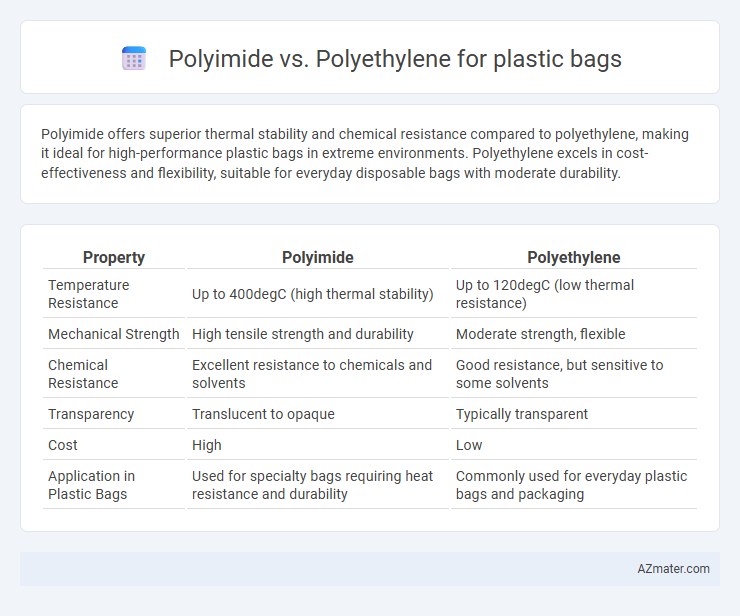
Polyimide offers superior thermal stability and chemical resistance compared to polyethylene, making it ideal for high-performance plastic bags in extreme environments. Polyethylene excels in cost-effectiveness and flexibility, suitable for everyday disposable bags with moderate durability.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Polyimide | Polyethylene |
|---|---|---|
| Temperature Resistance | Up to 400degC (high thermal stability) | Up to 120degC (low thermal resistance) |
| Mechanical Strength | High tensile strength and durability | Moderate strength, flexible |
| Chemical Resistance | Excellent resistance to chemicals and solvents | Good resistance, but sensitive to some solvents |
| Transparency | Translucent to opaque | Typically transparent |
| Cost | High | Low |
| Application in Plastic Bags | Used for specialty bags requiring heat resistance and durability | Commonly used for everyday plastic bags and packaging |
Introduction to Polyimide and Polyethylene
Polyimide is a high-performance polymer known for its exceptional thermal stability, chemical resistance, and mechanical strength, making it suitable for specialized industrial applications. Polyethylene, a widely used plastic, is valued for its flexibility, low cost, and excellent moisture barrier properties, making it the dominant material in everyday plastic bag production. The distinct chemical structures of polyimide and polyethylene result in significant differences in durability, temperature resistance, and cost-effectiveness for packaging solutions.
Chemical Structure and Composition
Polyimide plastic bags are composed of aromatic polyimide chains featuring imide linkages that provide exceptional thermal stability and chemical resistance, unlike polyethylene bags, which consist of saturated hydrocarbon chains forming long polyethylene chains with weak Van der Waals forces. The rigid, heterocyclic ring structures in polyimide create strong intermolecular interactions, enhancing durability and resistance to solvents and high temperatures, whereas polyethylene's nonpolar hydrocarbon chains result in flexible but less chemically resistant bags. Chemical composition differences directly impact mechanical properties, with polyimide exhibiting superior strength and thermal endurance compared to the simpler polyethylene polymer structure.
Mechanical Properties Comparison
Polyimide exhibits superior mechanical properties compared to polyethylene, with higher tensile strength and excellent thermal stability, making it suitable for heavy-duty applications requiring durability. Polyethylene offers greater flexibility and impact resistance but has lower tensile strength and less thermal resistance, limiting its use in high-temperature environments. The choice between polyimide and polyethylene for plastic bags depends on the balance between mechanical robustness and cost-effectiveness.
Thermal Resistance and Temperature Tolerance
Polyimide offers superior thermal resistance compared to polyethylene, maintaining structural integrity at temperatures up to 400degC, whereas polyethylene typically degrades above 80-100degC. This high-temperature tolerance makes polyimide ideal for applications requiring heat exposure or sterilization, while polyethylene is suitable for everyday use with lower thermal demands. The distinct thermal endurance of polyimide ensures durability in extreme environments, contrasting with polyethylene's cost-effectiveness and flexibility in standard temperature ranges.
Barrier Properties: Moisture and Gas Permeability
Polyimide exhibits superior barrier properties compared to polyethylene, with significantly lower moisture vapor transmission rates and gas permeability, making it ideal for applications requiring enhanced protection against oxygen and humidity. Polyethylene, while cost-effective and flexible, allows higher moisture and gas permeation, limiting its effectiveness in preserving sensitive contents. The dense aromatic backbone of polyimide contributes to its exceptional resistance, providing a robust barrier that extends shelf life in packaging solutions.
Flexibility and Durability in Plastic Bags
Polyimide offers exceptional flexibility and superior durability compared to polyethylene, making it ideal for heavy-duty plastic bags requiring high heat resistance and chemical stability. Polyethylene provides cost-effective flexibility but lacks the robust strength and thermal endurance of polyimide, often leading to quicker wear and tear under stressful conditions. For applications demanding long-lasting performance and resilience, polyimide significantly outperforms polyethylene in maintaining structural integrity and flexibility over extended use.
Environmental Impact and Recyclability
Polyethylene plastic bags dominate the market due to their low cost and ease of recycling, yet their environmental impact is significant because they degrade slowly, contributing to long-term pollution. Polyimide bags offer superior thermal stability and chemical resistance, but their complex molecular structure makes them challenging to recycle and less environmentally friendly. Choosing polyethylene optimizes recyclability and reduces environmental burden compared to polyimide, which is favored for specialized applications rather than mass-market bag production.
Cost and Availability in Packaging Industry
Polyethylene dominates the packaging industry for plastic bags due to its low cost and widespread availability, making it the preferred choice for mass production and everyday use. Polyimide, while offering superior thermal stability and chemical resistance, is significantly more expensive and less accessible, limiting its application primarily to niche, high-performance packaging needs. Cost-effective polyethylene's abundant supply and ease of processing sustain its broad adoption, whereas polyimide remains a specialized material for demanding environments.
Typical Applications of Polyimide vs Polyethylene Bags
Polyimide bags are ideal for high-temperature industrial applications such as electrical insulation, aerospace component protection, and chemical-resistant packaging due to their exceptional thermal stability and chemical resistance. Polyethylene bags dominate everyday use in retail, food storage, and waste management because of their flexibility, cost-effectiveness, and moisture resistance. The choice between polyimide and polyethylene bags depends on the required durability under extreme conditions versus general-purpose utility.
Conclusion: Choosing the Right Material for Plastic Bags
Polyethylene remains the preferred choice for plastic bags due to its cost-effectiveness, flexibility, and recyclability, making it ideal for everyday consumer use. Polyimide offers superior thermal stability and chemical resistance but at a significantly higher cost, limiting its application to specialized fields requiring durability under extreme conditions. Selecting polyethylene ensures efficient production and environmental management, while polyimide suits niche markets demanding enhanced performance.
Infographic: Polyimide vs Polyethylene for Plastic bag
 azmater.com
azmater.com