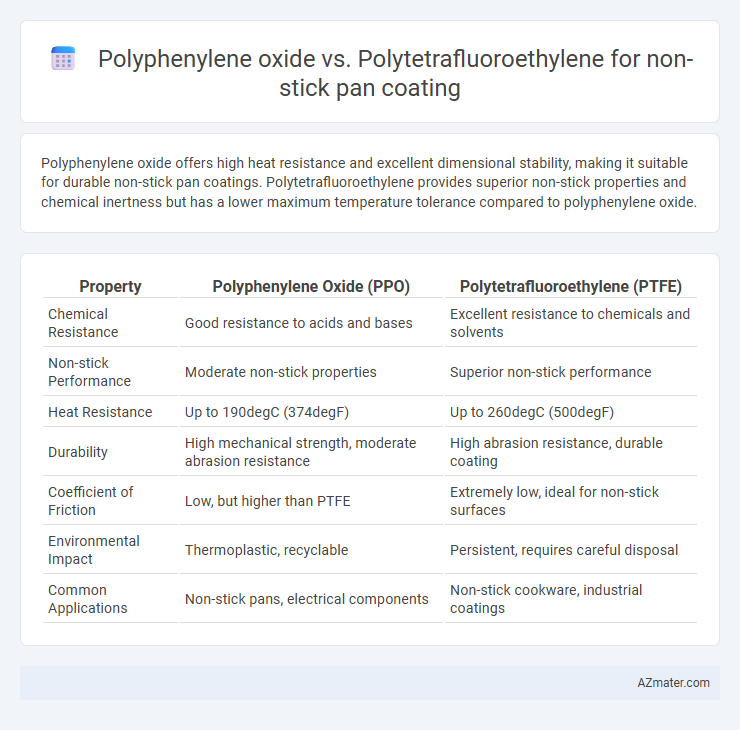
Polyphenylene oxide offers high heat resistance and excellent dimensional stability, making it suitable for durable non-stick pan coatings. Polytetrafluoroethylene provides superior non-stick properties and chemical inertness but has a lower maximum temperature tolerance compared to polyphenylene oxide.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Polyphenylene Oxide (PPO) | Polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE) |
|---|---|---|
| Chemical Resistance | Good resistance to acids and bases | Excellent resistance to chemicals and solvents |
| Non-stick Performance | Moderate non-stick properties | Superior non-stick performance |
| Heat Resistance | Up to 190degC (374degF) | Up to 260degC (500degF) |
| Durability | High mechanical strength, moderate abrasion resistance | High abrasion resistance, durable coating |
| Coefficient of Friction | Low, but higher than PTFE | Extremely low, ideal for non-stick surfaces |
| Environmental Impact | Thermoplastic, recyclable | Persistent, requires careful disposal |
| Common Applications | Non-stick pans, electrical components | Non-stick cookware, industrial coatings |
Introduction to Non-Stick Pan Coatings
Non-stick pan coatings primarily utilize materials like Polyphenylene oxide (PPO) and Polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE) due to their excellent heat resistance and low surface energy. PTFE, commonly known as Teflon, offers superior non-stick properties and chemical inertness, making it the industry standard for cookware surfaces. PPO-based coatings provide increased thermal stability and mechanical strength, though they are less prevalent than PTFE in commercial non-stick pans.
What is Polyphenylene Oxide (PPO)?
Polyphenylene oxide (PPO) is a high-performance thermoplastic known for its excellent thermal stability, chemical resistance, and mechanical strength, making it suitable for non-stick pan coatings that require durability under high temperatures. Unlike polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE), known as Teflon, PPO offers better rigidity and impact resistance but generally has lower non-stick properties and heat tolerance. In non-stick cookware, PPO coatings provide a balance of structural integrity and moderate release characteristics, while PTFE remains preferred for superior non-stick performance and higher heat resistance.
What is Polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE)?
Polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE) is a synthetic fluoropolymer known for its exceptional non-stick properties, chemical resistance, and high thermal stability, making it a popular choice for non-stick pan coatings. PTFE's low coefficient of friction significantly reduces food adhesion, ensuring easy release and cleanup during cooking. Its heat resistance can withstand temperatures up to approximately 260degC (500degF), though overheating beyond this can degrade the coating and release harmful fumes.
Chemical Structure and Properties Comparison
Polyphenylene oxide (PPO) features a rigid aromatic backbone with ether linkages, offering excellent thermal stability and mechanical strength, making it resistant to cracking and deformation under heat. Polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE), composed of carbon chains fully fluorinated, exhibits exceptional chemical inertness and an extremely low coefficient of friction, ensuring superior non-stick properties and resistance to most chemicals. While PPO provides better structural durability and heat resistance up to about 270degC, PTFE outperforms in non-stick performance and operates effectively up to 260degC but is more prone to degradation at higher temperatures.
Heat Resistance: PPO vs PTFE
Polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE) exhibits superior heat resistance compared to polyphenylene oxide (PPO), maintaining stability up to 260degC (500degF) without degradation, making it ideal for non-stick pan coatings exposed to high cooking temperatures. Polyphenylene oxide offers moderate heat resistance up to approximately 200degC (392degF), which limits its application in high-heat cooking scenarios. PTFE's ability to resist thermal breakdown ensures longer-lasting non-stick performance under rigorous heat exposure.
Non-Stick Performance and Cooking Experience
Polyphenylene oxide (PPO) offers moderate non-stick performance with good heat resistance, making it suitable for everyday cooking but less effective than Polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE) in preventing food adhesion. PTFE, widely known under the brand name Teflon, provides superior non-stick capabilities, ensuring effortless food release and easy cleanup while supporting higher cooking temperatures up to 260degC (500degF). The cooking experience with PTFE-coated pans is generally preferred due to smoother surface performance, reduced oil usage, and enhanced durability against sticking and staining compared to PPO coatings.
Durability and Longevity of the Coatings
Polyphenylene oxide (PPO) offers strong chemical resistance and moderate heat stability, making it durable for non-stick pan coatings but less resistant to extreme temperatures and abrasion compared to polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE). PTFE is widely recognized for its exceptional heat resistance up to 260degC (500degF) and superior non-stick properties, contributing to longer-lasting coatings that withstand frequent cooking and cleaning. The longevity of PTFE coatings surpasses PPO in typical kitchen environments due to its high thermal stability and low friction surface, minimizing wear and extending the service life of non-stick pans.
Safety and Food Compatibility
Polyphenylene oxide (PPO) offers excellent thermal stability and chemical resistance, making it a safe and food-compatible option for non-stick pan coatings without releasing harmful fumes at high temperatures. Polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE) is widely used for its superior non-stick properties, but it can degrade at temperatures above 260degC (500degF), potentially releasing toxic fumes and raising safety concerns. Both materials are FDA-approved for food contact, but PPO's higher thermal decomposition temperature ensures better safety during typical cooking conditions.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
Polyphenylene oxide (PPO) offers a more environmentally friendly alternative to polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE) for non-stick pan coatings due to its lower reliance on fluorinated chemicals, which are persistent and bioaccumulative pollutants. PTFE production involves per- and polyfluoroalkyl substances (PFAS) associated with significant environmental hazards, including groundwater contamination and long degradation periods. PPO's biodegradable properties and reduced toxic chemical footprint enhance sustainability, making it a preferable choice for eco-conscious cookware manufacturing.
Which is Better for Non-Stick Pans?
Polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE) offers superior non-stick performance due to its extremely low friction coefficient and excellent chemical resistance, making it the preferred choice for non-stick pan coatings. Polyphenylene oxide (PPO) provides good thermal stability and durability but lacks the same level of non-stick properties as PTFE. For optimal food release and ease of cleaning, PTFE-based coatings outperform PPO in non-stick cookware applications.
Infographic: Polyphenylene oxide vs Polytetrafluoroethylene for Non-stick pan coating
 azmater.com
azmater.com