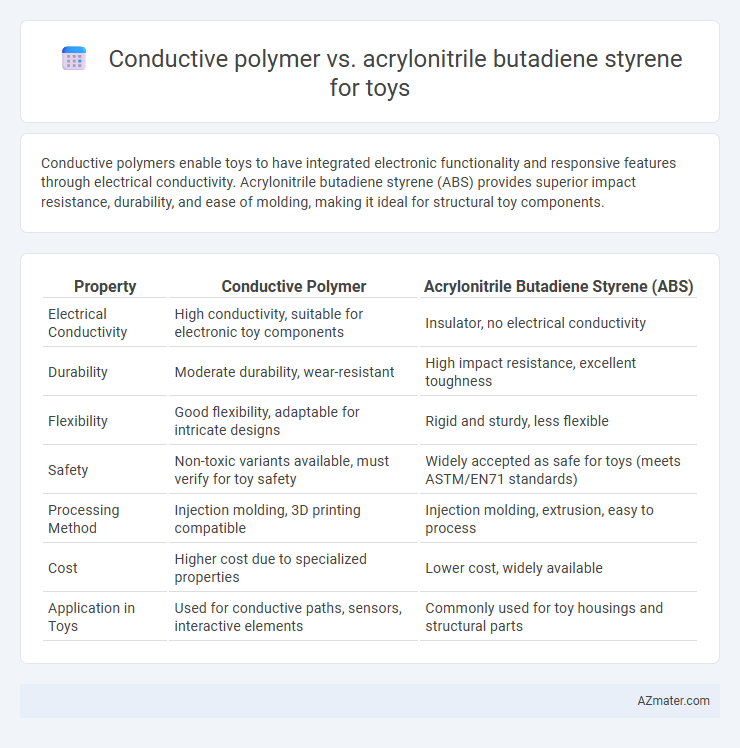
Conductive polymers enable toys to have integrated electronic functionality and responsive features through electrical conductivity. Acrylonitrile butadiene styrene (ABS) provides superior impact resistance, durability, and ease of molding, making it ideal for structural toy components.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Conductive Polymer | Acrylonitrile Butadiene Styrene (ABS) |
|---|---|---|
| Electrical Conductivity | High conductivity, suitable for electronic toy components | Insulator, no electrical conductivity |
| Durability | Moderate durability, wear-resistant | High impact resistance, excellent toughness |
| Flexibility | Good flexibility, adaptable for intricate designs | Rigid and sturdy, less flexible |
| Safety | Non-toxic variants available, must verify for toy safety | Widely accepted as safe for toys (meets ASTM/EN71 standards) |
| Processing Method | Injection molding, 3D printing compatible | Injection molding, extrusion, easy to process |
| Cost | Higher cost due to specialized properties | Lower cost, widely available |
| Application in Toys | Used for conductive paths, sensors, interactive elements | Commonly used for toy housings and structural parts |
Introduction to Toy Materials: Conductive Polymer vs ABS
Conductive polymers offer enhanced electrical conductivity and flexibility, making them ideal for interactive and electronic toys that require responsive materials. Acrylonitrile butadiene styrene (ABS) is a durable, impact-resistant thermoplastic widely used in toy manufacturing for its strength, ease of molding, and vibrant color retention. Choosing between conductive polymers and ABS depends on the toy's functional requirements, such as whether electrical properties or mechanical robustness are prioritized.
Overview of Conductive Polymers in Toy Manufacturing
Conductive polymers in toy manufacturing offer enhanced electronic integration through their intrinsic electrical conductivity, enabling interactive and responsive features in smart toys. These polymers provide flexibility, lightweight properties, and environmental stability compared to traditional plastics like Acrylonitrile Butadiene Styrene (ABS), which is valued for its toughness and surface finish but lacks electrical conductivity. Incorporating conductive polymers allows for innovative toy designs with embedded sensors and circuits, improving user experience while maintaining safety and durability standards.
