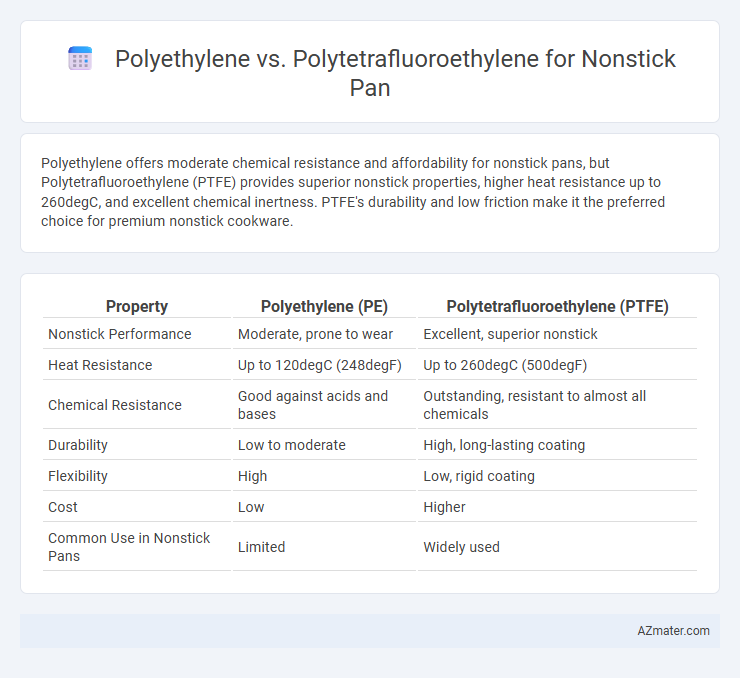
Polyethylene offers moderate chemical resistance and affordability for nonstick pans, but Polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE) provides superior nonstick properties, higher heat resistance up to 260degC, and excellent chemical inertness. PTFE's durability and low friction make it the preferred choice for premium nonstick cookware.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Polyethylene (PE) | Polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE) |
|---|---|---|
| Nonstick Performance | Moderate, prone to wear | Excellent, superior nonstick |
| Heat Resistance | Up to 120degC (248degF) | Up to 260degC (500degF) |
| Chemical Resistance | Good against acids and bases | Outstanding, resistant to almost all chemicals |
| Durability | Low to moderate | High, long-lasting coating |
| Flexibility | High | Low, rigid coating |
| Cost | Low | Higher |
| Common Use in Nonstick Pans | Limited | Widely used |
Introduction to Nonstick Cookware Materials
Polyethylene and polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE) are two polymers commonly compared for nonstick cookware applications due to their differing chemical properties and thermal stability. PTFE, known for its superior nonstick performance and high heat resistance up to approximately 260degC, is widely used in premium nonstick pans, while polyethylene, with a lower melting point around 115degC, is less suitable for direct cookware surfaces but often utilized in complementary kitchen tools or coatings. Understanding these material distinctions is crucial for selecting durable, safe, and effective nonstick cookware that meets cooking temperature requirements and enhances user convenience.
Overview of Polyethylene and Polytetrafluoroethylene
Polyethylene, a thermoplastic polymer made from ethylene monomers, is known for its durability, flexibility, and resistance to moisture, making it an economical choice in various applications but less ideal for high-temperature cooking surfaces. Polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE), commonly recognized as Teflon, excels in nonstick cookware due to its exceptionally low coefficient of friction, chemical inertness, and high heat resistance up to 260degC (500degF). PTFE-coated pans offer superior nonstick performance and ease of cleaning, while polyethylene lacks the nonstick qualities and thermal stability necessary for effective cookware coating.
Chemical Structure Comparison: PE vs PTFE
Polyethylene (PE) features a simple hydrocarbon polymer chain composed of repeating ethylene units (-CH2-CH2-), resulting in a flexible, non-polar structure with strong carbon-carbon and carbon-hydrogen bonds. Polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE), commonly known as Teflon, consists of a carbon backbone fully fluorinated with fluorine atoms (-CF2-CF2-), creating an exceptionally strong carbon-fluorine bond and a highly electronegative, non-reactive surface. The substitution of hydrogen atoms in PE by fluorine in PTFE leads to superior chemical inertness, high thermal stability, and significantly enhanced nonstick properties in cookware applications.
