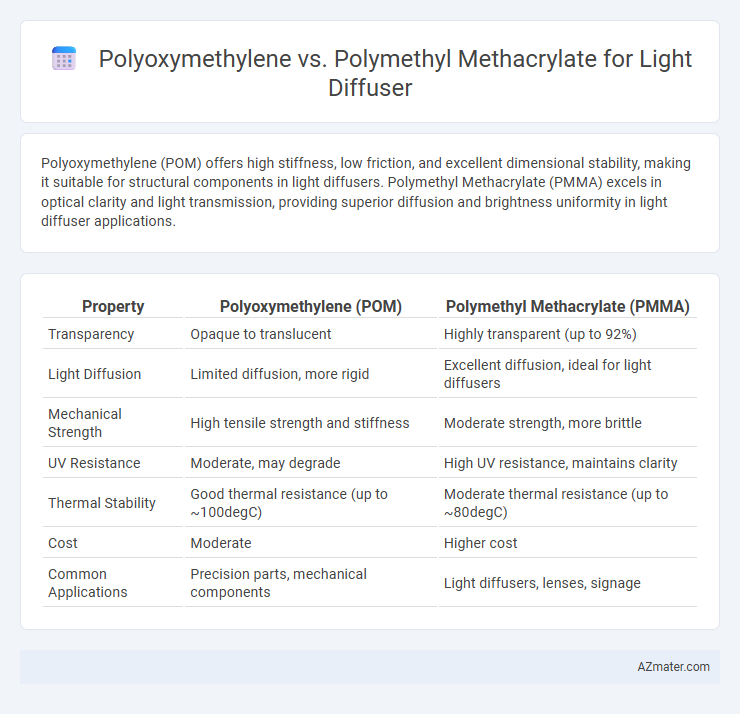
Polyoxymethylene (POM) offers high stiffness, low friction, and excellent dimensional stability, making it suitable for structural components in light diffusers. Polymethyl Methacrylate (PMMA) excels in optical clarity and light transmission, providing superior diffusion and brightness uniformity in light diffuser applications.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Polyoxymethylene (POM) | Polymethyl Methacrylate (PMMA) |
|---|---|---|
| Transparency | Opaque to translucent | Highly transparent (up to 92%) |
| Light Diffusion | Limited diffusion, more rigid | Excellent diffusion, ideal for light diffusers |
| Mechanical Strength | High tensile strength and stiffness | Moderate strength, more brittle |
| UV Resistance | Moderate, may degrade | High UV resistance, maintains clarity |
| Thermal Stability | Good thermal resistance (up to ~100degC) | Moderate thermal resistance (up to ~80degC) |
| Cost | Moderate | Higher cost |
| Common Applications | Precision parts, mechanical components | Light diffusers, lenses, signage |
Introduction to Light Diffuser Materials
Polyoxymethylene (POM) offers excellent dimensional stability and high stiffness, making it suitable for precise light diffuser applications requiring durability. Polymethyl Methacrylate (PMMA) provides superior optical clarity and high light transmittance, enhancing brightness and uniform diffusion in LED lighting systems. Selecting between POM and PMMA depends on balancing mechanical strength needs with optical performance requirements for efficient light diffusion.
Overview of Polyoxymethylene (POM)
Polyoxymethylene (POM) is a high-performance engineering thermoplastic characterized by excellent mechanical strength, low friction, and outstanding dimensional stability, making it suitable for precision light diffuser components requiring durability. Its inherent chemical resistance and resistance to UV degradation contribute to long-lasting optical clarity and minimal yellowing in light diffusion applications. Compared to Polymethyl Methacrylate (PMMA), POM offers superior impact resistance and wear properties, though PMMA provides better light transmittance and clarity for diffusers.
Properties and Applications of POM in Light Diffusers
Polyoxymethylene (POM) offers superior mechanical strength, low friction, and excellent dimensional stability compared to Polymethyl Methacrylate (PMMA), making it ideal for light diffuser components exposed to mechanical stress. Its high chemical resistance and low moisture absorption ensure durability in harsh environments, whereas PMMA provides better optical clarity but less impact resistance. POM's use in light diffusers is prevalent in automotive lighting and industrial applications where robust, long-lasting diffusers are essential.
