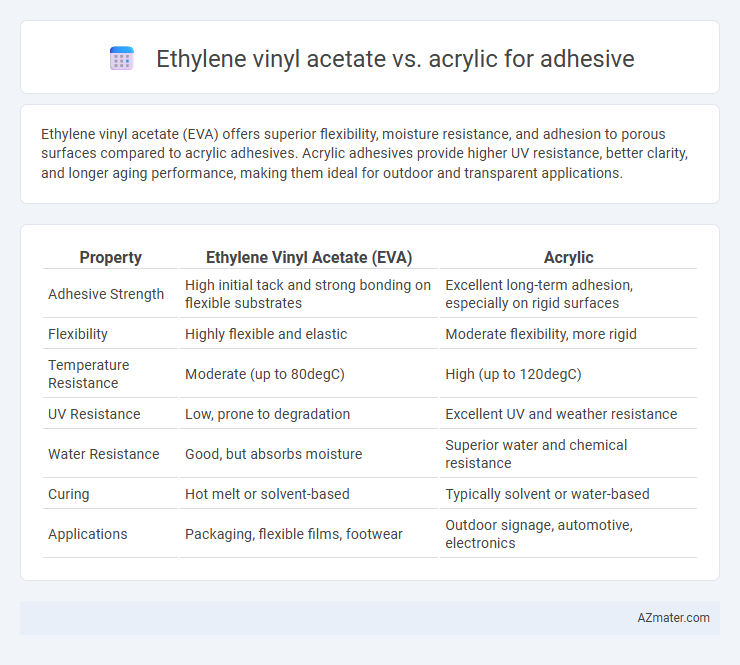
Ethylene vinyl acetate (EVA) offers superior flexibility, moisture resistance, and adhesion to porous surfaces compared to acrylic adhesives. Acrylic adhesives provide higher UV resistance, better clarity, and longer aging performance, making them ideal for outdoor and transparent applications.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Ethylene Vinyl Acetate (EVA) | Acrylic |
|---|---|---|
| Adhesive Strength | High initial tack and strong bonding on flexible substrates | Excellent long-term adhesion, especially on rigid surfaces |
| Flexibility | Highly flexible and elastic | Moderate flexibility, more rigid |
| Temperature Resistance | Moderate (up to 80degC) | High (up to 120degC) |
| UV Resistance | Low, prone to degradation | Excellent UV and weather resistance |
| Water Resistance | Good, but absorbs moisture | Superior water and chemical resistance |
| Curing | Hot melt or solvent-based | Typically solvent or water-based |
| Applications | Packaging, flexible films, footwear | Outdoor signage, automotive, electronics |
Introduction to Ethylene Vinyl Acetate and Acrylic Adhesives
Ethylene vinyl acetate (EVA) adhesives are known for their flexibility, excellent clarity, and strong bonding with a wide range of substrates, making them popular in packaging and lamination applications. Acrylic adhesives offer superior UV resistance, high durability, and strong adhesion to metals and plastics, commonly used in automotive and construction industries. Both types provide distinct advantages depending on the environmental exposure and substrate compatibility requirements of the application.
Chemical Composition and Structure Comparison
Ethylene vinyl acetate (EVA) is a copolymer composed of ethylene and vinyl acetate units, where the vinyl acetate content typically ranges from 10% to 40%, imparting flexibility and strong adhesive properties due to its semi-crystalline structure. Acrylic adhesives are based on polymers of acrylic acid or acrylate esters, characterized by a polymer backbone with ester functional groups that provide excellent UV resistance, clarity, and adhesion to diverse substrates. The chemical structure of EVA enables superior impact resistance and elasticity, while acrylic adhesives offer higher thermal stability and better resistance to environmental degradation.