Key Properties of Acrylonitrile Butadiene Styrene (ABS)
Acrylonitrile butadiene styrene (ABS) offers high impact resistance, excellent toughness, and superior rigidity, making it ideal for durable toy manufacturing. Its chemical resistance and ease of molding allow for intricate designs and long-lasting performance under rough play conditions. ABS also provides good heat resistance and surface finish, ensuring toys maintain shape and aesthetic appeal over time.
Durability: Which Material Withstands Play Better?
Conductive polymers offer moderate durability with the unique advantage of electrical conductivity, making them ideal for interactive or electronic toys, but they may degrade faster under mechanical stress compared to traditional plastics. Acrylonitrile butadiene styrene (ABS) excels in impact resistance and toughness, providing superior durability that withstands rough play and repeated drops commonly encountered in children's toys. For toys requiring robustness and longevity, ABS generally outperforms conductive polymers in maintaining structural integrity during extensive use.
Safety Considerations: Conductive Polymer and ABS in Toys
Conductive polymers offer enhanced electrical safety due to their controlled conductivity, reducing static buildup risks in toys. Acrylonitrile butadiene styrene (ABS) is widely recognized for its strong impact resistance and non-toxicity, making it safe for children's products. Both materials meet ASTM and EN71 safety standards, but conductive polymers require careful formulation to avoid potential skin irritation or allergic reactions.
Electrical Functionalities: Advantages of Conductive Polymers
Conductive polymers offer superior electrical functionalities for toys compared to Acrylonitrile Butadiene Styrene (ABS) by enabling built-in conductivity and electromagnetic shielding without adding heavy metal fillers. These polymers enhance sensor responsiveness and touch sensitivity in interactive toys through efficient charge transport, which ABS lacks due to its insulating nature. Furthermore, conductive polymers provide lightweight and flexible electrical pathways, improving durability and design versatility in electronic toy components.
Design Flexibility and Aesthetic Potential
Conductive polymers offer exceptional design flexibility due to their ability to be molded into complex shapes while incorporating electrical conductivity, ideal for interactive toys requiring responsive features. Acrylonitrile butadiene styrene (ABS) provides robust structural integrity and smooth surface finishes, enabling intricate aesthetic detailing and vibrant color customization important for visually appealing toy designs. Choosing between conductive polymers and ABS depends on balancing the need for electronic functionality with high-quality visual and tactile appeal in toy manufacturing.
Environmental Impact: Sustainability of Each Material
Conductive polymers offer enhanced sustainability due to their potential for recyclability and reduced reliance on fossil fuel-derived components compared to acrylonitrile butadiene styrene (ABS). ABS is a petroleum-based plastic known for its durability but poses challenges in biodegradability and generates more environmental pollutants during production and disposal. Choosing conductive polymers for toys can lower ecological footprints by minimizing toxic emissions and supporting circular material use cycles.
Cost Efficiency in Mass Production
Conductive polymers offer higher material costs compared to acrylonitrile butadiene styrene (ABS), but their unique electrical properties reduce the need for additional components, enhancing overall cost efficiency in mass-produced electronic toys. ABS remains preferred for its low price, ease of molding, and durability, making it highly cost-effective for large-scale production of non-electronic toys. Balancing material expenses with functional requirements, manufacturers often select ABS for structural parts and conductive polymers for integrated circuits to optimize production costs.
Future Trends: Innovations in Toy Materials
Conductive polymers in toys offer emerging possibilities for integrating interactive electronic functions and enhancing sensor-based play experiences, driven by advances in flexible, lightweight, and durable materials. Acrylonitrile butadiene styrene (ABS) remains a dominant choice for its robust mechanical properties and ease of molding, but ongoing research aims to improve its recyclability and reduce environmental impact. Future trends emphasize hybrid composites combining conductive polymers with ABS to create smart, sustainable toys that meet both safety standards and evolving consumer demands for innovation.
Infographic: Conductive polymer vs Acrylonitrile butadiene styrene for Toy
 azmater.com
azmater.com