Overview of Polymethyl Methacrylate (PMMA)
Polymethyl Methacrylate (PMMA) is a transparent thermoplastic known for its excellent optical clarity, high light transmittance of approximately 92%, and superior weather resistance, making it ideal for light diffuser applications. Its lightweight nature, combined with good impact resistance and UV stability, positions PMMA as a preferred material over Polyoxymethylene (POM), which lacks comparable optical properties. PMMA's ease of fabrication and ability to maintain structural integrity under prolonged exposure to sunlight further enhance its suitability for efficient light diffusion in architectural and lighting design.
Properties and Applications of PMMA in Light Diffusers
Polymethyl Methacrylate (PMMA) excels in light diffuser applications due to its superior optical clarity, high light transmittance of up to 92%, and excellent weather resistance compared to Polyoxymethylene (POM), which is primarily valued for mechanical strength rather than optical properties. PMMA's low hygroscopicity and good UV stability ensure consistent diffusion performance in outdoor and indoor lighting setups, making it ideal for LED light covers and architectural luminaires. Its ease of fabrication and ability to be molded or extruded into complex shapes further enhance its application versatility in high-quality, energy-efficient light diffusion solutions.
Optical Performance: POM vs PMMA
Polyoxymethylene (POM) offers excellent dimensional stability and toughness but exhibits lower optical clarity compared to Polymethyl Methacrylate (PMMA), making PMMA the preferred choice for light diffusers requiring high light transmission and uniform diffusion. PMMA provides superior light diffusion properties with a higher refractive index around 1.49, offering excellent transparency and minimal light scattering, optimizing brightness and clarity in diffuser applications. In contrast, POM's limited light transmission and higher light absorption reduce its effectiveness in enhancing optical performance in diffuser designs.
Mechanical Strength and Durability Comparison
Polyoxymethylene (POM) offers superior mechanical strength with high tensile and flexural strength, making it resistant to wear and fatigue, ideal for light diffusers requiring durability under mechanical stress. Polymethyl Methacrylate (PMMA) provides excellent optical clarity and weather resistance but has lower impact strength and can be more prone to cracking or UV degradation over time. For applications prioritizing mechanical robustness and long-term durability in light diffusers, POM outperforms PMMA despite PMMA's better light transmission properties.
Processing and Fabrication Differences
Polyoxymethylene (POM) offers excellent machinability and dimensional stability, making it suitable for precision light diffuser components requiring tight tolerances. Polymethyl Methacrylate (PMMA) excels in optical clarity and is typically processed through injection molding or extrusion, enabling smooth surface finishes essential for effective light diffusion. POM's higher melting point and crystallinity require controlled thermal processing to prevent warping, whereas PMMA's amorphous nature allows easier thermoforming but demands careful handling to avoid internal stresses and crazing.
Cost and Sustainability Considerations
Polyoxymethylene (POM) offers superior durability and chemical resistance with moderate cost, making it suitable for long-lasting light diffusers in industrial applications. Polymethyl Methacrylate (PMMA) excels in optical clarity and UV resistance but typically incurs higher material and processing costs, impacting budget-sensitive projects. From a sustainability perspective, PMMA is more readily recyclable and often produced with bio-based options, whereas POM's limited recyclability and petrochemical origin pose environmental challenges.
Selecting the Ideal Material for Light Diffusers
Polyoxymethylene (POM) offers superior mechanical strength and excellent dimensional stability, making it ideal for light diffusers requiring high impact resistance and precise molding. Polymethyl Methacrylate (PMMA) provides outstanding optical clarity and light transmission, ensuring uniform diffusion and minimal light loss in applications where visual performance is critical. Selecting between POM and PMMA depends on balancing durability needs with optical quality to achieve optimal performance in light diffuser applications.
Infographic: Polyoxymethylene vs Polymethyl Methacrylate for Light Diffuser
 azmater.com
azmater.com