Adhesion Properties: EVA vs Acrylic
Ethylene vinyl acetate (EVA) adhesives exhibit strong initial tack and excellent flexibility, making them ideal for bonding low surface energy substrates like polyethylene and polypropylene. Acrylic adhesives provide superior long-term adhesion, UV resistance, and higher temperature stability, ensuring durable bonds on a wide range of materials including metals and glass. Compared to EVA, acrylics maintain adhesion strength under harsh environmental conditions, while EVA is preferred for applications requiring quick setting and moderate temperature resistance.
Performance on Different Substrates
Ethylene vinyl acetate (EVA) adhesives offer excellent flexibility and strong bonding on porous substrates such as paper, fabric, and wood, making them ideal for packaging and textile applications. Acrylic adhesives exhibit superior performance on non-porous surfaces like glass, metals, and plastics due to their higher temperature resistance and durability against UV exposure. Choosing between EVA and acrylic depends on substrate characteristics and environmental conditions, with EVA excelling in elasticity and acrylic providing long-term stability on smooth, rigid materials.
Durability and Environmental Resistance
Ethylene vinyl acetate (EVA) adhesives demonstrate superior flexibility and excellent resistance to UV radiation, moisture, and temperature fluctuations, making them highly durable for outdoor and high-stress applications. Acrylic adhesives offer stronger bonding strength and improved chemical resistance, maintaining durability against harsh solvents and oxidizing agents, which enhances longevity in industrial environments. Both materials provide robust environmental resistance, but EVA excels in flexibility and moisture resistance, while acrylic surpasses in chemical and heat endurance.
Flexibility and Mechanical Strength
Ethylene vinyl acetate (EVA) adhesives exhibit superior flexibility due to their elastomeric properties, making them ideal for applications requiring dynamic movement and impact resistance. Acrylic adhesives provide higher mechanical strength and shear resistance, suitable for structural bonding where rigidity and durability under stress are critical. The choice between EVA and acrylic hinges on balancing flexibility demands with mechanical strength requirements in industrial and construction adhesives.
Application Methods and Ease of Use
Ethylene vinyl acetate (EVA) adhesives offer excellent flexibility and strong bonding for packaging, lamination, and foam bonding applications, typically applied using heat activation from hot melt glue guns or rollers. Acrylic adhesives provide superior weather resistance and aging stability, ideal for outdoor signage, automotive, and aerospace applications, and are commonly applied via solvent-based or UV-curable methods, requiring specialized equipment. EVA adhesives are generally easier to handle due to their lower activation temperatures and faster bonding times, while acrylics demand more precise application conditions to achieve optimal adhesion.
Cost Analysis and Economic Considerations
Ethylene vinyl acetate (EVA) adhesives generally offer lower raw material and production costs compared to acrylic adhesives, making them a more economical choice for large-scale applications. Acrylic adhesives provide superior durability and resistance to environmental factors, which can lead to lower long-term costs despite their higher initial price. Cost analysis reveals that while EVA adhesives excel in upfront affordability, acrylic adhesives may deliver better value through extended lifespan and enhanced performance in demanding conditions.
Industry Applications: EVA vs Acrylic
Ethylene vinyl acetate (EVA) adhesives are widely used in industries such as packaging, footwear, and automotive due to their flexibility, strong bonding to non-polar substrates, and good resistance to UV and environmental factors. Acrylic adhesives excel in electronics, signage, and medical device applications because of their superior clarity, long-term durability, and excellent adhesion to polar substrates. The choice between EVA and acrylic adhesives depends on specific industry requirements including bonding strength, environmental exposure, and substrate compatibility.
Choosing the Right Adhesive: Factors to Consider
Ethylene vinyl acetate (EVA) adhesives offer excellent flexibility, strong tack, and good resistance to UV and moisture, making them ideal for packaging and foam lamination applications. Acrylic adhesives provide superior aging resistance, high transparency, and strong bond strength on a variety of substrates, suitable for electronics or signage. When choosing between EVA and acrylic adhesives, consider factors such as environmental exposure, substrate compatibility, desired bond durability, and clarity requirements.
Infographic: Ethylene vinyl acetate vs Acrylic for Adhesive
 azmater.com
azmater.com