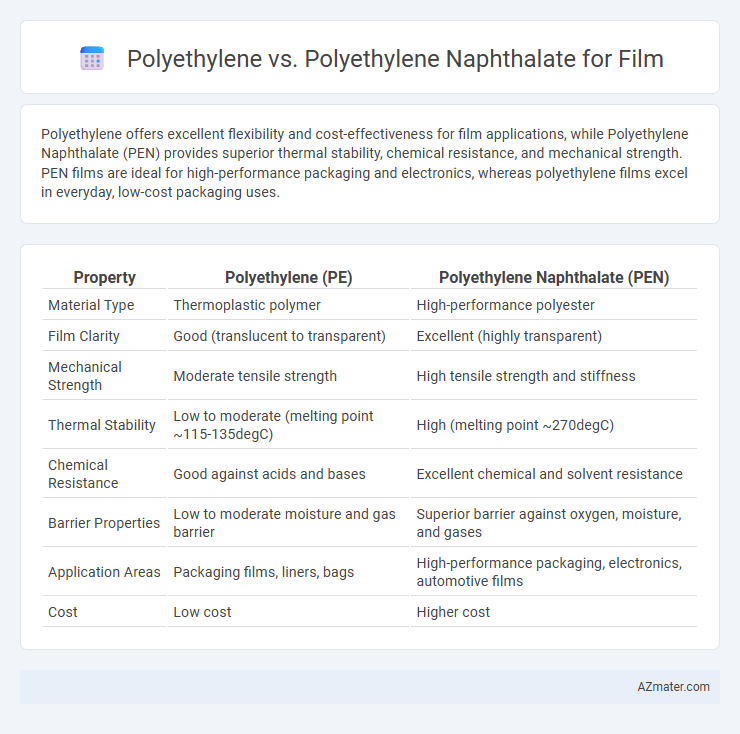
Polyethylene offers excellent flexibility and cost-effectiveness for film applications, while Polyethylene Naphthalate (PEN) provides superior thermal stability, chemical resistance, and mechanical strength. PEN films are ideal for high-performance packaging and electronics, whereas polyethylene films excel in everyday, low-cost packaging uses.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Polyethylene (PE) | Polyethylene Naphthalate (PEN) |
|---|---|---|
| Material Type | Thermoplastic polymer | High-performance polyester |
| Film Clarity | Good (translucent to transparent) | Excellent (highly transparent) |
| Mechanical Strength | Moderate tensile strength | High tensile strength and stiffness |
| Thermal Stability | Low to moderate (melting point ~115-135degC) | High (melting point ~270degC) |
| Chemical Resistance | Good against acids and bases | Excellent chemical and solvent resistance |
| Barrier Properties | Low to moderate moisture and gas barrier | Superior barrier against oxygen, moisture, and gases |
| Application Areas | Packaging films, liners, bags | High-performance packaging, electronics, automotive films |
| Cost | Low cost | Higher cost |
Introduction to Polyethylene and Polyethylene Naphthalate
Polyethylene (PE) is a widely used thermoplastic polymer known for its flexibility, chemical resistance, and cost-effectiveness in film applications, primarily utilized in packaging and agricultural films. Polyethylene Naphthalate (PEN) is a high-performance polyester that offers superior thermal stability, mechanical strength, and barrier properties compared to conventional polyethylene films. PEN's enhanced durability and resistance to moisture and gases make it ideal for advanced packaging and electronic applications where polyethylene films may fall short.
Chemical Structures: PE vs PEN
Polyethylene (PE) consists of long chains of repeating ethylene units with a simple hydrocarbon backbone, providing flexibility and low density ideal for packaging films. Polyethylene naphthalate (PEN) features aromatic naphthalene rings in its polyester structure, offering higher thermal stability, improved barrier properties, and greater mechanical strength compared to PE. The presence of rigid benzene rings in PEN's chemical structure significantly enhances its chemical resistance and dimensional stability over the aliphatic carbon chains in PE.
