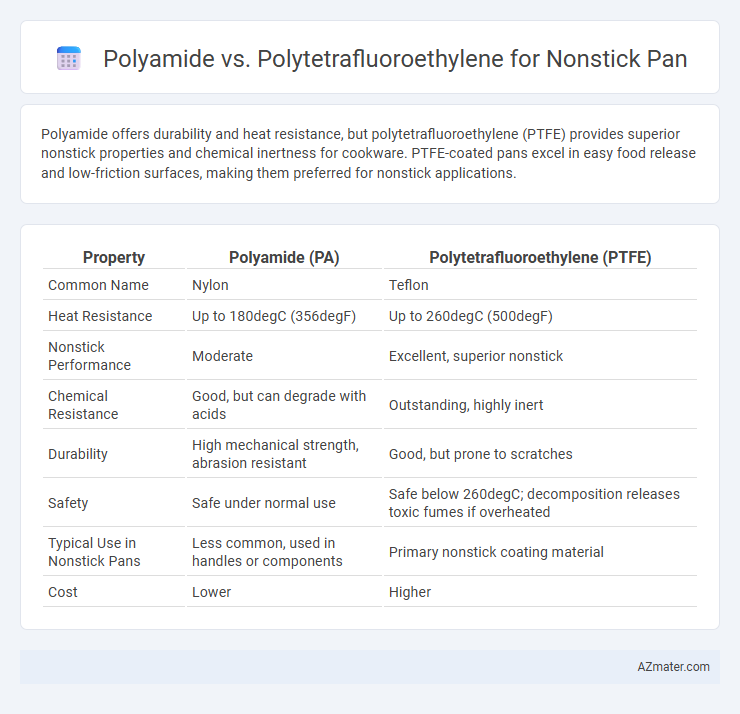
Polyamide offers durability and heat resistance, but polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE) provides superior nonstick properties and chemical inertness for cookware. PTFE-coated pans excel in easy food release and low-friction surfaces, making them preferred for nonstick applications.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Polyamide (PA) | Polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE) |
|---|---|---|
| Common Name | Nylon | Teflon |
| Heat Resistance | Up to 180degC (356degF) | Up to 260degC (500degF) |
| Nonstick Performance | Moderate | Excellent, superior nonstick |
| Chemical Resistance | Good, but can degrade with acids | Outstanding, highly inert |
| Durability | High mechanical strength, abrasion resistant | Good, but prone to scratches |
| Safety | Safe under normal use | Safe below 260degC; decomposition releases toxic fumes if overheated |
| Typical Use in Nonstick Pans | Less common, used in handles or components | Primary nonstick coating material |
| Cost | Lower | Higher |
Introduction to Nonstick Pan Materials
Nonstick pans commonly utilize materials such as polyamide and polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE) for their coatings, each offering distinct chemical properties and performance benefits. Polyamide provides good heat resistance and durability, making it suitable for moderate cooking temperatures and enhanced scratch resistance. PTFE, known for its exceptional nonstick capabilities and high-temperature tolerance up to around 260degC (500degF), is widely favored for professional-grade cookware requiring easy food release and minimal oil use.
Polyamide: Composition and Key Properties
Polyamide, commonly known as nylon, is a synthetic polymer composed of repeating amide linkages (-CONH-) that provide high mechanical strength, flexibility, and thermal resistance, making it suitable for nonstick cookware. Its key properties include excellent abrasion resistance, good chemical stability, and moderate heat endurance up to approximately 220degC (428degF), which supports durability in cooking applications. Compared to polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE), polyamide offers greater toughness and impact resistance but typically lower nonstick performance and heat resistance.
Polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE): Composition and Key Properties
Polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE) is a synthetic fluoropolymer composed of carbon and fluorine atoms, characterized by a strong carbon-fluorine bond that provides exceptional chemical resistance and thermal stability up to 260degC (500degF). PTFE's low coefficient of friction and non-reactive surface make it ideal for nonstick cookware, allowing easy food release and effortless cleaning. Unlike polyamide, PTFE exhibits outstanding resistance to heat, oils, and solvents, ensuring durability and safety in high-temperature cooking applications.
Heat Resistance Comparison: Polyamide vs PTFE
Polyamide exhibits moderate heat resistance, typically withstanding temperatures up to 200degC (392degF), making it suitable for some cooking applications but less ideal for high-heat use. Polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE), commonly known as Teflon, offers superior heat resistance, maintaining performance up to 260degC (500degF) without degradation. This higher threshold makes PTFE the preferred choice for nonstick pans subjected to frequent high-temperature cooking.
Nonstick Performance Analysis
Polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE) offers superior nonstick performance compared to polyamide due to its low surface energy and high chemical resistance, ensuring effortless food release and easy cleaning. Polyamide, while durable and heat-resistant, lacks the exceptional nonstick properties of PTFE, often resulting in increased food adhesion during cooking. PTFE's stability at high temperatures and resistance to abrasion make it the preferred coating for nonstick pans, enhancing cooking efficiency and longevity.
Durability and Longevity Factors
Polyamide coatings offer moderate durability for nonstick pans but tend to degrade under high heat and frequent use, leading to reduced longevity. Polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE), commonly known as Teflon, provides superior resistance to thermal breakdown and abrasion, resulting in enhanced durability and extended pan lifespan. The molecular structure of PTFE creates a low-friction, chemically inert surface, making it more resistant to scratches and wear compared to polyamide coatings.
Safety and Food Contact Considerations
Polyamide and polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE) are both used in nonstick pans with distinct safety profiles and food-contact considerations. PTFE coatings, commonly known as Teflon, offer excellent nonstick properties but can release harmful fumes when overheated above 260degC (500degF), posing health risks such as polymer fume fever. Polyamide coatings provide a safer alternative with higher heat resistance and fewer toxic emissions, making them suitable for everyday cooking without the same level of risk associated with PTFE degradation.
Cleaning and Maintenance Differences
Polyamide nonstick pans require gentle cleaning with mild detergents and soft sponges to prevent surface damage, as abrasive materials can degrade their coating quickly. Polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE) pans offer more robust stain resistance and can often tolerate slightly harsher scrubbing without compromising nonstick properties. PTFE coatings typically demand less frequent maintenance and are easier to clean due to their superior chemical inertness and reduced surface energy compared to polyamide coatings.
Cost and Market Availability
Polyamide pans generally offer a more budget-friendly option compared to polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE) nonstick pans, making them accessible for a wider range of consumers. PTFE coatings, known under brand names like Teflon, dominate the market due to their superior nonstick properties and heat resistance, but they often come at a higher price point. Market availability favors PTFE pans as they are widely produced and distributed globally, while polyamide nonstick cookware is less common and found mostly in niche or eco-friendly product lines.
Conclusion: Choosing the Right Material for Nonstick Pans
Polyamide offers durability and moderate nonstick properties suitable for everyday cooking, while Polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE) provides superior nonstick performance with enhanced resistance to high temperatures and chemical inertness. For high-heat cooking and ease of cleaning, PTFE-coated pans are preferred, whereas polyamide pans are more cost-effective and versatile for lower-temperature applications. Selecting the right nonstick pan material depends on cooking habits, temperature requirements, and maintenance preferences to balance performance and longevity.
Infographic: Polyamide vs Polytetrafluoroethylene for Nonstick Pan
 azmater.com
azmater.com