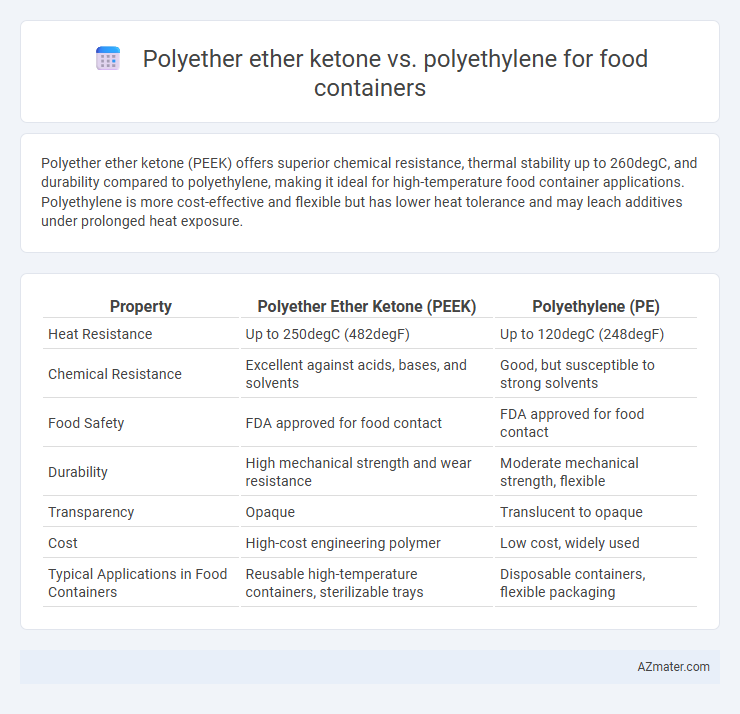
Polyether ether ketone (PEEK) offers superior chemical resistance, thermal stability up to 260degC, and durability compared to polyethylene, making it ideal for high-temperature food container applications. Polyethylene is more cost-effective and flexible but has lower heat tolerance and may leach additives under prolonged heat exposure.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Polyether Ether Ketone (PEEK) | Polyethylene (PE) |
|---|---|---|
| Heat Resistance | Up to 250degC (482degF) | Up to 120degC (248degF) |
| Chemical Resistance | Excellent against acids, bases, and solvents | Good, but susceptible to strong solvents |
| Food Safety | FDA approved for food contact | FDA approved for food contact |
| Durability | High mechanical strength and wear resistance | Moderate mechanical strength, flexible |
| Transparency | Opaque | Translucent to opaque |
| Cost | High-cost engineering polymer | Low cost, widely used |
| Typical Applications in Food Containers | Reusable high-temperature containers, sterilizable trays | Disposable containers, flexible packaging |
Introduction to Polyether Ether Ketone (PEEK) and Polyethylene (PE)
Polyether Ether Ketone (PEEK) is a high-performance engineering thermoplastic known for its exceptional chemical resistance, thermal stability up to 250degC, and superior mechanical strength, making it suitable for demanding food container applications requiring sterilization and long-term durability. Polyethylene (PE), widely used in food containers, offers excellent chemical inertness, flexibility, and cost-effectiveness but has lower thermal resistance, typically up to 80-100degC, limiting its use in high-temperature food processing. The choice between PEEK and PE depends on the specific food preservation conditions, with PEEK favored for high-temperature environments and PE preferred for everyday, low-cost applications.
Material Composition and Structure
Polyether ether ketone (PEEK) is a high-performance thermoplastic characterized by a rigid, crystalline structure with excellent chemical resistance and thermal stability, making it suitable for repeated sterilization in food containers. Polyethylene (PE), typically low-density or high-density, consists of a simpler linear or branched polymeric structure with lower melting points and less chemical resistance but offers flexibility and cost-effectiveness. The aromatic ketone groups in PEEK provide enhanced mechanical strength and durability compared to the hydrocarbon chains in PE, influencing long-term food safety and container lifespan.