Mechanical Properties Comparison
Polyethylene Naphthalate (PEN) exhibits superior mechanical properties compared to standard Polyethylene (PE) films, including higher tensile strength and enhanced dimensional stability, making PEN ideal for demanding applications requiring durability. PEN films demonstrate significantly improved elasticity and resistance to deformation under stress, attributed to their rigid aromatic backbone structure. In contrast, PE films, though more flexible and cost-effective, offer lower mechanical robustness and are more prone to creep and puncture under high load conditions.
Thermal Stability and Heat Resistance
Polyethylene Naphthalate (PEN) exhibits superior thermal stability and heat resistance compared to Polyethylene (PE), making it ideal for high-temperature film applications. PEN films maintain mechanical integrity and dimensional stability at temperatures exceeding 150degC, whereas PE films typically soften around 80-120degC. The enhanced heat resistance of PEN is due to its rigid aromatic naphthalate structure, which provides a higher melting point and better performance under thermal stress.
Barrier Properties: Moisture, Gas, and Chemicals
Polyethylene Naphthalate (PEN) offers superior barrier properties compared to traditional Polyethylene (PE), exhibiting significantly lower permeability to moisture, gases such as oxygen and carbon dioxide, and various chemicals. PEN's denser molecular structure and higher crystallinity enhance its resistance, making it ideal for packaging applications requiring extended shelf life and protection against environmental factors. In contrast, PE provides moderate moisture barrier but falls short in gas and chemical resistance, limiting its use in high-performance film applications.
Optical and Clarity Differences
Polyethylene naphthalate (PEN) films exhibit superior optical clarity and higher light transmittance compared to conventional polyethylene (PE) films, making PEN highly suitable for applications requiring enhanced transparency and precision imaging. PEN offers a lower haze percentage, resulting in crisper, clearer visuals, while PE films typically present higher haze levels due to their amorphous polymer structure. The improved optical properties of PEN are attributed to its rigid aromatic backbone and better molecular orientation, which contribute to sharper clarity and reduced light scattering in film applications.
Processing and Manufacturability
Polyethylene (PE) offers superior ease of processing with its low melting point and excellent flow characteristics, making it highly suitable for fast, cost-effective film extrusion and blow molding. Polyethylene Naphthalate (PEN), characterized by a higher melting temperature and greater thermal stability, demands more precise processing conditions such as elevated extrusion temperatures and controlled cooling rates to maintain film integrity. While PE is favored for its manufacturability in high-volume, low-cost applications, PEN delivers enhanced dimensional stability and mechanical strength, appealing in niche markets requiring high-performance films.
Environmental Impact and Recyclability
Polyethylene (PE) films offer high recyclability due to widespread infrastructure and simpler chemical composition, enabling efficient mechanical recycling and lower environmental impact through reduced energy consumption. Polyethylene Naphthalate (PEN) films provide superior barrier properties and thermal stability but pose greater challenges in recycling because of limited collection streams and more complex polymer structure, leading to higher environmental costs. Choosing PE supports circular economy goals with minimal ecological footprint, whereas PEN requires advanced recycling technologies to mitigate its environmental impact.
Cost Analysis and Market Availability
Polyethylene (PE) films are generally more cost-effective than Polyethylene Naphthalate (PEN) films due to lower raw material and production expenses, making PE the preferred choice for budget-sensitive applications. PEN films offer superior thermal stability, chemical resistance, and barrier properties but come at a significantly higher price, limiting their market availability to specialized sectors like electronics and high-performance packaging. Market data indicate PE dominates global film production volumes, while PEN remains a niche segment with constrained but growing demand in advanced industrial applications.
Applications in Film Industry: Use Cases and Recommendations
Polyethylene (PE) films are widely used in packaging, agricultural sheeting, and food wrap due to their excellent flexibility, moisture resistance, and cost-effectiveness. Polyethylene Naphthalate (PEN) films offer superior thermal stability, gas barrier properties, and dimensional stability, making them ideal for high-performance electronics, medical packaging, and flexible displays. For applications requiring durability and resistance to heat and oxygen, PEN is recommended, while PE remains the preferred choice for economical, general-purpose films.
Infographic: Polyethylene vs Polyethylene Naphthalate for Film
 azmater.com
azmater.com