuring consistent supply and lower procurement costs. PBT, while providing superior thermal and mechanical properties, faces limited availability and higher raw material expenses, impacting overall cost competitiveness in cable insulation applications.
Conclusion: Choosing Between PBT and PVC for Cable Insulation
Polybutylene terephthalate (PBT) offers superior thermal stability, chemical resistance, and mechanical strength compared to polyvinyl chloride (PVC), making it ideal for high-performance cable insulation applications. PVC remains popular due to its cost-effectiveness, good flame retardancy, and flexibility, suitable for general-purpose wiring and lower temperature environments. Selecting between PBT and PVC depends on specific requirements such as operational temperature range, environmental exposure, and budget constraints.
Infographic: Polybutylene terephthalate vs Polyvinyl chloride for Cable Insulation
 azmater.com
azmater.com