Nonstick Properties: Which Performs Better?
Polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE) offers superior nonstick properties compared to polyethylene due to its low surface energy and exceptional chemical resistance, ensuring food releases easily and cleanup is effortless. Polyethylene, while resistant to moisture, lacks the same high-temperature stability and nonstick effectiveness, making it less suitable for cookware applications. PTFE-based coatings maintain their durability and nonstick performance under frequent heat exposure, positioning them as the preferred choice for nonstick pans.
Temperature Resistance and Heat Stability
Polyethylene exhibits lower temperature resistance, typically withstanding heat up to about 120degC, making it unsuitable for high-temperature cooking applications compared to polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE), which can endure temperatures up to 260degC without degrading. PTFE's superior heat stability prevents warping and maintains its nonstick properties even under intense heat, whereas polyethylene may melt or release harmful substances when exposed to higher temperatures. This makes PTFE a more reliable and safe coating material for nonstick pans requiring consistent performance during frying and sauteing.
Safety and Food Contact Regulations
Polyethylene (PE) and Polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE) are commonly used materials in nonstick cookware, but PTFE is preferred for superior heat resistance and chemical inertness, ensuring no harmful substances leach into food under typical cooking temperatures. PE is less heat-resistant and may degrade at high temperatures, posing potential safety concerns when used in nonstick coatings that require high heat stability. Both materials must comply with FDA and EFSA food contact regulations, with PTFE-based coatings often meeting stricter standards for non-reactivity and thermal stability, making PTFE safer and more reliable for nonstick pan applications.
Durability and Lifespan in Daily Cooking
Polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE) offers superior durability and a longer lifespan compared to polyethylene in nonstick pans due to its high heat resistance and chemical stability. While polyethylene may degrade or melt at typical cooking temperatures, PTFE withstands temperatures up to 260degC (500degF) without breaking down, ensuring sustained nonstick performance. This resilience makes PTFE-coated pans more reliable for daily cooking tasks, reducing the need for frequent replacements.
Maintenance and Cleaning Requirements
Polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE) nonstick pans require gentle cleaning with non-abrasive sponges to preserve their coating and prevent damage, while polyethylene pans offer higher durability but may need more frequent deep cleaning due to their less effective nonstick properties. PTFE's resistance to high temperatures reduces the risk of residue buildup, facilitating easier maintenance compared to polyethylene, which can degrade under heat and absorb oils. Selecting PTFE ensures longer-lasting nonstick performance with minimal effort, whereas polyethylene demands attentive upkeep to maintain its usability.
Environmental Impact and Recyclability
Polyethylene (PE) and Polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE) differ significantly in environmental impact and recyclability when used in nonstick pans. PE, derived from natural gas or petroleum, is more readily recyclable through common plastic recycling streams (e.g., codes #2 and #4), degrading more easily under industrial recycling conditions, while PTFE, known for its chemical resistance and heat durability, poses challenges in recycling due to its fluorinated polymer structure and potential release of toxic compounds during degradation. The environmental persistence and difficulty in recycling PTFE contribute to greater ecological concerns compared to the comparatively lower-impact, more recyclable polyethylene coatings.
Final Verdict: Best Choice for Nonstick Pans
Polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE) outperforms polyethylene for nonstick pans due to its superior heat resistance, chemical inertness, and exceptional nonstick properties. PTFE coatings provide durable, easy-release surfaces that withstand high cooking temperatures without degrading or releasing harmful substances. For optimal cooking performance and safety, PTFE-based nonstick pans remain the best choice compared to polyethylene alternatives.
Infographic: Polyethylene vs Polytetrafluoroethylene for Nonstick Pan
 azmater.com
azmater.com