Mechanical Properties Comparison
Polyether ether ketone (PEEK) exhibits superior mechanical properties compared to polyethylene (PE) for food container applications, offering higher tensile strength, stiffness, and impact resistance. PEEK maintains structural integrity at elevated temperatures up to 250degC, whereas polyethylene softens and deforms at much lower temperatures around 80-130degC. The enhanced durability and thermal stability of PEEK make it an ideal choice for food containers requiring long-term mechanical resilience and repeated sterilization cycles.
Chemical Resistance and Food Safety
Polyether ether ketone (PEEK) offers superior chemical resistance compared to polyethylene, withstanding strong acids, bases, and organic solvents, making it highly durable for food container applications. PEEK's high thermal stability and inertness ensure no harmful leaching, enhancing food safety during storage and heating processes. In contrast, polyethylene is more susceptible to chemical degradation and potential contamination under harsh conditions, limiting its use for long-term or high-temperature food storage.
Temperature Tolerance and Thermal Stability
Polyether ether ketone (PEEK) exhibits superior temperature tolerance, maintaining structural integrity at continuous use temperatures up to 250degC, whereas polyethylene (PE) typically withstands up to 80-120degC before deforming. PEEK's thermal stability supports repeated high-temperature sterilization without degradation, making it ideal for food containers requiring harsh heat treatments. In contrast, polyethylene's lower melting point and susceptibility to thermal deformation limit its application in high-temperature food storage or processing environments.
Durability and Lifespan in Food Storage
Polyether ether ketone (PEEK) offers superior durability compared to polyethylene in food storage due to its high chemical resistance, thermal stability up to 250degC, and exceptional mechanical strength, ensuring a longer lifespan under harsh conditions. Polyethylene, while cost-effective and widely used, has lower thermal resistance and is more prone to degradation when exposed to repeated temperature cycling and certain food acids. Choosing PEEK for food containers extends usability by maintaining structural integrity and safety in demanding storage environments, whereas polyethylene may require more frequent replacement.
Regulatory Approvals for Food Contact
Polyether ether ketone (PEEK) is highly favored in food container applications due to its compliance with stringent regulatory approvals such as FDA 21 CFR 177.2415 and EU Regulation 10/2011, confirming its safety for repeated food contact. Polyethylene (PE), widely recognized for food packaging, meets FDA 21 CFR 177.1520 and EU Regulation 10/2011 requirements, supporting its extensive use in direct food contact but with lower thermal and chemical resistance compared to PEEK. Regulatory validation of both polymers ensures adherence to migration limits and overall food safety standards critical in the food industry.
Cost Analysis and Manufacturing Considerations
Polyether ether ketone (PEEK) offers superior chemical resistance and thermal stability compared to polyethylene (PE), making it suitable for high-performance food containers, but its cost is significantly higher, often limiting its use to specialized applications. Manufacturing PEEK containers involves complex processing techniques such as injection molding at elevated temperatures, increasing production costs and requiring specialized equipment, whereas polyethylene benefits from well-established, cost-effective manufacturing processes like blow molding and extrusion. The economic trade-off between PEEK's durability and PE's affordability impacts material selection based on budget constraints and performance requirements in food container production.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
Polyether ether ketone (PEEK) offers superior chemical resistance and thermal stability compared to polyethylene (PE), making it more durable and less prone to degradation in food container applications, which reduces waste over time. However, polyethylene is more widely recyclable and derived from less energy-intensive processes, contributing to a lower carbon footprint during production. Evaluating environmental impact, polyethylene's recyclability and lower embodied energy support sustainability goals better than PEEK, despite PEEK's longer lifespan and performance benefits.
Conclusion: Choosing the Right Material for Food Containers
Polyether ether ketone (PEEK) offers superior chemical resistance, high-temperature stability up to 250degC, and excellent mechanical strength, making it ideal for reusable food containers exposed to harsh cleaning processes. Polyethylene (PE), while cost-effective and widely used for disposable or low-temperature applications, lacks the durability and thermal resistance needed for repeated use or sterilization. Selecting the right material depends on the container's intended use, with PEEK preferred for long-term, high-performance food storage and PE suited for everyday, short-term applications.
Infographic: Polyether ether ketone vs Polyethylene for Food Container
 azmater.com
azmater.com